Present Continuous Tense เป็นหนึ่งใน 12 tense ในภาษาอังกฤษที่สำคัญที่สุด เพื่อให้สามารถพัฒนาระดับภาษาอังกฤษของตัวเองได้อย่างรวดเร็ว คุณต้องเชี่ยวชาญความรู้พื้นฐานเหล่านี้ ดังนั้นในบทความต่อไปนี้ ELSA Speak จะแบ่งปันและแนะนำอย่างละเอียดเกี่ยวกับโครงสร้าง หลักการใช้งาน และแบบฝึกหัดทั่วไปของ Present Continuous Tense!

Present Continuous Tense คืออะไร
Present Continuous คือ tense ที่ใช้เพื่อแสดงการกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่ในขณะที่พูดหรือรอบ ๆ ประเด็นของการพูด
สอบก่อนเข้าฟรี

Present Continuous Tense ตัวอย่างประโยค
- My husband is taking a shower, so he can’t come to the phone.
(สามีของฉันกำลังอาบน้ำ เขาจึงไม่สามารถมารับสายได้)
→ การกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่ในขณะที่พูด
- These days, I’m reading a good book.
(วันนี้ฉันกำลังอ่านหนังสือดีๆ)
→ การกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่รอบ ๆ ประเด็นของการพูด
→ นอกจากนี้ Present Continuous Tense ยังมีหน้าที่อื่นๆ และเราจะพูดถึงหน้าที่ของ Present Continuous Tense ในเชิงลึกในส่วนที่ 5
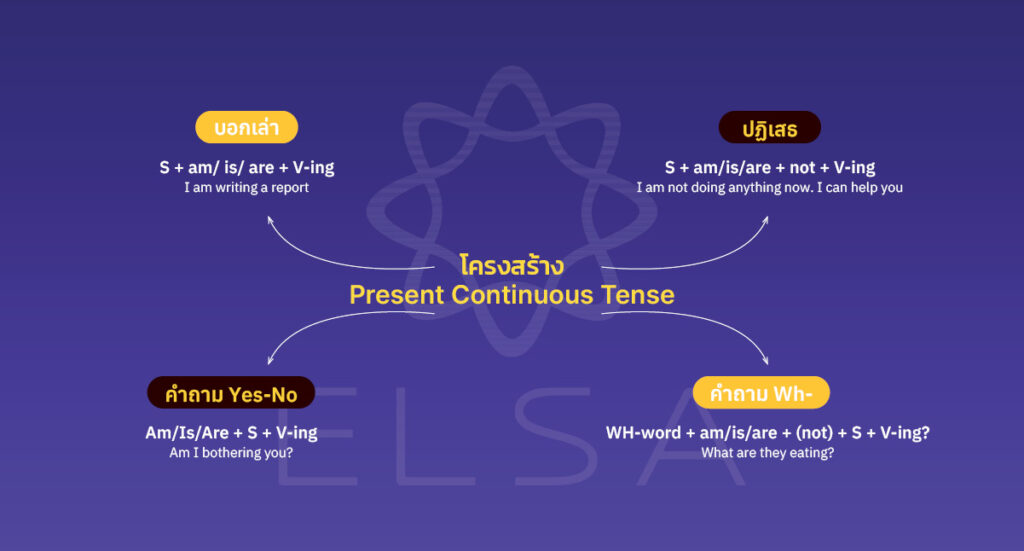
โครงสร้าง Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense โครงสร้างในรูปแบบประโยค:
- บอกเล่า: S + am/ is/ are + V-ing
- ปฏิเสธ: S + am/ is/ are + not + V-ing
- คำถาม Yes/No: (Yes/ No) Am/ Is/ Are + S+ V-ing?
- คำถาม Wh-: Wh- + am/ is/ are + (not) + S + V-ing?
รูปแบบประโยคบอกเล่า
| S + am/ is/ are + V-ing + … (be) |
หมายเหตุ
- I am = I’m
- She/ He is = She’s/ He’s
- They are = They’re
ตัวอย่าง
- I am writing a report.
(ฉันกำลังเขียนรายงาน)
- That employee is talking to her boss.
(พนักงานคนนั้นกำลังคุยกับเจ้านายของเธอ)
- My parents are watching TV in the living room.
(พ่อแม่ของฉันกำลังดูทีวีอยู่ในห้องนั่งเล่น)
รูปแบบประโยคปฏิเสธ
| S + am/ is/ are + not + V-ing + … (be) |
หมายเหตุ
- I am not = I’m not
- She/ He is not = She’s/ He’s not = She/ He isn’t
- They are = They’re not = They aren’t
ตัวอย่าง
- I am not doing anything now. I can help you.
(ตอนนี้ฉันไม่ได้ทำอะไรอยู่ ฉันช่วยคุณได้)
- Our son isn’t doing homework. He’s playing games.
(ลูกชายเราไม่ทำการบ้าน เขากำลังเล่นเกม)
- Those employees aren’t talking about the new project.
(พนักงานเหล่านั้นไม่ได้พูดถึงโครงการใหม่)

รูปแบบประโยคคำถาม
คำถาม Yes/No
| Am/ Is/ Are + S+ V-ing + …? (be) |
| Yes, S + am/ is/ are.No, S + am/ is/ are + not |
ตัวอย่าง
- Is our daughter playing in the garden?
(ลูกสาวของเรากำลังเล่นอยู่ในสวนใช่ไหม)
Yes, she is.
(ใช่แล้ว)
- Am I bothering you?
(ฉันกำลังรบกวนคุณหรือเปล่า)
No, you’re not.
(ไม่นะ)
- Are the employees talking about the new policy?
(พนักงานกำลังพูดถึงนโยบายใหม่หรือไม่?)
No, they aren’t.
(พวกเขาไม่ได้พูดถึง)
คำถาม Wh-
คำใช้ถามที่ไม่ใช่หัวเรื่อง
| What/ Where/ When/ Why/ How/ Who(m) + am/ is/ are + (not) + S + V-ing + …? (be) |

ตัวอย่าง
- What are they eating?
(พวกเขากำลังกินอะไรอยู่)
- Where is she having lunch?
(เธอกินข้าวกลางวันที่ไหน)
- When are you flying to Korea?
(เมื่อไหร่คุณจะบินไปเกาหลี)
(หน้าที่นี้จะได้แนะนำในส่วนที่ 5)
- Why aren’t our daughters doing homework?
(ทำไมลูกสาวเราไม่ทำการบ้าน)
- How is my son studying these days?
(ลูกชายของฉันเรียนเป็นอย่างไรบ้างช่วงนี้)
- Who(m) is our boss talking to?
(เจ้านายของเรากำลังคุยกับใคร)
✍ คำใช้ถามคือหัวเรื่อง
What/ Who + is + V-ing + …? (be)
ตัวอย่าง
- What is upsetting him?
(อะไรทำให้เขาไม่พอใจ)
- Who is singing?
(ใครกำลังร้องเพลง)
หลักการเติม -ing ใน Present Continuous Tense
หมายเหตุ: หากคำกริยาที่จะผันไม่ได้อยู่ในสถานการณ์ด้านล่างนี้ ให้เติม -ing ต่อกริยาตามปกติ
คำกริยาที่ลงท้ายด้วย “e”
เมื่อคำกริยาที่จะผันลงท้ายด้วย “e” เราต้องทิ้ง “e” แล้วเติม -ing
ตัวอย่าง
- They are racing. (race → racing)
(พวกเขากำลังแข่ง)
- Look! She’s waving at us. (wave → waving)
(ดูสิ! เธอกำลังโบกมือให้พวกเรา)
คำกริยาที่ลงท้ายด้วย “ie”
ในกรณีนี้ เราต้องเปลี่ยน “ie” เป็น “y” แล้วเติม -ing
ตัวอย่าง
- Her cat is lying in my bed. (lie → lying)
(แมวของเธอกำลังนอนอยู่บนเตียงของฉัน)
- There’s too much to do. I’m dying. (die → dying)
(มีมากเกินไปที่จะทำ ฉันกำลังจะตาย)
คำกริยาที่มี 1 พยางค์ ลงท้ายด้วยพยัญชนะ นำหน้าด้วยสระ
ในกรณีนี้ เราเพิ่มพยัญชนะตัวสุดท้ายเป็นสองเท่า แล้วเติม -ing
ตัวอย่าง
- The hairdresser is cutting my hair. (cut → cutting)
(ช่างตัดผมกำลังตัดผม)
- They are putting fruits into the fridge. (put → putting)
(พวกเขากำลังใส่ผลไม้เข้าไปในตู้เย็น)
คำกริยาที่มี 2 พยางค์ ลงท้ายด้วยพยัญชนะ นำหน้าด้วยสระ เน้นเสียงอยู่ที่พยางค์ที่ 2
ในกรณีนี้ เรายังเพิ่มพยัญชนะตัวสุดท้ายเป็นสองเท่า แล้วเติม -ing
ตัวอย่าง
Leaves are beginning to fall. (begin→ beginning)
(ใบไม้กำลังเริ่มร่วงหล่น)
คำกริยาที่ไม่ได้ผันใน Present Continuous Tense
คำกริยาแสดงอารมณ์ ชอบ เกลียด ความต้องการ…
- like: ชอบ
- love: รัก
- dislike: ไม่ชอบ
- hate: เกลียด
- want: อยาก
- prefer: ชอบมากกว่า (การเลือก)
- need: ต้องการ
หมายเหตุ: คำกริยา ‘like’, ‘love’, ‘dislike’ และ ‘hate’ ยังสามารถนำมาใช้ใน Present Continuous Tense เมื่อผู้พูดต้องการเน้นความเป็นชั่วคราวของอารมณ์ แต่กรณีนี้ไม่เป็นที่นิยม
คำกริยาแสดงความคิด ความเห็น…
- think: คิด
- believe: เชื่อใน
- know: รู้ว่า
- understand: เข้าใจ
- remember: จำบางสิ่งในอดีต / จำสิ่งที่ต้องทำ
- forget: ลืมบางสิ่งในอดีต / ลืมทำบางสิ่ง
- realize: ตระหนักว่า
หมายเหตุ: เมื่อคำกริยา ‘think’ หมายถึง “คิดถึงใครบางคน/บางสิ่ง” และตามด้วย ‘of/ about’ + คำนาม เราสามารถใช้ ‘think’ ใน Present Continuous Tense
คำกริยาเชื่อมโยง (linking verbs) และเกี่ยวข้องกับการรับรู้ทางประสาทสัมผัส
- taste: รส
- smell: เหม็น
- feel: รู้สึก (This place feels cozy. – สถานที่นี้ให้ความรู้สึกอบอุ่น)
- sound: ฟังดูเหมือน
- seem: ดูเหมือน
- look: ดูเหมือนว่า
หมายเหตุ: เมื่อคำกริยาข้างต้นไม่ได้ทำหน้าที่เชื่อมโยง และไม่แสดงการรับรู้ทางประสาทสัมผัส แต่ทำหน้าที่ของคำกริยาการกระทำและแสดงการกระทำ เราสามารถใช้คำนั้นได้ใน Present Continuous Tense เมื่อมีความหมายต่อไปนี้:
- taste: เพื่อลิ้มรส
- smell: กลิ่น
- feel: รู้สึกอย่างไร
- sound: เพื่อสร้างเสียง/ทำให้เกิดเสียง
- look at something: ดูบางอย่าง
คำกริยาเชื่อม ‘be’
‘be’ ไม่ค่อยได้ใช้ใน Continuous Tense คุณต้องหลีกเลี่ยงการแปลโดยตรงจากภาษาไทยเป็นภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อไม่ให้เกิดข้อผิดพลาดในการใช้ ‘be’ ใน Continuous Tense เมื่อไม่จำเป็นหรือไม่ควรใช้
ตัวอย่าง
คุณมีประโยคภาษาไทยในหัวอยู่แล้วว่า “เธอกำลังเศร้า”
จากนั้นพยายามแปลเป็นภาษาอังกฤษว่า “She is BEING sad.”
ในขณะที่วิธีพูดที่ถูกต้องตามหลักไวยากรณ์และเป็นธรรมชาติที่สุดก็คือ “She is sad.”
ดังนั้นแทนที่จะคิดเป็นภาษาไทยแล้วแปลเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ คุณเพียงแค่พิจารณาจากแนวคิดที่คุณต้องการพูด จากนั้นเลือกโครงสร้างและคำศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษที่เหมาะสมเพื่อแสดงแนวคิดนั้น
อย่างไรก็ตาม ยังมีบางกรณีที่ผู้พูดใช้ ‘be’ ใน Present Continuous Tense เพื่อเน้นเรื่องชั่วคราว
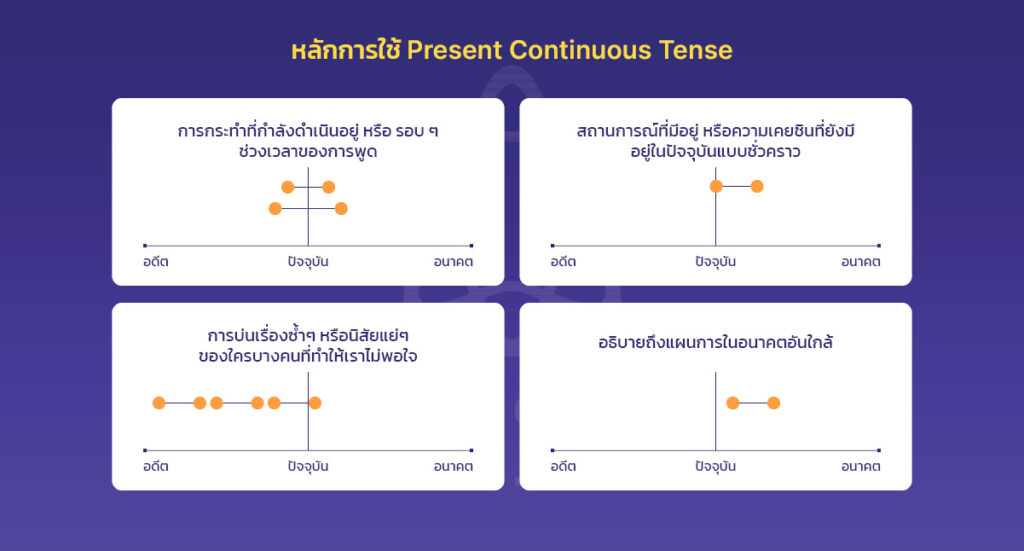
หลักการใช้ Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous หลักการใช้:
- แสดงการกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่ในขณะที่พูด
- แสดงการกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่รอบ ๆ ประเด็นของการพูด
- แสดงสถานการณ์ที่มีอยู่ หรือนิสัยที่คงอยู่ในปัจจุบัน ซึ่งเกิดขึ้นชั่วคราว
- การบ่นเรื่องซ้ำๆ หรือนิสัยแย่ๆ ที่ทำให้เราไม่พอใจ
- แสดงถึงแผนการในอนาคตอันใกล้ที่มีความเป็นไปได้สูงที่จะเกิดขึ้น มักจะมาพร้อมกับช่วงเวลา
แสดงการกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่ในขณะที่พูด
ตัวอย่าง
- I’m writing an important report. I’ll check that later.
(ฉันกำลังเขียนรายงานสำคัญ ฉันจะตรวจสอบในภายหลัง)
→ วิเคราะห์: เมื่อพูดประโยคข้างต้น ผู้พูดกำลัง “เขียนรายงานสำคัญ”
- My wife is shopping at the moment. Can you call back later?
(ภรรยาของผมกำลังช้อปปิ้ง คุณสามารถโทรกลับในภายหลังได้ไหมครับ?)
→ วิเคราะห์: ภรรยา “ช้อปปิ้ง” กำลังเกิดขึ้นในเวลาที่ประโยคข้างต้นได้กล่าว

แสดงการกระทำที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่ในรอบ ๆ ช่วงเวลาของการพูด
Teacher (in class): ‘(These days,) I’m reading a good book.’
→ อาจารย์ (ในชั้นเรียน): “(ทุกวันนี้) ฉันกำลังอ่านหนังสือเล่มดีๆ”
→ วิเคราะห์: ไม่ว่าจะมีวลี “ทุกวันนี้” หรือไม่ก็ตาม ตามบริบทแล้ว “อ่านหนังสือเล่มดีๆ” ก็ไม่สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ในเวลาที่อาจารย์พูด การกระทำนี้เกิดขึ้นในรอบ ๆ ช่วงเวลาของการพูด อาจารย์อ่านหนังสือมาก่อนและยังไม่จบ หลังจากสอนเสร็จ ถึงจุดเวลาหนึ่ง อาจารย์ก็จะมาอ่านหนังสือเล่มนั้นต่อ
สถานการณ์ที่มีอยู่ หรือความเคยชินที่ยังมีอยู่ในปัจจุบันแบบชั่วคราว ผิดปกติ เมื่อเทียบกับสภาพหรือนิสัยที่เป็นมายาวนาน
My mom always drives to work, but this month, she’s taking the bus.
→ แม่ของฉันขับรถไปทำงานเสมอ แต่เดือนนี้เธอขึ้นรถเมล์
→ วิเคราะห์: นิสัยที่คงอยู่เป็นเวลานานคือการ “ขับรถไปทำงาน” นิสัยนี้ถูกขัดจังหวะด้วยนิสัยชั่วคราวใน “เดือนนี้” คือ การขึ้นรถเมล์
การบ่นเรื่องซ้ำๆ หรือนิสัยแย่ๆ ที่ทำให้เราไม่พอใจ
ในประโยค มักจะมีคำวิเศษณ์และวลีที่แสดงความถี่สูง เช่น ‘always’, ‘usually’, ‘constantly’, ‘all the time’,…
- That employee is always missing deadlines.
(พนักงานคนนั้นขาดกำหนดเวลาเสมอ)
→ วิเคราะห์: การทำซ้ำ/นิสัยแย่ๆ ที่ทำให้ผู้พูดไม่พอใจ: “ขาดกำหนดเวลา”
- That student is speaking in class all the time.
(นักเรียนคนนั้นพูดในชั้นเรียนตลอดเวลา)
→ วิเคราะห์: การทำซ้ำ/นิสัยแย่ๆ ที่ทำให้ผู้พูดไม่พอใจ: “พูดในชั้นเรียน”
อธิบายถึงแผนการในอนาคตอันใกล้ที่มีความเป็นไปได้สูงที่จะเกิดขึ้น มักจะมาพร้อมกับช่วงเวลา
- We are flying to Australia this Friday.
(พวกเราจะบินไปออสเตรเลียวันศุกร์นี้)
→ วิเคราะห์: การ “บินไปออสเตรเลีย” จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตอันใกล้คือ “วันศุกร์นี้” ซึ่งมีความเป็นไปได้สูงและมาพร้อมกับช่วงเวลา “วันศุกร์นี้”
- Manny and Mitchell are throwing a party this weekend.
(แมนนี่และมิทเชลจะจัดงานปาร์ตี้สุดสัปดาห์นี้)
→ วิเคราะห์: การ “จัดงานปาร์ตี้” จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตอันใกล้: “สุดสัปดาห์นี้”, ซึ่งมีความเป็นไปได้สูงและมาพร้อมกับช่วงเวลา “สุดสัปดาห์นี้”
ติดตามบทความ Present Perfect Tense และ Present Perfect Continuous Tense เพื่อจะไม่สับสนกับ Present Continuous Tense ในกระบวนการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษ
สัญญาณการรับรู้ Present Continuous Tense
มีวลีระบุเวลาพูด
- now: ตอนนี้
- right now: ตอนนี้เลย
- at the moment: ในขณะนี้
- at present: ปัจจุบัน
- ….
มีวลีระบุเวลารอบ ๆ ประเด็นของการพูด
- these days: ช่วงนี้
- this month: เดือนนี้
- this week: สัปดาห์นี้
- ….
มีวลี คำวิเศษณ์ หรือวลีความถี่สูง
- always: เสมอ
- usually: มักจะ
- constantly: อย่างต่อเนื่อง
- all the time: ตลอดเวลา
คำสั่งสั้น ๆ เพื่อดึงดูดความสนใจไปยังสิ่งที่กำลังเกิดขึ้น
- Look! (ดูสิ!)
- Listen! (ฟังสิ!)
- Watch out! (ระวัง!)
นอกจากนี้ Present Continuous Tense ยังได้รับรู้ผ่านโครงสร้างในส่วนที่ 2

แยกความแตกต่างระหว่าง Present Continuous Tense กับโครงสร้างและ tense ที่ทำให้สับสนง่าย
Present Continuous Tense กับโครงสร้าง be going to
เหมือนกัน: มีหน้าที่หนึ่งที่เหมือนกัน นั่นคือการแสดงแผนในอนาคต
ความแตกต่างเกี่ยวกับหน้าที่นี้:
| Present Continuous Tense | be going to |
|---|---|
| แสดงถึงแผนการในอนาคตอันใกล้ที่มีความเป็นไปได้สูงที่จะเกิดขึ้นและมักมาจะพร้อมกับเวลาที่กำหนด | แสดงแผน/ตารางเวลาที่กำหนด ยาก หเปลี่ยนแปลงไปยาก เช่น – ตารางรถไฟ รถยนต์ เครื่องบิน ฯลฯ – ตารางเดินทาง – ตารางเรียน… |
| ตัวอย่าง: I’m flying to Japan this weekend. (ฉันจะบินไปญี่ปุ่นสุดสัปดาห์นี้) | ตัวอย่าง: Your plane takes off at 5pm. (เครื่องบินจะออกไปตอนเวลา 17.00 น.) |
Present Continuous Tense กับ Simple Present Tense
เหมือนกัน: มีสิ่งเดียวที่ทำให้เกิดความสับสนคือ ทั้ง 2 tense นี้มีหน้าที่เหมือนกันในความสัมพันธ์กับอนาคต
ความแตกต่างเกี่ยวกับหน้าที่นี้:
| Present Continuous Tense | Simple Present Tense |
|---|---|
| เวลาที่วางแผนไว้ใกล้เคียงกับปัจจุบันมากขึ้น – มีแนวโน้มที่จะเกิดขึ้น | เวลาที่วางแผนไว้อยู่ไกลจากปัจจุบัน – มีโอกาสเกิดขึ้นน้อย |
| ตัวอย่าง: I’m flying to Japan this weekend. (ฉันจะบินไปญี่ปุ่นสุดสัปดาห์นี้) | ตัวอย่าง: I’m going to fly to Japan next month. (ฉันจะบินไปญี่ปุ่นเดือนหน้า) |
หมายเหตุ
- นอกเหนือจากประเด็นข้างต้น ทั้ง 2 tense นี้ไม่มีอะไรเกี่ยวข้องกัน
- หากคุณยังสงสัยว่า ความแตกต่างระหว่าง 2 tense นี้คืออะไร คุณสามารถเข้าใจได้ง่ายๆ ว่า หน้าที่หลักของ Present Continuous Tense คือ แสดงการกระทำที่เกิดขึ้นในขณะที่พูดหรือรอบๆ ช่วงเวลาของการพูด ส่วน Simple Present Tense ส่วนใหญ่จะแสดงความจริงตามธรรมชาติเกี่ยวกับโลก สังคม และข้อมูล ข้อเท็จจริงที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไปยากเกี่ยวกับบุคคลใดๆ (ชื่อ อายุ บุคลิกภาพ ฯลฯ)
- เพื่อแยกความแตกต่างให้ชัดเจนยิ่งขึ้น โปรดอ่านให้ละเอียด ส่วนที่ 5 หลักการใช้ Present Continuous Tense (หรือที่เรียกว่า หน้าที่) และรวบรวมหน้าที่ของ Simple Present Tense อย่างสมบูรณ์
แบบฝึกหัดเกี่ยวกับ Present Continuous Tense
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1: เติม -ing ให้กับคำกริยาด้านล่าง
| 1. play | 6. cook |
| 2. run | 7. wave |
| 3. swim | 8. die |
| 4. write | begin |
| 5. lie | 10. create |
คำตอบ:
| 1. playing | 6. cooking |
| 2. running | 7. waving |
| 3. swimming | 8. dying |
| 4. writing | 9. beginning |
| 5. lying | 10. creating |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2: เติม am/is/are (not) ลงในช่องว่างให้ถูกต้อง
1. Our boss________ talking to an important customer at the moment.
2. These days, I________ reading a good book.
3. This week, our teachers________ giving us a lot of homework.
4. Look! Ms. Brown________ waving at us.
5. What________ you doing? Why________ you doing your homework?
6. We________ flying to New York this weekend.
7. Our daughter________ playing in the garden. I couldn’t find her there.
คำตอบ:
| 1. is | 2. am | 3. are | 4. is | 5. are- aren’t | 6. are | 7. isn’t |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3: เลือกคำ/วลีที่เหมาะสมเพื่อเติมลงในช่องว่างให้ถูกต้อง
1. Where________ the children playing?
A. is B. be C. are D. was
2. Jack and I ________ (bake) a cake.
A. am baking B. are bakeing C. are baking D. is baking
3. Look! That child________ (play) near that big dog. It’s dangerous!
A. playing B. are playing C. is playing D. is playing
4. Who________ our sisters visiting this Friday?
A. are B. is C. am D. was
5. That employee________ (borrow) my money all the time.
A. borrows B. is borrowing C. borrowed D. are borrowing
6. Anna, you________ (think) I took the money, right?
A. are thinking B. thinks C. are think D. think
7. This cake________ (look) good.
A. look B. is looking C. looking D. looks
คำตอบ:
| 1. C | 2. C | 3. D | 4. A | 5. B | 6. D | 7. D |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 4: ผันคำกริยาในวงเล็บลงใน Present Continuous Tense
1. That employee________ always________ (miss) deadlines.
2. These days, my mom________________ (do) yoga.
3. I________________ (buy) a new phone this Saturday.
4. Look! Those young men________________ (race).
5. Do you hear that? Someone________________ (sing).
6. They________________ (taste) the dishes from the new menu.
7. You________________ (lie) to me. You can’t even look into my eyes.
คำตอบ:
1. is always missing
2. is doing yoga
3. am buying
4. are racing
5. is singing
6. are tasting
7. are lying
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 5: จับคู่ประโยคในคอลัมน์ด้านซ้ายกับคอลัมน์ด้านขวา
| 1. I always go to work by motorbike. | A. We are taking them to Disneyland this weekend. |
| 2. The teacher needs to talk to that student. | B. She is missing deadlines all the time. |
| 3. He doesn’t like vegetables. | C. He is constantly losing them. |
| 4. Our children are very excited right now. | D. But this week, he is eating a lot of carrot. |
| 5. Look! | E. But I’m taking the bus this month. |
| 6. Our boss doesn’t like that employee. | F. The bus is coming. |
| 7. I won’t lend him my pens anymore. | G. He is always using his phone in class. |
คำตอบ:
| 1. E | 2. G | 3. D | 4. A | 5. F | 6. B | 7. C |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 6: จัดเรียงคำด้านล่างเพื่อสร้างประโยคที่ถูกต้อง
1. are/ my parents/ reading/ at the moment/ newspapers/ .
2. singing karaoke/ at night/ our neighbor/ constantly/ is/ .
3. the students/ doing/ what/ are/ at the moment/ ?
4. visiting/ us/ is/ this Friday/ my sister/ .
5. our apple tree/ climbing up/ that girl/ is/ .
6. a lot/ these days/ is speaking/ that quiet guy/ .
7. is watching/ this month/ our dad/ an interesting series/ .
คำตอบ:
1. My parents are reading newspapers at the moment.
2. Our neighbour is constantly singing karaoke at night.
3. What are the students doing at the moment?
4. My sister is visiting us this Friday.
5. That girl is climbing up our apple tree.
6. That quiet guy is speaking a lot these days.
7. Our dad is watching an interesting series this month.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 7: แต่ละประโยคด้านล่างมีข้อผิดพลาด 1 ข้อ โปรดค้นหาและแก้ไขให้ถูกต้อง
1. Look! Those two are raceing.
2. The children are playying in the living room.
3. Wow! This cake is smelling good.
4. My sisters is wearing my clothes all the time.
5. My friend are flying to Paris this Sunday.
6. David and I am taking the bus to school this month.
7. That co-worker is geting to work late all the time.
คำตอบ:
1. raceing → racing
2. playying → playing
3. is smelling → smells
4. is wearing → are wearing
5. are flying → is flying
6. are taking → am taking
7. geting → getting
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 8: ผันคำกริยาในวงเล็บใน Present Continuous Tense เพื่อเติมข้อความด้านล่างให้สมบูรณ์
I have just changed my job. Currently, things________________ (1. go) well. Since I’m a newbie, I ________ still________ (2. learn). I ________________ (3. try) my best to adapt to the new environment. My co-workers are very friendly and nice. They ________________ (4. help) me a lot. My boss ________ also________ (5. show) me how to complete some important tasks. Although I ________ still________ (6. feel) a little nervous these days, I think it will be alright.
คำตอบ:
1. are going
2. am still learning
3. am trying
4. are helping
5. is also showing
6. am still feeling
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 9: ตั้งคำถามสำหรับส่วนที่ขีดเส้นใต้
1. This month, I’m reading a novel.
2. They are discussing the problem in the meeting room.
3. My husband is talking to our daughter’s homeroom teacher.
4. The kids are playing happily and noisily.
5. Susan is writing 3 reports.
6. We are visiting our parents this Sunday.
7. I’m going to the gym this month.
คำตอบ:
1. What are you reading this month?
2. Where are they discussing the problem?
3. Who/ Whom is your husband talking to?
4. How are the kids playing?
5. How many reports is Susan writing?
6. When are you visiting your parents?
When are we visiting our parents?
7. What are you doing this month?
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 10: ตอบคำถามปลายเปิดด้านล่าง
1. Are you doing anything special these days? What is it?
2. What is a bad habit of your (best) friend(s)?
3. What is a bad habit of your co-worker(s)?
4. Are you doing anything special that you normally don’t? What is it?
>>> Read more
- [การ review อย่างละเอียด] App เรียนภาษาอังกฤษสำหรับเด็กดีหรือไม่ราคาเท่าไหร่
- [รีวิวแบบละเอียด] ELSA Speak คืออะไร? แอปฝึกพูดภาษาอังกฤษสำหรับคนทำงานที่มีเวลาน้อย
คำตอบ:
นี่เป็นคำถามปลายเปิด ดังนั้นจึงไม่มีคำตอบเฉพาะสำหรับแต่ละคำถาม คุณเพียงแค่ต้องใช้ Present Continuous Tense ในการตอบ
คำถามสอดคล้องกับหน้าที่ต่อไปนี้:
1. การกระทำที่เกิดขึ้นในรอบ ๆ ประเด็นของการพูด
2. นิสัย (ไม่ดี)/การกระทำ (ไม่ดี) ที่ทำซ้ำๆ ทำให้ผู้พูดไม่พอใจ
3. นิสัย (ไม่ดี)/การกระทำ (ไม่ดี) ที่ทำซ้ำๆ ทำให้ผู้พูดไม่พอใจ
4. สถานการณ์ที่มีอยู่ หรือนิสัยที่คงอยู่ในปัจจุบัน ซึ่งเกิดขึ้นชั่วคราว ผิดปกติ เมื่อเทียบกับสภาพหรือนิสัยที่เป็นมายาวนาน
ELSA Speak ได้รวบรวมสิ่งที่ควรทราบเกี่ยวกับ Present Continuous Tense อย่างครบถ้วนแล้ว เพื่อให้คุณสามารถเห็นภาพรวมของไวยากรณ์ที่สำคัญนี้ได้ดียิ่งขึ้น ขอให้เรียนดีๆนะ!






