Parts of Speech ในภาษาอังกฤษมีบทบาทและหน้าที่เฉพาะ ซึ่งมีส่วนสนับสนุนโครงสร้างของประโยคและแสดงความหมายที่สมบูรณ์ของประโยค ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณอาจไม่เข้าใจคำพูดที่ว่า “She is mother.” (“เธอคือแม่”) เนื่องจากประโยคไม่มีคำสันธานหรือคำนำหน้านาม ทำให้คุณสงสัยว่า “เธอ” คือแม่ของใคร
ในบทความนี้ ELSA Speak จะรวบรวมองค์ความรู้ที่สมบูรณ์ที่สุดเกี่ยวกับ Part of Speech เพื่อช่วยให้คุณสร้างประโยคได้ถูกต้องมากขึ้นและมีความมั่นใจมากขึ้นเมื่อสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษ มาติดตามเพื่อเรียนรู้ความรู้ที่เป็นประโยชน์เพิ่มเติมกันนะ!

ในภาษาอังกฤษมี Part of Speech 9 ประเภท ซึ่งแต่ละประเภทจะมีหน้าที่ บทบาท และตำแหน่งเฉพาะในประโยค:
สอบก่อนเข้าฟรี

- คำนาม (Noun)
- คำสรรพนาม (Pronoun)
- คำคุณศัพท์ (Adjective)
- คำกริยา (Verb)
- คำวิเศษณ์ (Adverb)
- คำนำหน้านาม (Determiner)
- คำบุพบท (Preposition)
- คำสันธาน (Conjunction)
- คำอุทาน (Interjection)
>>> Read more:
- วิธีใช้ Relative Pronoun ในภาษาอังกฤษ
- A an the ใช้ยังไง
คำนามในภาษาอังกฤษ (Noun)
คำนาม คือ คำที่กล่าวถึงบุคคล สิ่งของ เหตุการณ์ แนวคิด ปรากฏการณ์ หรือสถานที่ต่างๆ
ตัวอย่าง:
- car (รถยนต์)
- lady (ผู้หญิง)
- Paris (เมืองปารีส)

ตำแหน่งของคำนามในประโยค:
| ตำแหน่ง | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| ขึ้นต้นประโยคและหลังคำวิเศษณ์บอกเวลา (ถ้ามี) | Mr. Tan went on a picnic with his family last week. = Last week, Mr. Tan went on a picnic with his family. | คุณตันไปปิกนิกกับครอบครัวเมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้ว = อาทิตย์ที่แล้ว คุณตันไปปิกนิกกับครอบครัว |
| หลังคำคุณศัพท์ปกติ | That is a naughty boy. | นั่นเป็นเด็กผู้ชายที่ซุกซน |
| หลังคำคุณศัพท์แสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ | – He is my father. – She put her pencil in the case. | – เขาคือพ่อของฉัน – เธอใส่ดินสอลงในกล่อง |
| หลังคำกริยาเมื่อทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรม | – They love cats. – Linda gave books to her friends. | – พวกเขารักแมว – ลินดามอบหนังสือให้กับเพื่อนของเธอ |
| อยู่ข้างหลัง “enough” | He didn’t have enough money to buy that luxury car. | เขาไม่มีเงินมากพอที่จะซื้อรถหรูคันนั้น |
| หลังคำ Article เช่น a, an, the หรือคำชี้นำ เช่น this, that, these, those,… | – This cat is so adorable. – She has bought a dress for her mother. | – แมวตัวนี้น่ารักมาก – เธอซื้อชุดให้แม่ของเธอ |
| ตามหลังคำว่า each, every, all, both, no, some any, few, a few, little, a little,… | – There are a few cookies left in the fridge. – Every child needs love and care. | – มีคุกกี้เหลืออยู่สองสามชิ้นในตู้เย็น – เด็กทุกคนต้องการความรักและความเอาใจใส่ |
| หลังคำบุพบท เช่น in, on, of, with, under, about, at,… | – Sarah is afraid of mice. – John is very interested in comedy. | – ซาร่าห์กลัวหนูมาก – จอห์นสนใจเรื่องตลกมาก |

สัญญาณการรับรู้คำนาม: คำนามในภาษาอังกฤษมักจะได้รับรู้โดยส่วนต่อท้ายต่อไปนี้:
| ส่วนต่อท้ายของคำนาม | ตัวอย่าง |
| –tion | education/imagination/nation |
| –sion | vision/television/impression |
| –ment | movement/environment/pavement |
| –ce | difference/preference/appliance |
| –ness | kindness/happiness/carefulness |
| –er/or(มักจะเป็นคำนามที่หมายถึงบุคคล) | worker/driver/coordinator/mentor |
| –ity/ty | identity/cruelty/quality |
| –ship | friendship/leadership/partnership |
| –ics | politics/economics/physics |
| –dom | freedom/kingdom/boredom |
| –ture | nature/picture/creature |
| –ism | optimism/socialism/capitalism |
| –phy | philosophy/geography |
| –logy | biology/psychology/theology |
| –cy | constancy/privacy/competency |
| –an/ian | musician/politician/magician |
| –ette | cigarette/etiquette |
| –itude | attitude/multitude/solitude |
| –age | carriage/marriage/voyage |
| –th | length/growth/youth |
| –ry/try | industry/bakery |
| –hood | childhood/motherhood/fatherhood |
คำกริยาในภาษาอังกฤษ (Verb)
คำกริยาคือคำที่บ่งบอกถึงการกระทำหรือสถานะของบุคคลหรือสิ่งของ
ตัวอย่าง:
- drive (ขับ)
- cook (ทำอาหาร)
- run (วิ่ง)
- feel (รู้สึก)
- hope (หวัง)

ตำแหน่งของคำกริยาในประโยค:
| ตำแหน่ง | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| หลังหัวเรื่อง | – The dog likes playing in the garden. – He walks about two kilometers every morning. | – สุนัขชอบเล่นในสวน – เขาเดินประมาณสองกิโลเมตรทุกเช้า |
| คำกริยาที่อยู่หลังคำวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่ เช่น always, usually, often, sometimes, seldom, rarely, never,… | – I usually go to school by bus. – He seldom has breakfast. | – ฉันมักจะไปโรงเรียนโดยรถประจำทาง – เขาไม่ค่อยทานอาหารเช้า |
สัญญาณการรับรู้คำกริยา: คำกริยาในภาษาอังกฤษมักจะมีส่วนต่อท้ายต่อไปนี้:

| ส่วนต่อท้ายของคำกริยา | ตัวอย่าง |
| –ate | irritate/demonstrate/illustrate |
| –en | lengthen/soften/shorten |
| –ify | clarify/identify/beautify |
| –ise/ize | minimize/maximize/realize/industrialize |
คำคุณศัพท์ในภาษาอังกฤษ (Adjective)
คำคุณศัพท์ คือคำที่อธิบายคุณสมบัติของสิ่งของ เหตุการณ์ หรือปรากฏการณ์ต่างๆ
ตัวอย่าง:
- hot (ร้อน)
- beautiful (สวยงาม)
- kind (ใจดี)

ตำแหน่งของคำคุณศัพท์ในประโยค:
| ตำแหน่ง | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| ก่อนคำนาม เพิ่มข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมให้คำนาม | Yesterday I met a handsome man. | เมื่อวานฉันได้เจอคนหล่อมาก |
| หลังกริยา to be | – Tom is hardworking. – The movie is interesting. | – ทอมขยันหมั่นเพียรมาก – หนังน่าสนใจมาก |
| หลังคำวิเศษณ์ | The play we watched yesterday evening was extremely thrilling. | ละครที่เราดูเมื่อเย็นวานนี้น่าตื่นเต้นมาก |
| หลังคำกริยาทางสัณฐานวิทยา เช่น seem, appear, feel, taste, look,… | – Lan seems tired now. – This dish tastes delicious. | – แลนดูเหนื่อยแล้ว – อาหารจานนี้รสชาติอร่อย |
| ก่อน “enough” | She is clever enough to participate in that competition. | เธอฉลาดพอที่จะเข้าร่วมการแข่งขันนั้น |
| หลัง “too” หรือ “so” | – It’s too late to come to the party right now. – The weather was so hot that my family decided to go swimming. | – มันสายเกินไปแล้วที่จะมางานเลี้ยงตอนนี้ – อากาศร้อนมากจนครอบครัวของฉันตัดสินใจไปว่ายน้ำ |
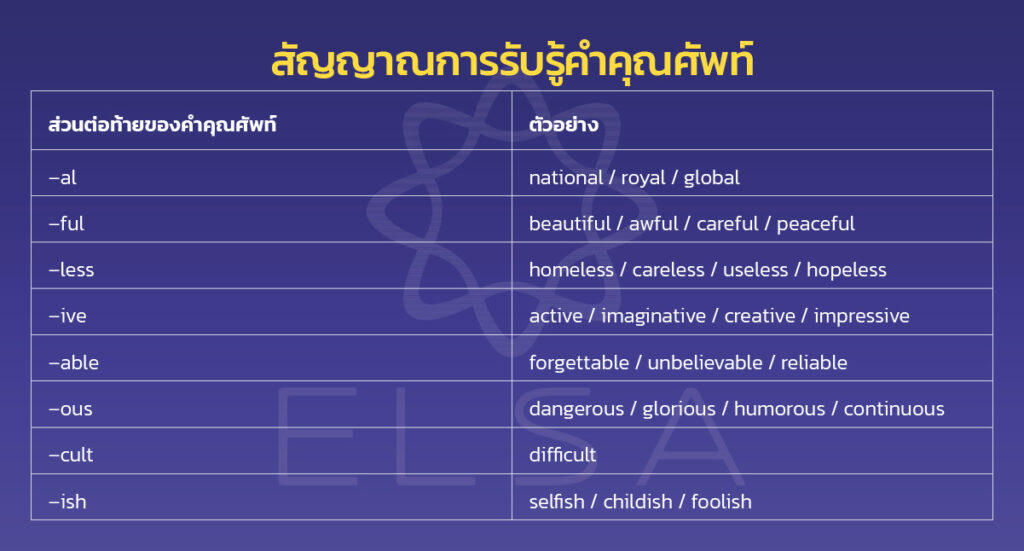
สัญญาณการรับรู้คำคุณศัพท์: คำคุณศัพท์มักจะมาพร้อมกับส่วนต่อท้ายต่อไปนี้:
| ส่วนต่อท้ายของคำคุณศัพท์ | ตัวอย่าง |
| –al | national/royal/global |
| –ful | beautiful/awful/careful/peaceful |
| –less | homeless/careless/useless/hopeless |
| –ive | active/imaginative/creative/impressive |
| –able | forgettable/unbelievable/reliable |
| –ous | dangerous/glorious/humorous/continuous/famous |
| –cult | difficult |
| –ish | selfish/childish/foolish |
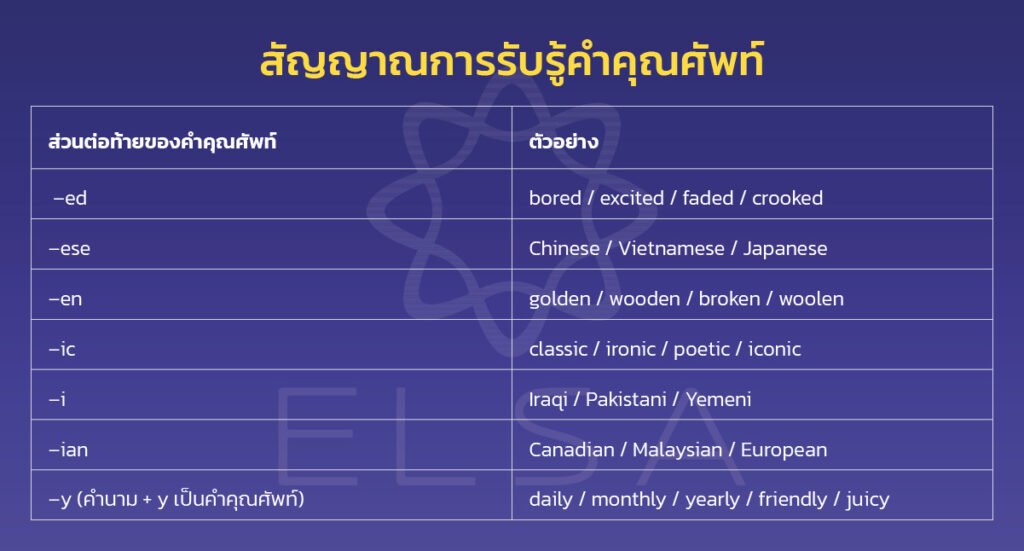
| –ed | bored/excited/faded/crooked |
| –ese | Chinese/Vietnamese/Japanese |
| –en | golden/wooden/broken/woolen |
| –ic | classic/ironic/poetic/iconic |
| –i | Iraqi/Pakistani/Yemeni |
| –ian | Canadian/Malaysian/European |
| –y (คำนาม + y เป็นคำคุณศัพท์) | daily/monthly/yearly/friendly/juicy |
เข้าใจแนวทางการใช้กาลต่างๆในภาษาอังกฤษอย่างมั่นคง:
- ประโยคอดีตกาลต่อเนื่อง (Past Continuous Tense): โครงสร้างและแบบฝึกหัด
- ประโยคอนาคตกาล ( Future Simple Tense ): โครงสร้างและแบบฝึกหัด
- Present Continuous Tense: โครงสร้าง หลักการใช้งาน
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- ประโยคปัจจุบันกาล (Present Simple Tense): โครงสร้าง การใช้งาน
- อนาคตกาลสมบูรณ์ต่อเนื่อง (Future Perfect Continuous Tense)
- Future Continuous Tense: โครงสร้างและหลักการใช้งาน
คำวิเศษณ์ในภาษาอังกฤษ (Adverb)
คำวิเศษณ์ คือคำที่แสดงสภาพของบุคคล สิ่งของ หรือปรากฏการณ์
ตัวอย่าง:
- quickly (อย่างรวดเร็ว)
- well (อย่างดี)
- interestingly (อย่างน่าสนใจ)

ตำแหน่งของคำวิเศษณ์ในประโยค:
| ตำแหน่ง | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| ก่อนคำกริยา infinitive (โดยเฉพาะคำวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่: often, always, usually, seldom….) | – He often stays up late. – I totally disagree with that viewpoint. | – เขามักจะนอนดึก – ฉันไม่เห็นด้วยกับมุมมองนั้นโดยสิ้นเชิง |
| ระหว่างคำกริยาช่วยกับคำกริยา infinitive | The children have recently finished their homework. | เด็กๆเพิ่งทำการบ้านเสร็จ |
| หลังคำกริยา to be/seem/look/feel/appear/sound… และก่อนคำคุณศัพท์ | – They seem very excited when watching the show. – This melody sounds extremely familiar. I must have heard it. | – ดูเหมือนพวกเขาจะสนใจดูรายการนั้นมาก – ท่วงทำนองนี้ฟังดูคุ้นเคยอย่างยิ่ง ฉันต้องเคยได้ยินมาก่อน |
| หลัง “too” | The man speaks too slowly. | ผู้ชายพูดช้าเกินไป |
| ก่อน “enough” | He ran quickly enough to catch the bus. | เขาวิ่งเร็วพอที่จะขึ้นรถบัส |
| คำวิเศษณ์ใช้ในโครงสร้าง so….that | He drove so carelessly that he caused a serious accident. | เขาขับรถโดยประมาทจนทำให้เกิดอุบัติเหตุร้ายแรง |
| คำวิเศษณ์ยังอยู่ขึ้นต้นประโยค หรือตรงกลางของประโยค และแยกออกจากส่วนอื่นของประโยคด้วยเครื่องหมายจุลภาค (,) | – Certainly, they will be here for dinner. – Unfortunately, I did not have enough time to complete the test. | – แน่นอน พวกเขาจะมาที่นี่เพื่อทานอาหารเย็น – น่าเสียดาย ฉันมีเวลาไม่พอที่จะทำแบบทดสอบให้เสร็จ |
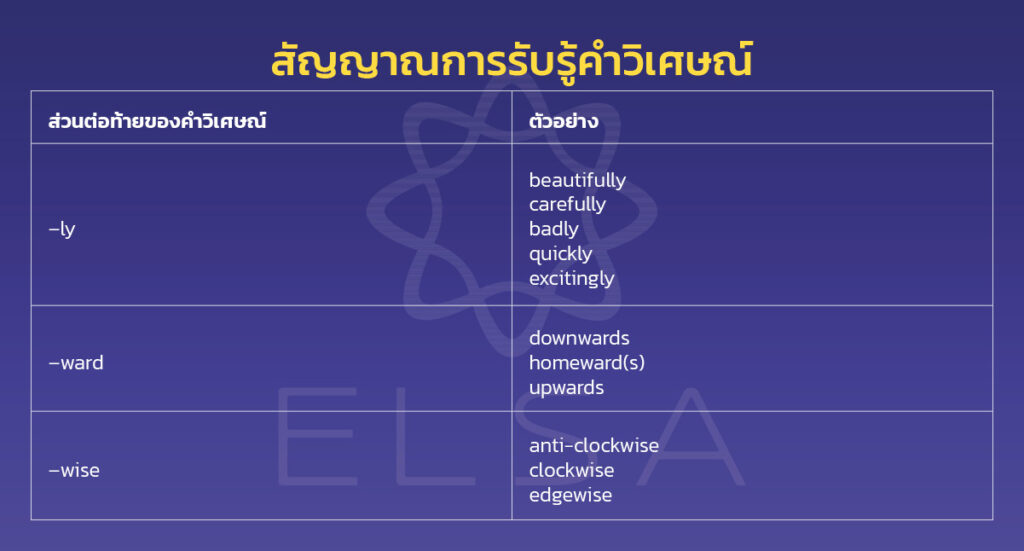
สัญญาณการรับรู้คำวิเศษณ์: คำวิเศษณ์มักจะมาพร้อมกับส่วนต่อท้ายต่อไปนี้:
| ส่วนต่อท้ายของคำวิเศษณ์ | ตัวอย่าง |
| –ly | beautifully/carefully/badly/quickly/excitingly |
| –ward | downwards/homeward(s)/upwards |
| –wise | anti-clockwise/clockwise/edgewise |
คำบุพบทในภาษาอังกฤษ (Preposition)
คำบุพบทคือคำที่แสดงความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างคำวัตถุ วัตถุในวลี ในประโยค ภาษาอังกฤษมีคำบุพบทที่คุ้นเคย เช่น in, on, at, with, for, under, above,… คำที่มักตามหลังคำบุพบทได้แก่ คำกรรม อาการนาม หรือ นามวลี…

ตำแหน่งของคำบุพบทในประโยค:
| ตำแหน่ง | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| คำบุพบทอยู่ที่หลังกริยา TO BE และก่อนคำนาม | – The pictures are on the wall. – The cat is under the bed. | – รูปภาพอยู่บนผนัง – แมวอยู่ใต้เตียง |
| คำบุพบทอยู่หลังคำกริยา infinitive | – Tom is standing between Linda and Jack. – The firefighters immediately put out the fire. | – ทอมยืนอยู่ระหว่างลินดากับแจ็ค – เจ้าหน้าที่ดับเพลิงเร่งดับไฟทันที |
| คำบุพบทอยู่หลังคำคุณศัพท์ | – She is fond of cooking. – I am terrified of heights. | – เธอชอบทำอาหาร – ฉันกลัวความสูง |
การจำแนกประเภทของคำบุพบททั่วไปในภาษาอังกฤษ:
| ประเภทคำบุพบท | คำบุพบททั่วไป | แปลภาษาไทย |
| คำบุพบทบอกเวลา | At | ตอนที่ (มักจะไปกับเวลา) |
| On | ใน (มักจะไปกับวัน) | |
| In | ใน (ใช้กับเดือน ปี ฤดู ศตวรรษ) | |
| Before | ก่อน | |
| After | หลังจาก | |
| During | ในช่วง (รวมนามของเวลา) | |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ | At | ที่ (ตามสถานที่เล็กๆ เช่น โรงเรียน โรงพยาบาล …) |
| In | – ใน (ชี้ภายใน)– ที่ (เมืองใหญ่ จังหวัด ประเทศ ทวีป…) | |
| On, above, over | บน | |
| On | ด้านบนและสัมผัสกับพื้นผิว | |
| คำบุพบทบอกการกระจัด | To, into, onto | มาถึง– To: เข้าหาเฉพาะคน สิ่งของ หรือสถานที่– Into: เข้าใกล้และเข้าไปในวัตถุหรือสถานที่นั้น– Onto: เข้าใกล้และสัมผัสกับพื้นผิว ด้านนอกของวัตถุ สถานที่ |
| From | ชี้ถึงแหล่งกำเนิด | |
| Across | ผ่าน | |
| Along | ตาม | |
| Round, around, about | รอบๆ | |
| คำบุพบทบอกลักษณะ | With | กับ |
| Without | ไม่ ไม่มี | |
| According to | ตาม | |
| In spite of | ทั้งๆที่มี | |
| Instead of | แทน | |
| คำบุพบทบอกวัตถุประสงค์ | To | เพื่อ |
| In order to | เพื่อ | |
| For | ให้, สำหรับ | |
| So as to | เพื่อ | |
| คำบุพบทบอกสาเหตุ | Thanks to | ด้วย |
| Through | เพราะ | |
| Because of | เพราะว่า | |
| Owing to | เนื่องจาก | |
| By means of | ด้วยวิธีการ |
| การทำความเข้าใจ Part of Speech ทั้ง 9 ประเภทในภาษาอังกฤษ ช่วยให้ผู้เรียนวิเคราะห์โครงสร้างประโยคได้อย่างถูกต้อง และสามารถพิจารณาได้อย่างชัดเจน whether คำใดทำหน้าที่เป็นคำนาม คำกริยา หรือคำเชื่อมในบริบทต่าง ๆ ความรู้พื้นฐานนี้จึงเป็นรากฐานสำคัญของการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษอย่างแม่นยำ |
คำนำหน้านามในภาษาอังกฤษ (Determiner)
คำนำหน้านาม คือคำที่นำหน้าคำนามหรือนามวลีเพื่อจำกัดและกำหนดคำนาม/นามวลีนั้น ซึ่งช่วยให้ความหมายของสิ่งของ เหตุการณ์ และบุคคลที่กล่าวถึงในประโยคได้ชัดเจนขึ้น
ตัวอย่าง:
- There are ten students in the class. (มีนักเรียนสิบคนในชั้นเรียน)
- She wants to take her son to the national museum. (เธออยากพาลูกชายไปที่พิพิธภัณฑ์แห่งชาติ)

การจำแนกประเภทของคำนำหน้านามในภาษาอังกฤษ:
| ประเภทของคำนำหน้านาม | รายการ | ตัวอย่าง |
| Article | a, an, the | The boy I met yesterday was extremely naughty. (เด็กชายที่ฉันพบเมื่อวานนี้ซนมาก) |
| Demonstrative Determiners | this, that, these, those | Those apples are rotten. You should throw them away. (แอปเปิ้ลเหล่านั้นเน่าเสียแล้ว คุณควรทิ้งมันไป) |
| Quantifiers | – all, every, most, many, much, some, few, little, any, no.… – one, two, three,… – first, second, third,… | – We don’t have much oil for the fried chicken. (เราไม่มีน้ำมันมากสำหรับไก่ทอด) – She received many gifts on her birthday. (เธอได้รับของขวัญมากมายในวันเกิดของเธอ) – I only have two coins left. (ฉันเหลือแค่สองเหรียญ) – She won the third prize. (เธอได้รับรางวัลที่สาม) |
| Interrogative Determiners | whose, which, what | – Whose car did you borrow? (คุณยืมรถของใคร?) – Which books have you read? (คุณอ่านหนังสือเล่มไหน?) |
คำสรรพนามในภาษาอังกฤษ (Pronoun)
คำสรรพนามคือคำที่อ้างถึงบุคคลหรือสิ่งของที่ใช้แทนคำนามหรือวลีนามเฉพาะ จุดประสงค์ของการใช้คำสรรพนามคือเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการใช้คำนามซ้ำหลายครั้งเกินไป และทำให้ประโยคเป็นธรรมชาติมากขึ้น
มาเปรียบเทียบสองตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้:
- John is buying some reference books because John needs some reference books for John’s study. (จอห์นกำลังซื้อหนังสืออ้างอิงเพราะจอห์นต้องการหนังสืออ้างอิงสำหรับการศึกษาของจอห์น) (1)
- John is buying some reference books because he needs them for his study. (จอห์นกำลังซื้อหนังสืออ้างอิงเพราะเขาต้องการใช้มันในการศึกษาของเขา) (2)
-> ตามหลักไวยากรณ์ ทั้งสองประโยคข้างต้นต่างก็ถูกต้อง อย่างไรก็ตาม ประโยค (1) เกิดข้อผิดพลาดในการทำซ้ำหลายครั้งเมื่อพูดคำว่า “John”, “some reference books” ซ้ำ ๆ ซ้ำ ๆ ทำให้ประโยคดูยาว แต่สับสนและไม่ต่อเนื่องกัน ในขณะเดียวกัน ประโยค (2) มีความหมายเหมือนกันแต่ใช้คำสรรพนาม “he” (แทน “John”) และ “them” (แทน “some reference books”) ด้วยเหตุนี้ ประโยคจึงหลีกเลี่ยงข้อผิดพลาดในการทำซ้ำ กลายเป็นสั้นลง กระชับและสอดคล้องกันมากขึ้น

การจำแนกประเภทของคำสรรพนามในภาษาอังกฤษ:
| ประเภทของคำสรรพนาม | หลักการใช้ | คำสรรพนาม | ตัวอย่าง |
| บุรุษสรรพนาม | ใช้แทนคน/กลุ่มคนและสิ่งของเฉพาะ | I – me You – you We – us They – them He – him She – her It – it | She will come to the party. (เธอจะมางานเลี้ยง) |
| สรรพนามแสดงตนเอง | ใช้เมื่อหัวเรื่องและกรรมเป็นวัตถุเดียวกัน | myself yourself ourselves themselves himself herself itself | I made a cake for myself on my birthday. (ฉันทำเค้กให้ตัวเองในวันเกิด) |
| สรรพนามบ่งชี้ | แสดงการชี้เฉพาะเจาะจงว่าเป็นสิ่งไหน อันไหน หรือว่าคนไหน | this that these those | This is the most wonderful book I have ever read. (นี่เป็นหนังสือที่ยอดเยี่ยมที่สุดที่ฉันเคยอ่านมา) |
| สรรพนามเจ้าของ | ใช้เพื่อระบุว่าวัตถุเป็นของใคร | mine yours ours their his hers its | All of these presents are yours. (ของขวัญทั้งหมดนี้เป็นของคุณ) |
| สรรพนามที่ใช้เชื่อมประโยค | ใช้แทนคำนามนำหน้าซึ่งมีหน้าที่เชื่อมอนุประโยคใจความหลักกับอนุประโยคใจความรองใน relative clause | who – whom which that whose | I love my mother who always supports me. (ฉันรักแม่ คนที่คอยสนับสนุนฉันเสมอมา) |
| สรรพนามไม่เจาะจง | ชี้ 1 หรือหลาย (บุคคล/สิ่งของ) ที่ไม่เจาะจง | another each either much neither both few many others all any more most… | – There isn’t any milk in the fridge. (ไม่มีนมในตู้เย็น) – She spent some of the money fixing her car. (เธอใช้เงินบางส่วนในการซ่อมรถของเธอ) – None of them knows the truth. (ไม่มีใครรู้ความจริง) |
| Intensive pronouns | มักจะตามด้วยคำนามหรือคำสรรพนามเพื่อเน้นย้ำ ซึ่งหมายถึง “คนนั้น/สิ่งนั้น” | myself yourself ourselves themselves himself herself itself | The movie itself wasn’t very interesting but I love the main character. (ตัวหนังก็ไม่น่าสนใจมากนัก แต่ฉันชอบพระเอก) |

คำสันธานในภาษาอังกฤษ (Conjunction)
คำสันธานคือคำที่ใช้เพื่อเชื่อมคำ วลี หรืออนุประโยคเข้าด้วยกันเพื่อสร้างประโยคที่เป็นเอกภาพ
ตัวอย่าง:
- He was disappointed because he did not win the first prize. (เขาผิดหวังเพราะเขาไม่ได้รางวัลที่หนึ่ง)
- Mino got sick but he could still meet the deadline. (มินห์ป่วยแต่เขาก็ยังทำให้เสร็จตรงเวลา)

การจำแนกประเภทของคำสันธานในภาษาอังกฤษ:
| ประเภทของคำสันธาน | หลักการใช้ | ตัวอย่าง |
| Coordinating Conjunction | จับคู่ (หรือมากกว่า) หน่วยคำที่เทียบเท่ากัน (ประโยค อนุประโยค วลี) | and (และ) so (ดังนั้น) yet (แต่) but (แต่) for (เพราะ) as (เพราะ) |
| Correlative Conjunction | ใช้คู่กันเสมอใช้เชื่อม 2 อนุประโยค ประโยค หรือวลี | not only… but also… (ไม่เพียง… แต่ยัง…) either… or… (หรือ… หรือ…) neither… nor… (หรือไม่… หรือไม่…) |
| Subordinating Conjunction | ก่อนอนุประโยคใจความรองเพื่อเชื่อมอนุประโยคใจความรองกับอนุประโยคใจความหลักในประโยค | as long as (ตราบเท่าที่) although (แม้ว่า) before (ก่อน) after (หลัง) |
คำอุทานในภาษาอังกฤษ (Interjection)
คำอุทานเป็นคำที่ใช้เพื่อแสดงความรู้สึกของผู้พูด แม้ว่าคำประเภทนี้จะไม่มีคุณค่าที่แท้จริงในแง่ของไวยากรณ์ แต่ก็มีการใช้ค่อนข้างบ่อยโดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งในการสื่อสาร คำอุทานมักใช้แยกกันและตามด้วยเครื่องหมายอัศเจรีย์ (!) เมื่อเขียน
ตัวอย่าง:
- Oh my God! She is so gorgeous! (โอ้พระเจ้า! เธอสวยมาก!)
- Oh dear! I forgot to turn off the light. (โอ้ที่รัก! ฉันลืมปิดไฟแล้ว!)

ข้อสอบ Part of Speech ในภาษาอังกฤษ (พร้อมเฉลย)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1: เลือก Part of Speech ที่ถูกต้องสำหรับคำที่ขีดเส้นใต้ในประโยคต่อไปนี้
1. Mary is always late for school.
- คำนาม
- คำกริยา
- คำสรรพนาม
2. I want to move to Italy now.
- คำกริยา
- คำวิเศษณ์
- คำบุพบท
3. Mr. John is sitting over there.
- คำคุณศัพท์
- คำนาม
- คำบุพบท
4. There are two posters on the wall.
- คำสรรพนาม
- คำนำหน้านาม
- คำนาม
5. The teacher put our plan into action.
- คำคุณศัพท์
- คำนาม
- คำสรรพนาม
6. Carley is learning about Japanese culture.
- คำนาม
- คำคุณศัพท์
- คำอุทาน
7. Jane is watching the movie which she likes the most.
- คำสรรพนาม
- คำสันธาน
- คำคุณศัพท์
8. My cousins live in different parts of America.
- คำคุณศัพท์
- คำบุพบท
- คำวิเศษณ์
9. That was an enjoyable journey.
- คำคุณศัพท์
- คำอุทาน
- คำวิเศษณ์
10. She was extremely surprised when she passed the exam.
- คำคุณศัพท์
- article
- คำวิเศษณ์
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2: เลือกคำที่แตกต่างจากคำที่เหลือ
1.
- her
- woman
- another
- yourself
2.
- quickly
- absolutely
- important
- effectively
3.
- some
- which
- call
- the
4.
- along
- yet
- although
- before
5.
- bored
- active
- royal
- but
6.
- cold
- high
- happy
- Hey!
7.
- good
- great
- well-known
- well
8.
- the
- them
- second
- a
9.
- sad
- from
- without
- above
10.
- every
- those
- during
- which
11.
- angry
- an
- awful
- anxious
12.
- clean
- large
- able
- yours
13.
- table
- capable
- comfortable
- enjoyable
14.
- great
- Hi!
- Hello!
- Hmm…
15.
- fast
- and
- as
- since
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3: จงเลือกคำที่ผิดในประโยคต่อไปนี้
1. Because she gets sick yesterday, she decided to stay at home.
- gets
- sick
- decided
- at
2. Have us prepared enough carrots for the soup?
- have
- us
- carrots
- for
3. The man ran too slow to catch the thief.
- The
- too
- slow
- catch
4. We had dinner at a famous Korea restaurant.
- We
- at
- Korea
- restaurant
5. My brother wasn’t strong enough to lift these heavy box.
- My
- strong
- to lift
- these
6. I helped his find it.
- I
- his
- find
- it
7. The weather was rather hot on day.
- The
- was
- rather
- on
8. My friend said, “Oh! What a lovely hat!”
- My
- said
- Oh!
- lovely
9. The beautiful of the city at night impressed us.
- beautiful
- of
- at
- us
10. We got home late last night and went to sleep immediate. We were very tired.
- got
- late
- immediate
- very
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 4: จงเลือกคำตอบที่ถูกต้องในประโยคต่อไปนี้
1. The bag which I want to buy is …
- afford
- affordance
- affordable
2. The letter was sent … my cousins in Australia.
- along
- to
- round
3. Did you see a blue lunch box? It’s …
- my
- mine
- I
4. Sorry but I didn’t understand it. Can you …?
- explanation
- explanatory
- explain
- 5. …! My skin is bleeding.
- Ouch
- Eh
- Ah
6. My mother is good … at work … at taking care of my family.
- not only – but also
- either – or
- neither – nor
7. We couldn’t sleep last night because our neighbor sang …
- noise
- noisily
- noisy
8. I haven’t heard this … before.
- informative
- inform
- information
9. My parents love living in the countryside because it is …
- peace
- peacefully
- peaceful
10. He has worked as … engineer for 5 years.
- a
- any
- an
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 5: เติม Part of Speech ที่เหมาะสมด้วยคำที่กำหนดในวงเล็บ
1. Jane is very……….(care). She seldom makes mistakes.
2. The clown………..(attractive) us by standing and dancing on the ball.
3. Ben has a lot of………….(confident).
4. Thanks to my teacher, I have gained more………(know).
5. I think he has tried………(hard) in his first movie.
6. He has to be…………(responsibility) for what he did.
7. Don’t go out late at night. It’s………..(danger).
8. I………(suggestion) going to the cinema.
9. The meeting room should be……….(space) enough to contain about 20 people.
10. You should join outdoor………….(active) if you want to make more friends.
ข้อสรุป Part of Speech
การเชี่ยวชาญ Part of Speech ในภาษาอังกฤษและหลักการใช้คำเหล่านั้น จะช่วยให้คุณสร้างโครงสร้างประโยคที่ถูกต้องมากขึ้น ซึ่งจะช่วยพัฒนาความสามารถทางภาษาอังกฤษของคุณได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ฝึกฝนนิสัยการเรียนรู้คำศัพท์รวมกับ Part of Speech คือการพัฒนาระดับภาษาอังกฤษของคุณทุกวันนะ