Author: Bao Ngan Nguyen
คำถาม How are you doing ไม่ใช่แค่คำถามเกี่ยวกับสุขภาพ แต่ยังแสดงความห่วงใยผู้อื่นด้วย เข้าร่วม ELSA Speak เพื่อเรียนรู้วิธีใช้และตอบคำถามนี้ในการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวันกันเลย
How are you doing แปลไทยคืออะไร?
คำถาม How are you doing เป็นวิธีทั่วไปในการถามเกี่ยวกับสุขภาพ อารมณ์ หรือสถานการณ์ของบุคคล ประโยคนี้มักใช้ในการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวัน โดยเฉพาะในการสนทนาที่เป็นกันเอง มันแสดงความห่วงใยผู้อื่นและสามารถตอบได้หลากหลายวิธี รวมถึงคำตอบสั้นๆ เช่น I’m fine, Thank you ไปจนถึงคำตอบที่ละเอียดมากขึ้นเกี่ยวกับอารมณ์หรือสถานการณ์ของตน
คำถามนี้ไม่ใช่แค่คำถามด้านสุขภาพ แต่ยังเป็นวิธีสร้างความสัมพันธ์และรักษาความเชื่อมโยงในการสื่อสารอีกด้วย
ตัวอย่าง:
- Hey, John! How are you doing today? (เฮ้ จอห์น วันนี้คุณเป็นยังไงบ้าง?)
- I havent seen you in a while. How are you doing? (ไม่เจอคุณนานแล้ว เป็นยังไงบ้าง?)
- How are you doing with your new job? (งานใหม่ของคุณเป็นยังไงบ้าง?)

ความแตกต่างระหว่าง How are you doing, How are you, What are you doing และ How do you do
| คำถาม | ความหมาย | บริบทการใช้งาน | ตัวอย่าง |
| How are you doing? | ถามถึงสภาพหรือความรู้สึกของใครบางคน | มักใช้ในการสื่อสารที่เป็นกันเองกับเพื่อนฝูง | Hey, Sarah! How are you doing? I heard you were sick. (เฮ้ ซาร่าห์ เป็นยังไงบ้าง ฉันได้ยินมาว่าคุณไม่สบาย) |
| How are you? | ถามเกี่ยวกับสุขภาพหรืออารมณ์ของใครบางคน | เป็นที่นิยมทั้งในสถานการณ์ที่ไม่เป็นทางการและเป็นทางการ | Hello, Mr. Smith! How are you? สวัสดี คุณสมิธ สบายดีไหม?) |
| What are you doing? | ถามเกี่ยวกับกิจกรรมปัจจุบันของผู้อื่น | ใช้เมื่อคุณต้องการรู้ว่าคนอื่นกำลังทำอะไรอยู่ในปัจจุบัน | What are you doing right now? (ทำอะไรกันอยู่คะ/ครับ?) |
| How do you do? | การทักทายอย่างเป็นทางการ มักใช้เมื่อพบกันครั้งแรก | มักพบเห็นในพิธีการและงานพิธีการต่างๆ | How do you do? My name is Alex. Nice to meet you. (สบายดีไหม ฉันชื่ออเล็กซ์ ยินดีที่ได้รู้จัก) |
- How are you doing? และ How are you? ทั้งสองประโยคแสดงความดูแลผู้อื่น แต่ How are you doing มักใช้ในการสนทนาที่ไม่เป็นทางการมากกว่า
- What are you doing? มุ่งเน้นไปที่การกระทำในปัจจุบันและไม่จำเป็นต้องแสดงความกังวลเกี่ยวกับอารมณ์
- How do you do? เป็นคำถามทักทายอย่างเป็นทางการและไม่ต้องการคำตอบโดยละเอียด มักจะตอบด้วยคำถามเดียวกัน

How are you doing ตอบอย่างไร?
คำตอบสั้น
| สภาพการณ์ | คำตอบ | ความหมาย |
| ดี | I’m doing great. | ฉันสบายดี |
| Never been better. | ไม่เคยรู้สึกดีไปกว่านี้ | |
| Full of beans. | มีชีวิตชีวามาก (คำไม่เป็นทางการ) มีสุขภาพแข็งแรง | |
| Can’t complain. | ก็โอเค ก็ดี | |
| I’m doing amazing. | ฉันสบายดี | |
| It’s all good. | ฉันโอเคเลย | |
| I am pretty good. / I am pretty well. | ฉันรู้สึกดีมาก | |
| So far, so good. | ก็ดี | |
| ธรรมดา | Fine. | สบายดี |
| Just the usual. | ก็ปกติ ทั่วไป | |
| Not bad. | ไม่แย่ | |
| Just the same old same old. | ซ้ำๆเดิมๆ | |
| Nothing. | ไม่มีอะไร | |
| Fair to middling. | พอใช้ได้ พอยอมรับได้ | |
| I’m hanging in there. | อย่ายอมแพ้ ทนอีกหน่อย อย่าท้อ สู้ๆ | |
| So-so. | พอใช้ได้ | |
| Still alive. | ยังไหวอยู่ | |
| I’m alive / I’m surviving. | ยังไหวอยู่ | |
| Good enough. | พอดี | |
| แย่ | Rotten. | แย่สุด ๆ |
| I’m struggling a bit. | ฉันก็กำลังดิ้นรนอยู่นิดหน่อย | |
| It couldn’t be worse. | แย่กว่านี้ไม่ได้แล้ว | |
| I’m snowed under. | งานท่วมหัว | |
| Not great. | ไม่ค่อยดี | |
| I’ve been feeling down lately. | ฉันรู้สึกหดหู่ในช่วงนี้ | |
| I’m not doing so well. | ฉันไม่ค่อยสบาย | |
| It’s been a bit of a tough week. | มันเป็นสัปดาห์ที่ยากลำบากเล็กน้อย | |
| I’m not having an easy time at the moment. | ฉันไม่ได้มีช่วงเวลาที่ง่ายในขณะนี้ | |
| หลีกหนี | You don’t want to know. | คุณไม่อยากรู้เลย |
| Honestly, just don’t ask me. | จริงๆ แล้วอย่าถามฉันเลย | |
| Do I have to answer that? | ฉันต้องตอบคำถามนั้นไหม? |

คำตอบยาว
ในชีวิตประจำวัน การตอบคำถาม How are you doing อย่างละเอียดสามารถช่วยแสดงความรู้สึกและสภาพของตัวเองได้ชัดเจนยิ่งขึ้น ด้านล่างนี้เป็นคำตอบยาวๆ และสุภาพ พร้อมคำแปลให้การใช้
| คำตอบ | ความหมาย |
| I had a busy day at work, but I’m feeling accomplished. | วันทำงานของฉันยุ่งมาก แต่ฉันก็รู้สึกว่าตัวเองประสบความสำเร็จแล้ว |
| Things are good, how about you? | ทุกสิ่งทุกอย่างก็ดีแล้วคุณล่ะ? |
| I’m doing just fine. Thanks for asking! | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณที่ถามนะ! |
| Not too much to complain about. How about you? | ไม่มีอะไรจะบ่นมากไปกว่านี้แล้วคุณล่ะ? |
| I’m feeling pretty good, thanks for asking! | ฉันรู้สึกดีมาก ขอบคุณที่ถาม! |
| I’m doing just fine. How’s your week been? | ฉันสบายดี สัปดาห์นี้คุณเป็นยังไงบ้าง? |

>>> Read more: 11 วิธีพูด Thank you – ขอบคุณภาษาอังกฤษที่สมบูรณ์ที่สุด
คำตอบที่ใช้ในสถานการณ์ที่เป็นทางการ
ในบริบทที่เป็นทางการ การตอบคำถาม How are you doing ควรทำอย่างมืออาชีพและมีไหวพริบ คำตอบด้านล่างไม่เพียงแต่แสดงความสุภาพเท่านั้น แต่ยังให้ความรู้สึกที่ดีต่อทัศนคติและสไตล์การทำงานของคุณด้วย
| คำตอบ | ความหมาย |
| I’m doing well, thanks for checking in. How can I assist you today? | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณที่แวะมาเยี่ยม วันนี้ฉันจะช่วยคุณได้อย่างไร? |
| I’m doing fine, thank you for asking. I’m interested in learning more about your objectives. | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณที่ถาม ฉันสนใจที่จะเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับเป้าหมายของคุณ |
| I’m great. Thank you for inquiring. I appreciate your attention to detail. | ฉันโอเค ขอบคุณที่ถามไถ่ ฉันชื่นชมความใส่ใจในรายละเอียดของคุณ |
| I’m doing well, thanks for asking. I’m confident we can find a solution. | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณที่ถาม ฉันมั่นใจว่าเราจะหาทางออกได้ |
| I’m doing well. Thank you for checking in. It’s a busy day, but I’m managing. | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณที่แวะมา วันนี้เป็นวันที่ยุ่งมาก แต่ฉันก็จัดการได้ |
| I’m good, thank you. I appreciate the opportunity to speak with you today. | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณมาก ฉันยินดีที่ได้มีโอกาสพูดคุยกับคุณในวันนี้ |
| I’m doing well, thanks for inquiring. I’m confident about our progress so far. | ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณที่ถามไถ่ ฉันมั่นใจในความก้าวหน้าของเราจนถึงตอนนี้ |
| I’m doing fine, and I appreciate your care. I’m excited to get started on the project’s details. | ฉันสบายดีและขอบคุณที่คุณดูแล ฉันตื่นเต้นที่จะเริ่มลงรายละเอียดโครงการ |

คำตอบที่ใช้เมื่อคุณอยู่ในสถานการณ์ที่ยากลำบาก
เมื่อเผชิญกับช่วงเวลาที่ยากลำบาก การแบ่งปันอย่างตรงไปตรงมาแต่รักษาทัศนคติเชิงบวกเมื่อตอบโต้ How are you doing เป็นวิธีแสดงความจริงใจ ด้านล่างนี้คือคำตอบและคำแปลที่แนะนำเพื่อให้คุณนำไปใช้ได้อย่างง่ายดาย
| คำตอบ | ความหมาย |
| To be honest, I’m struggling. But I appreciate your concern. | จริงๆ แล้ว ฉันก็กำลังลำบากอยู่ และฉันซาบซึ้งในความกังวลของคุณมาก |
| I’m going through a tough period. But I’m doing my best to cope. | ฉันกำลังเผชิญช่วงเวลาที่ยากลำบาก แต่ฉันก็พยายามอย่างเต็มที่เพื่อรับมือกับมัน |
| Today has been challenging, but I’m trying to focus on the positives. | วันนี้เป็นวันที่ท้าทาย แต่ฉันจะพยายามโฟกัสสิ่งดีๆ |
| I’m not doing very well today, but I’m trying to stay strong. | วันนี้ฉันทำได้ไม่ดีนัก แต่ฉันก็พยายามที่จะเข้มแข็งอยู่ |
| Im having a hard time today, but I know Im not alone in this. | วันนี้ฉันมีช่วงเวลาที่ยากลำบาก แต่ฉันรู้ว่าฉันไม่ได้เป็นคนเดียวที่ประสบปัญหานี้ |

ตัวอย่างบทสนทนาที่ใช้ How are you doing?
ในการสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษ คำถาม How are you doing? ใช้ได้อย่างยืดหยุ่นในหลาย ๆ สถานการณ์เพื่อถามหรือเริ่มการสนทนา ด้านล่างนี้คือตัวอย่างบทสนทนาที่อธิบายวิธีใช้คำถามนี้ในแต่ละบริบท พร้อมแปลไทย
ตัวอย่างบทสนทนาเพื่อเริ่มการสนทนา
คำถาม How are you doing คือการกล่าวเปิดที่เป็นกันเอง เหมาะสำหรับบริบทการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวันหลายๆ อย่าง ต่อไปนี้เป็นสถานการณ์ตัวอย่างสองสถานการณ์: การพบปะเพื่อนฝูงและการทักทายเพื่อนร่วมงานในตอนเช้า บทสนทนารวมถึงวิธีการถามคำถาม ตอบอย่างสุภาพ และดำเนินบทสนทนาต่อไปอย่างเป็นธรรมชาติ ทำให้ง่ายต่อการนำไปใช้ในการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวัน
| บุคคล | บทสนทนา | ความหมาย |
| สนทนาที่ 1: พบปะเพื่อนฝูงที่ร้านกาแฟ | ||
| John | Hi, Lisa! How are you doing? | สวัสดี ลิซ่า สบายดีไหม? |
| Lisa | Hey, John! I’m doing great, thanks. How about you? | เฮ้ จอห์น ฉันสบายดี ขอบคุณ แล้วคุณล่ะ? |
| John | Not bad. It’s nice to finally catch up with you. | ไม่เลว ดีใจที่ได้เจอคุณสักที |
| สนทนาที่ 2: การทักทายเพื่อนร่วมงานในตอนเช้า | ||
| Anna | Good morning, Mike! How are you doing today? | สวัสดีตอนเช้า ไมค์ วันนี้คุณเป็นยังไงบ้าง? |
| Mike | Morning, Anna! I’m doing well. Ready for the big meeting? | สวัสดีตอนเช้า แอนนา ฉันสบายดี พร้อมสำหรับการประชุมใหญ่แล้วหรือยัง? |
| Anna | Absolutely! Let’s make it a productive day. | แน่นอน! มาทำให้วันนี้เป็นวันทำงานที่มีประสิทธิภาพกันเถอะ |

>>> Read more: ทักทายภาษาอังกฤษ : คำถาม คำตอบกลับ ทุกสถานการณ์ที่ควรรู้
ตัวอย่างบทสนทนาถามถึงสถานการณ์ทั่วไป
How are you doing เป็นวิธีที่มีประสิทธิภาพในการถามเกี่ยวกับความก้าวหน้าหรือสถานะของงานหรือการมอบหมายงานอีกด้วย ตัวอย่างด้านล่างแสดงวิธีการถามและตอบคำถามในสภาพแวดล้อมทางวิชาชีพหรือทางวิชาการ การสนทนาเหล่านี้ไม่เพียงแต่ช่วยสร้างความสัมพันธ์เท่านั้น แต่ยังแสดงความใส่ใจอย่างทันท่วงทีอีกด้วย
| บุคคล | บทสนทนา | ความหมาย |
| สนทนาที่ 1: เพื่อนร่วมงานถามถึงความคืบหน้าของโครงการ | ||
| John | Hey, Tom! How are you doing with the new project? | เฮ้ ทอม โปรเจ็กต์ใหม่ของคุณเป็นยังไงบ้างครับ? |
| Tom | It’s coming along well. Just need a bit more time to finalize the details. | โปรเจ็กต์นี้คืบหน้าไปมากแล้ว แค่ต้องการเวลาอีกนิดหน่อยเพื่อสรุปรายละเอียด |
| John | Great to hear! Let me know if you need any help. | ฟังดูดีนะ โปรดแจ้งให้ฉันทราบหากคุณต้องการความช่วยเหลือ |
| สนทนาที่ 2: ครูถามนักเรียนเกี่ยวกับการบ้าน | ||
| Teacher | Hi everyone! How are you doing with your assignments? | สวัสดีทุกคน! พวกคุณทำการบ้านกันยังไงบ้าง? |
| Student | Most of us are doing fine, but the last question is a bit tricky. | พวกหนูก็ทำได้ดี แต่คำถามสุดท้ายค่อนข้างจะยากหน่อย |
| Teacher | Alright, let’s go over it together. | เอาล่ะ มาทบทวนกันหน่อย |

>>> Read more: 160+ วิธีบอก ขอให้เป็นวันที่ดี ภาษาอังกฤษ (have a nice day) ให้ทุกคน
ตัวอย่างบทสนทนาเพื่อถามเมื่อเกิดปัญหา
การใช้ How are you doing หลังจากเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นวิธีการแสดงความห่วงใยและการสนับสนุนที่ละเอียดอ่อน สถานการณ์ตัวอย่างด้านล่าง เช่น การถามเพื่อนร่วมงานหลังจากปัญหาทางเทคนิคหรือเพื่อนหลังจากย้ายบ้าน จะช่วยคุณนำคำถามนี้ไปใช้ในสถานการณ์ที่เหมาะสม ซึ่งจะสร้างความสัมพันธ์และให้กำลังใจแก่คู่ของคุณ
| บุคคล | บทสนทนา | ความหมาย |
| สนทนาที่ 1: การถามเพื่อนร่วมงานหลังจากปัญหาทางเทคนิค | ||
| Tim | Hi, Sarah. How are you doing after that system crash yesterday? | สวัสดี ซาราห์ เมื่อวานระบบล่มเป็นยังไงบ้าง? |
| Sarah | It was a bit stressful, but everything is back on track now. Thanks for asking! | เครียดนิดหน่อย แต่ตอนนี้ทุกอย่างกลับมาเป็นปกติแล้ว ขอบคุณที่ถามนะ! |
| Tim | That’s a relief. Let’s hope it doesn’t happen again. | โล่งอกไปที หวังว่าคงจะไม่เกิดขึ้นอีก |
| สนทนาที่ 2: แสดงความห่วงใยกับเพื่อนหลังจากที่ประสบปัญหา | ||
| Anna | Hey, Jake. How are you doing after the move? | เฮ้ เจค คุณเป็นยังไงบ้างหลังจากย้ายบ้าน |
| Jake | It’s been hectic, but I’m settling in slowly. | วุ่นวายอยู่เหมือนกัน แต่ตอนนี้ฉันเริ่มปรับตัวได้แล้ว |
| Anna | Glad to hear that. Let me know if you need help with anything. | ดีใจจังที่ได้ยินแบบนั้น บอกฉันด้วยถ้าคุณต้องการความช่วยเหลืออะไร |
คำถาม How are you doing ไม่เพียงแต่เป็นส่วนสำคัญของการสื่อสารในแต่ละวันเท่านั้น แต่ยังช่วยให้คุณเชื่อมโยงและสร้างความสัมพันธ์อีกด้วย เพื่อพัฒนาทักษะการสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษ คุณสามารถใช้แอปพลิเคชัน ELSA Speak ,มันจะช่วยปรับปรุงการออกเสียงและมีความมั่นใจมากขึ้นในการสื่อสาร ซึ่งคุณสามารถใช้คำถาม How are you doing และตอบได้ง่ายขึ้น และประโยคการสื่อสารอื่นๆ ที่ยากขึ้นอีกด้วย
โครงสร้างของ enough ถูกใช้อย่างมากในการสื่อสารและการเรียนรู้ในชีวิตประจำวัน อย่างไรก็ตาม คุณยังไม่รู้ว่าสถานการณ์ใดที่เหมาะสมที่จะใช้ อย่ากังวลเลยเพราะในบทความนี้ ELSA Speak จะช่วยคุณเข้าใจอย่างรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับโครงสร้าง enough และวิธีใช้ถูกต้องที่สุด เรามาดูกันเถอะ
Enough มันคืออะไร?

Enough หมายความว่า พอหรือจำนวนที่พอเพียง enough อ่านว่า /ɪˈnʌf/ ในความหมายเชิงลบ not enough แปลว่า ไม่เพียงพอหรือน้อยกว่าที่ต้องการ อย่างไรก็ตาม ขึ้นอยู่กับบริบทและวัตถุประสงค์ของการใช้ enough จะมีความหมายที่แตกต่างกัน enough ยังสามารถใช้เพื่อระบุว่าปริมาณหรือขนาดของวัตถุนั้นเพียงพอหรือไม่
Enough ตัวอย่างประโยค :
- I don’t have enough money to buy that dress. (ฉันมีเงินไม่พอที่จะซื้อชุดนั้น)
- She is intelligent enough to understand the problem. (เขาฉลาดพอที่จะเข้าใจปัญหาได้)
โครงสร้าง enough ในภาษาอังกฤษ
โครงสร้าง enough ในภาษาอังกฤษได้ใช้เพื่อแสดงความเพียงพอของบางสิ่งบางอย่าง โครงสร้างของ enough ที่พบบ่อยในภาษาอังกฤษ เช่น:
โครงสร้าง enough + คำนาม (เพียงพอ + คำนาม)
หาก enough ใช้ร่วมกับคำนาม –> enough จะอยู่หน้าคำนาม
| ประโยค | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง | แปล |
| บอกเล่า | S + V + enough + noun + (for sb) + to V | She has enough money to buy the car. | เธอมีเงินพอที่จะซื้อรถคันนั้น |
| ปฏิเสธ | S + did/do/does + not + V + Enough + noun + (for sb) + to V | She doesn’t have enough money to buy a chair. | เธอมีเงินไม่พอที่จะซื้อเก้าอี้ |
| คำถาม | Did/do/does + S + V + enough + noun + (for sb) + to V? | Will they have enough evidence to prove John is a thief? | พวกเขาจะมีหลักฐานเพียงพอที่จะพิสูจน์ว่าจอห์นเป็นขโมยหรือไม่? |
| ประโยคคำสั่ง (แนะนำ) | Be + enough + Noun + to V + O | Be enough confident to speak in public. | จงมีความมั่นใจเพียงพอที่จะพูดต่อหน้าสาธารณชน |

โครงสร้าง enough + adj
หาก enough ใช้ร่วมกับคำคุณศัพท์ enough จะอยู่หลังคำคุณศัพท์
| ประโยค | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง | แปล |
| บอกเล่า | S + be + adj + enough + (for somebody) + to V | The movie was interesting enough to watch again. | หนังเรื่องนี้น่าสนใจพอที่จะดูซ้ำอีกครั้ง |
| ปฏิเสธ | S + be + not + adj + enough + (for somebody) + to V | The test was not easy enough for me to pass. | การทดสอบนั้นไม่ง่ายพอที่ฉันจะผ่านได้ |
| คำถาม | Is/Are + S + adj + enough + for O? | Is this room big enough for the party? | ห้องนี้ใหญ่พอสำหรับงานปาร์ตี้หรือเปล่า? |
| ประโยคคำสั่ง (แนะนำ) | Be + enough + adj | Be enough careful while driving. | จงระมัดระวังให้เพียงพอขณะขับรถ |
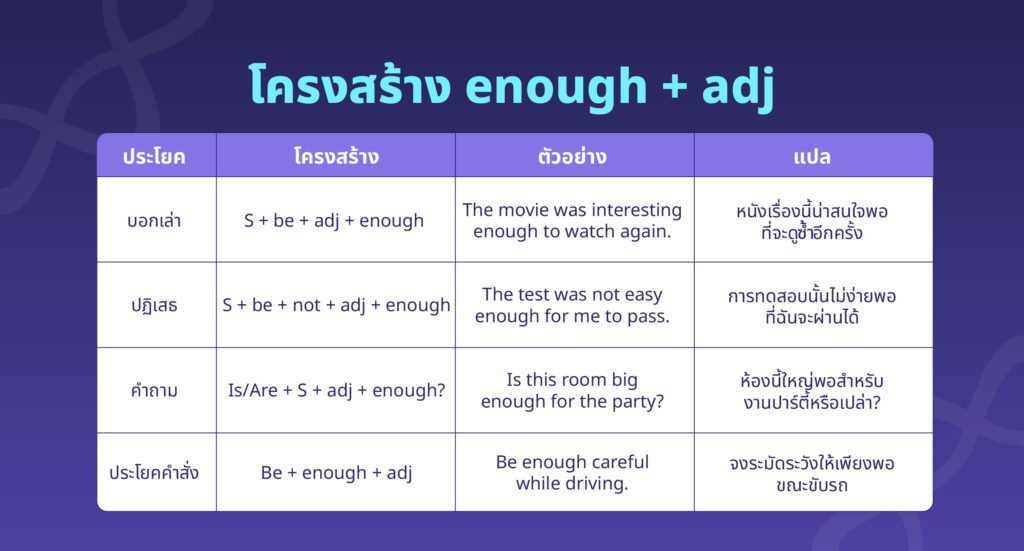
โครงสร้าง Enough + คำวิเศษณ์ (เพียงพอ+คำวิเศษณ์)
หาก enough ใช้ร่วมกับคำกริยาวิเศษณ์ enough จะอยู่หลังคำกริยาวิเศษณ์นั้น
| ประโยค | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง | แปล |
|---|---|---|---|
| บอกเล่า | S + verb + adv + enough + (for object) + to V | She runs fast enough to win the race. | เขาวิ่งเร็วพอที่จะชนะการแข่งขัน |
| ปฏิเสธ | S + don’t/doesn’t/didn’t + V + adv + enough + (for sb) + to V | He didn’t study hard enough to pass the exam. | เขาไม่ได้ตั้งใจเรียนพอที่จะสอบผ่าน |
| คำถาม | กริยาช่วย + S + adv + enough + to V + O? | Is she working hard enough to finish the project? | เธอกำลังทำงานหนักพอที่จะเสร็จโครงการหรือไม่? |
| ประโยคคำสั่ง (แนะนำ) | Be + enough + adv | Be enough careful when crossing the street. | จงระมัดระวังให้พอเมื่อข้ามถนน |
โครงสร้าง Enough + as + คำนาม
โครงสร้างนี้มีความหมายว่า เพียงพอ + ที่จะเป็น หรือ พอที่จะเป็น
ตัวอย่าง:
- He’s old enough as a voter. (เขามีอายุพอที่จะเป็นผู้มีสิทธิ์เลือกตั้ง)
- This room is big enough as a bedroom. (ห้องนี้ใหญ่พอที่จะเป็นห้องนอน)
โครงสร้าง Enough … to (พอที่จะทำ)
โครงสร้างนี้คล้ายๆ กับโครงสร้าง enough + คำคุณศัพท์/คำกริยาวิเศษณ์ + to V แต่สามารถละคำกริยาได้หากบริบทชัดเจน
ตัวอย่าง:
- This bag is light enough to carry. (กระเป๋านี้เบาพอที่จะถือ) → This bag is light enough. (กระเป๋านี้เบาพอ)
- He ran fast enough to catch the bus. (เขาวิ่งเร็วพอที่จะทันรถบัส) → He ran fast enough. (เขาวิ่งเร็วพอ)

ข้อควรรู้เกี่ยวกับวิธีการใช้ enough
ละเว้น Too, so, very, very, extreme… นำหน้าคำคุณศัพท์/กริยาวิเศษณ์
เมื่อใช้โครงสร้าง enough + คำคุณศัพท์/คำกริยาวิเศษณ์ + to V คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องเติมคำวิเศษณ์ too, so, very, quite, extremely อยู่หน้าคำคุณศัพท์หรือคำวิเศษณ์ เพราะคำว่า enough นั้นมีความหมายพอชัดเจน และไม่จำเป็นต้องมีการเน้นเพิ่มเติม
| ประโยคเดิม | ประโยคผิด | ประโยคถูกต้อง |
| She is very tall enough to reach the top shelf. | She is very tall enough to reach the top shelf. (เธอสูงมากพอที่จะหยิบของจากชั้นวางสูงสุดได้) | She is tall enough to reach the top shelf. (เธอสูงพอที่จะหยิบของจากชั้นวางสูงสุด) |
| The soup is quite hot enough to burn your tongue. | The soup is quite hot enough to burn your tongue. (ซุปค่อนข้างร้อนพอที่จะเผาลิ้นของคุณได้) | The soup is hot enough to burn your tongue. (ซุปนี้ร้อนพอที่จะเผาลิ้นของคุณได้) |
| He works so hard enough to achieve success. | He works so hard enough to achieve success. (เขาทำงานหนักพอมากที่จะประสบความสำเร็จ) | He works hard enough to achieve success. (เขาทำงานหนักพอที่จะประสบความสำเร็จ) |
| This bag is too heavy enough for me to carry. | This bag is too heavy enough for me to carry. (กระเป๋าใบนี้หนักเกินไปสำหรับฉันที่จะถือได้) | This bag is heavy enough for me to carry. (กระเป๋านี้หนักพอสำหรับฉันที่จะถือ) |
| The weather is extremely cold enough for snow. | The weather is extremely cold enough for snow. (อากาศหนาวจัดพอที่จะมีหิมะตก) | The weather is cold enough for snow. (อากาศหนาวพอที่จะมีหิมะ) |
| She is very smart enough to solve the puzzle. | She is very smart enough to solve the puzzle. (เธอฉลาดมากพอที่จะไขปริศนาได้) | She is smart enough to solve the puzzle. (เธอฉลาดพอที่จะไขปริศนาได้) |
| The car is so expensive enough for most people. | The car is so expensive enough for most people. (รถคันนี้มีราคาแพงมากพอสำหรับคนส่วนใหญ่) | The car is expensive enough for most people. (รถคันนี้มีราคาแพงพอที่คนส่วนใหญ่สามารถซื้อได้) |
| He didn’t run too fast enough to win the race. | He didn’t run too fast enough to win the race. (เขาวิ่งได้ไม่เร็วพอที่จะชนะการแข่งขัน) | He didn’t run fast enough to win the race. (เขาวิ่งไม่เร็วพอที่จะชนะการแข่งขัน) |
| The box is quite small enough to fit in the closet. | The box is quite small enough to fit in the closet. (กล่องนี้ค่อนข้างเล็กพอที่จะใส่ในตู้เสื้อผ้า) | The box is small enough to fit in the closet. (กล่องนี้เล็กพอที่จะใส่ในตู้เสื้อผ้า) |
| This chair is extremely comfortable enough to use. | This chair is extremely comfortable enough to use. (เก้าอี้ตัวนี้สะดวกสบายมากพอที่จะใช้) | This chair is comfortable enough to use. (เก้าอี้ตัวนี้สะดวกสบายพอที่จะใช้) |

ละเว้น Much, many, a lot of, lots of… นำหน้าคำนาม
| ประโยคเดิม | ประโยคผิด | ประโยคถูกต้อง |
| I have a lot of money, but not enough. | I have money, but not enough. | I have enough money. (ฉันมีเงินพอ) |
| She doesn’t read many books, but she has enough. | She doesn’t read books, but she has enough. | She doesn’t read enough books. (เธออ่านหนังสือไม่มากพอ) |
| We need a lot of time to finish, but we have enough. | We need time to finish, but we have enough. | We need enough time to finish.(เราต้องการเวลาเพียงพอที่จะทำให้เสร็จ) |
| They don’t have lots of experience, but they are enough qualified. | They don’t have experience, but they are enough qualified. | They are qualified enough. (พวกเขามีคุณสมบัติเพียงพอ) |
| There isn’t much food left, but there is enough. | There isn’t food left, but there is enough. | There is enough food left. (ยังมีอาหารเหลือเพียงพอ) |
| He doesn’t see many opportunities, but he has enough. | He doesn’t see opportunities, but he has enough. | He has enough opportunities. (เขามีโอกาสเพียงพอ) |
| I want lots of help, but I have enough. | I want help, but I have enough. | I have enough help. (ฉันได้รับความช่วยเหลือเพียงพอ) |

ละเว้น for sb หลังโครงสร้าง enough ถ้าประธานอยู่ใน 2 ประโยคเหมือนกัน
เมื่อใช้ enough + คำนาม คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องเติมคำ เช่น much, many, a lot of, lots of ก่อนคำนาม เพราะ enough มีความหมายว่า พอแล้ว แสดงปริมาณที่ตรงตามความต้องการโดยไม่จำเป็นต้องขยายเพิ่มเติม
ตัวอย่างประโยคถูกและผิด
| ประโยคเดิม | ประโยคผิด | ประโยคถูกต้อง |
| John is intelligent. He can become a doctor. | John is intelligent enough | John is intelligent enough to become a doctor. (จอห์นฉลาดพอที่จะเป็นหมอได้) |
| I am free. I can visit you tomorrow | I am free enough | I am free enough to go visit you tomorrow. (ฉันว่างพอที่จะไปเยี่ยมคุณในวันพรุ่งนี้) |
| Tom is smart. He is the smartest in his school. | Tom is smart enough | Tom is smart enough to be the smartest in his school. (ทอมฉลาดพอที่จะเป็นคนที่ฉลาดที่สุดในโรงเรียนของเขา) |
ละเว้นกรรมของประโยคที่สอง ถ้าประธานของประโยคแรกและกรรมของประโยคที่สองอ้างถึงวัตถุเดียวกัน
เมื่อประธานของประโยคแรกและกรรมของประโยคที่สองอ้างถึงวัตถุเดียวกัน สามารถละเว้นวัตถุในประโยคที่สองได้เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการกล่าวซ้ำโดยไม่จำเป็น ซึ่งจะทำให้ประโยคสั้นลง เป็นธรรมชาติมากขึ้น และเข้าใจง่ายขึ้น
| ประโยคเดิม | ประโยคผิด | ประโยคถูกต้อง |
| The coffee is quite hot. I can’t drink it. | The coffee isn’t cold enough for me to drink it. | The coffee isn’t cold enough for me to drink. (กาแฟไม่เย็นพอที่ฉันจะดื่มได้) |
| This task is very easy. She can finish it. | This task is easy enough for her to finish it. | This task is easy enough for her to finish. (หน้าที่นี้ง่ายพอที่เขาจะทำเสร็จได้) |
| She is very lovely. He falls for her. | She is lovely enough for him to fall for her. | She is lovely enough for him to fall for. (เธอน่ารักพอที่เขาจะตกหลุมรักเธอ) |

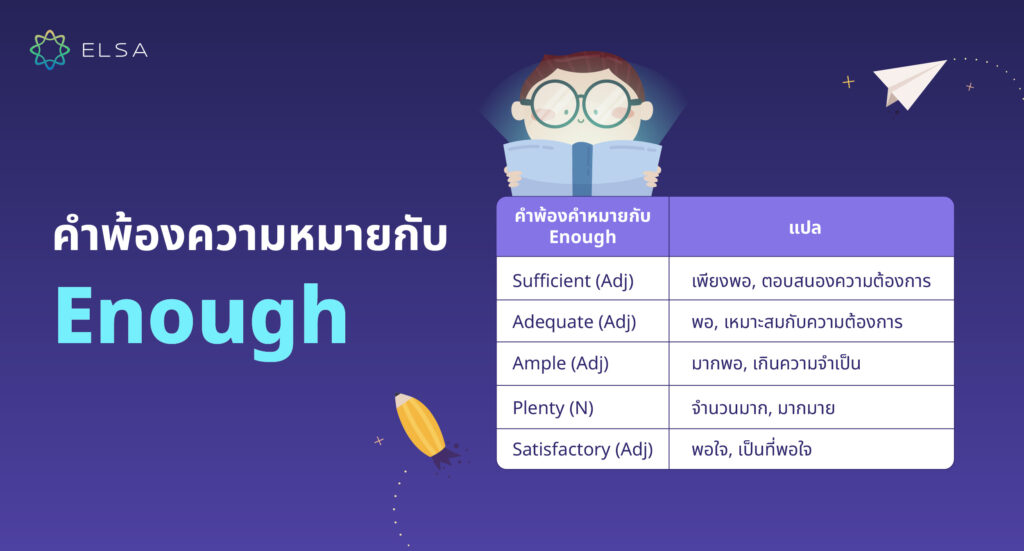
คำพ้องความหมายกับ Enough
| คำพ้องคำหมายกับ Enough | แปล | ตัวอย่าง |
| Sufficient (Adj) | เพียงพอ, ตอบสนองความต้องการ | We have sufficient food for the trip.(เรามีอาหารเพียงพอสำหรับการเดินทาง) |
| Adequate (Adj) | พอ, เหมาะสมกับความต้องการ | Her performance was adequate for the role.(การแสดงของเขาเพียงพอสำหรับบทบาทนี้) |
| Ample (Adj) | มากพอ, เกินความจำเป็น | There is ample room for all the guests.(มีพื้นที่มากพอสำหรับแขกทั้งหมด) |
| Plenty (N) | จำนวนมาก, มากมาย | We have plenty of time to finish this project.(เรามีเวลามากพอที่จะทำโครงการนี้ให้เสร็จ) |
| Satisfactory (Adj) | พอใจ, เป็นที่พอใจ | The feedback was satisfactory enough for the client.(ความคิดเห็น (หรือข้อเสนอแนะ) นั้นน่าพอใจพอสำหรับลูกค้า) |
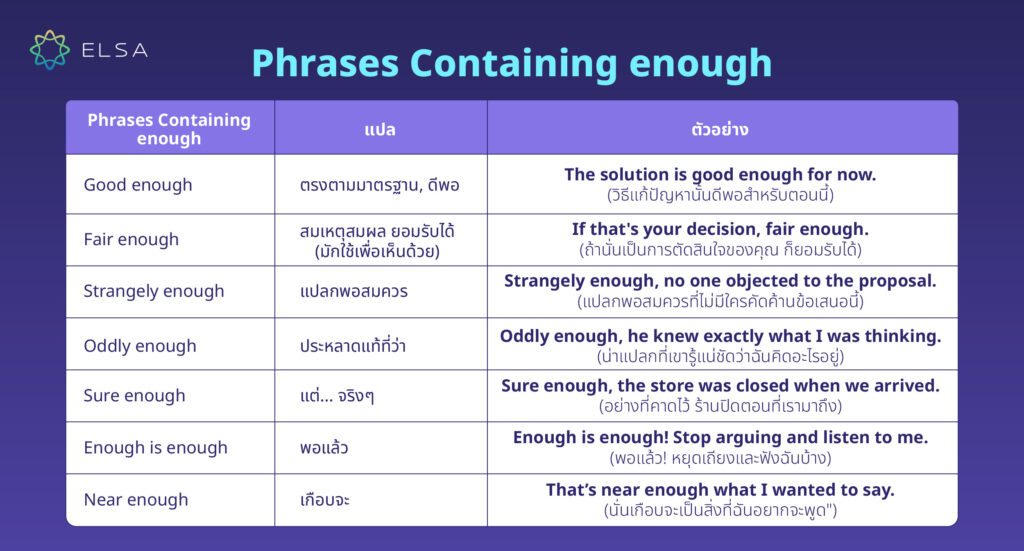
วลีที่มี enough
| Phrases Containing enough | แปล | ตัวอย่าง |
| Good enough | ตรงตามมาตรฐาน, ดีพอ | The solution is good enough for now.(วิธีแก้ปัญหานั้นดีพอสำหรับตอนนี้) |
| Fair enough | สมเหตุสมผล ยอมรับได้ (มักใช้เพื่อเห็นด้วย) | If that’s your decision, fair enough.(ถ้านั่นเป็นการตัดสินใจของคุณ ก็ยอมรับได้) |
| Strangely enough | แปลกพอสมควร | Strangely enough, no one objected to the proposal.(แปลกพอสมควรที่ไม่มีใครคัดค้านข้อเสนอนี้) |
| Oddly enough | ประหลาดแท้ที่ว่า | Oddly enough, he knew exactly what I was thinking.(น่าแปลกที่เขารู้แน่ชัดว่าฉันคิดอะไรอยู่) |
| Sure enough | แต่… จริงๆ | Sure enough, the store was closed when we arrived.(อย่างที่คาดไว้ ร้านปิดตอนที่เรามาถึง) |
| Enough is enough | พอแล้ว | Enough is enough! Stop arguing and listen to me.(ก็พอแล้ว! หยุดเถียงและฟังฉันบ้าง) |
| Near enough | เกือบจะ | That’s near enough what I wanted to say.(นั่นเกือบจะเป็นสิ่งที่ฉันอยากจะพูด) |
แบบฝึกหัดเกี่ยวกับ enough
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1: เติมประโยคที่สองให้สมบูรณ์ด้วยคำในวงเล็บ
1. I’ve got 80 euros. The chair costs 100 euros. (money)
I haven’t ___________________________________
2. You need to be very smart to do this job. Louis isn’t very smart. (smart)
Louis isn’t ___________________________________
3. They need 250 grams of flour to make this cake. They’ve only got 100 grams. (flour)
They haven’t got ___________________________________
4. This village won’t win the World Heritage award. It’s too plain. (impressive)
This village isn’t ___________________________________
5. She needed to swim fast to win races. She couldn’t swim very fast. (fast)
She couldn’t ___________________________________
6. I’m very busy today. I can’t go to the cinema with you. (time)
I don’t have ___________________________________
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2: เลือกวลีที่ถูกต้องจากช่องด้านล่างเพื่อเติมลงในช่องว่าง
| enough money | large enough | enough people | enough time | enough experience |
| well enough | tall enough | clean enough | convincingly enough | warm enough |
- Clean this room again, Bobby. It’s not ______ for our guests to stay in.
- If you can lend me £5, I will have ______ to buy the T-shirt.
- I don’t think we have ______ to go to the supermarket. Let’s go home now.
- Mary got sick because her clothes weren’t ______.
- I couldn’t get the book on the top of the shelf because I’m not ______.
- If ______ sign this petition, we can prevent them from demolishing the central post office.
- Our team lost the match simply because we didn’t play ______.
- Ricky knows he doesn’t have ______ for the job, so he won’t waste time going for an interview.
- This theatre isn’t ______ for the play to be performed here.
- The boy argued ______ to make his parents believe that he couldn’t go to school.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3: เติมคำให้ถูกต้อง: too หรือ enough
- He isn’t old ______ to start smoking and drinking.
- My elder sister can’t sleep because she drinks ______ much coffee.
- It is ______ difficult to solve this puzzle in five minutes.
- We didn’t try hard ______ to rescue the koala.
- Do you have ______ information to help me with this problem?
- She left the coffee for a minute to cool. It was ______ hot for her to drink.
- The little boy wasn’t strong ______ to lift that heavy box.
- There aren’t ______ policemen in our town.
- I didn’t buy the scarf because it was ______ expensive.
- I’m afraid I don’t have ______ much time to prepare lunch for you.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 4: จับคู่ประโยค
| 1. We studied hard enough 2. I was too nervous during the interview 3. They didn’t have enough time to visit the square 4. I haven’t got enough clothes 5. She doesn’t like this fizzy drink 6. We couldn’t see anything 7. I can’t drink this coffee 8. If you don’t get enough sleep, 9. He is tall enough 10. My mom was too worried | A. because it’s too hot. B. to play basketball in the NBA. C. because it’s too sweet. D. your health will suffer. E. because it was too foggy. F. and it was too crowded as well. G. so she stayed up all night. H. and I blew it. I. for such a long trip. J. to pass the English exam. |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 5: เติมประโยคด้วย too หรือ enough และคำคุณศัพท์ในวงเล็บ
- I’d like to buy a new house and a better car, but I’m just not ______________ to do it. (rich)
- Kelly is ______________ to travel alone. She’s only 9. (young)
- The soup isn’t ______________. We’d like it to be hotter. (hot)
- Don’t eat that chicken! It’s ______________ for you. (spicy)
- The beach was ______________ yesterday, so we decided to go somewhere else. (crowded)
- She is a good swimmer, but she isn’t ______________ to enter a championship. (good)
- David is quite a fast runner, but he isn’t ______________ to beat the Sweden runner, who is considered to be the best. (fast)
- They wanted to go to London last weekend, but the plane tickets were ______________ , so they stayed at home. (expensive)
- Nick is ______________ to become a police officer. He’s only 1.6 cm tall. (short)
- We didn’t buy the sofa because it wasn’t ______________. (comfortable)

คำถามที่พบบ่อย
Enough is enough คืออะไร?
คำว่า Enough is enough แปลว่า พอแล้วหรือนั่นก็เพียงพอแล้ว มักใช้เพื่อแสดงการสิ้นสุดความอดทน เมื่อมีคนรู้สึกว่าทนไม่ไหวอีกต่อไป ประโยคนี้มักใช้ในสถานการณ์ที่บุคคลรู้สึกกดดัน รำคาญ หรือไม่พอใจกับสถานการณ์บางอย่าง และต้องการยุติสถานการณ์นั้น
Enough วางอยู่ไหนในประโยค?
คำว่า enough สามารถวางไว้ในตำแหน่งต่าง ๆ ในประโยคขึ้นอยู่กับการใช้งาน ตำแหน่งทั่วไป ได้แก่ หน้าคำนาม หลังคำคุณศัพท์หรือคำวิเศษณ์และท้ายประโยค
Enough + อะไร?
โครงสร้าง enough + อะไร ได้ใช้เพื่อแสดงถึงความเพียงพอของบางสิ่งบางอย่าง ซึ่งเกิดขึ้นได้ 2 วิธีหลักๆ Enough + คำนามเมื่อ enough อยู่หน้าคำนาม เป็นการแสดงออกถึงปริมาณหรือระดับที่เพียงพอของคำนามนั้น เมื่อ enough อยู่หลังคำกริยาวิเศษณ์ มันอธิบายว่าระดับของคำคุณศัพท์นั้นเพียงพอที่จะดำเนินการบางอย่างได้
Enough คือคำประเภทไหน?
Enough สามารถใช้กับคำได้หลายประเภท ขึ้นอยู่กับบริบทในประโยค Enough มักจะทำหน้าที่เป็นคำคุณศัพท์ คำวิเศษณ์ หรือคำสรรพนาม
บทความนี้เป็นบทสรุปความรู้เกี่ยวกับโครงสร้าง enough และวิธีการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษที่ ELSA Speak อยากแบ่งปัน หวังว่าผู้เรียนจะสามารถนำไปใช้ในกระบวนการเรียนรู้ภาษาอังกฤษได้ ผู้เรียนควรทบทวนความรู้นี้เป็นประจำเพื่อให้จดจำได้นานและนำไปใช้อย่างเหมาะสมในแต่ละบริบท
เงินเป็นหนึ่งในหัวข้อยอดนิยมเมื่อเรียนการสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษ แล้วเงินในภาษาอังกฤษคืออะไร? วิธีอ่านชื่อสกุลเงินไทยเป็นภาษาอังกฤษยังไง? มาเรียนรู้วิธีตอบอย่างละเอียดกับ ELSA Speak ในบทความต่อไปนี้
เงินในภาษาอังกฤษคืออะไร?

เงินภาษาอังกฤษคือ money และสกุลเงินในภาษาอังกฤษคือ currency ซึ่งเป็นคำนามทั่วไปในภาษาอังกฤษที่อ้างถึงระบบสกุลเงินที่ใช้เป็นวิธีการแลกเปลี่ยนในประเทศหรือภูมิภาค สกุลเงินประกอบด้วยธนบัตร เหรียญ และเงินในรูปแบบอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ มีบทบาทสำคัญในกิจกรรมทางเศรษฐกิจ การค้า และการเงิน
บาท ภาษาอังกฤษ คืออะไร?

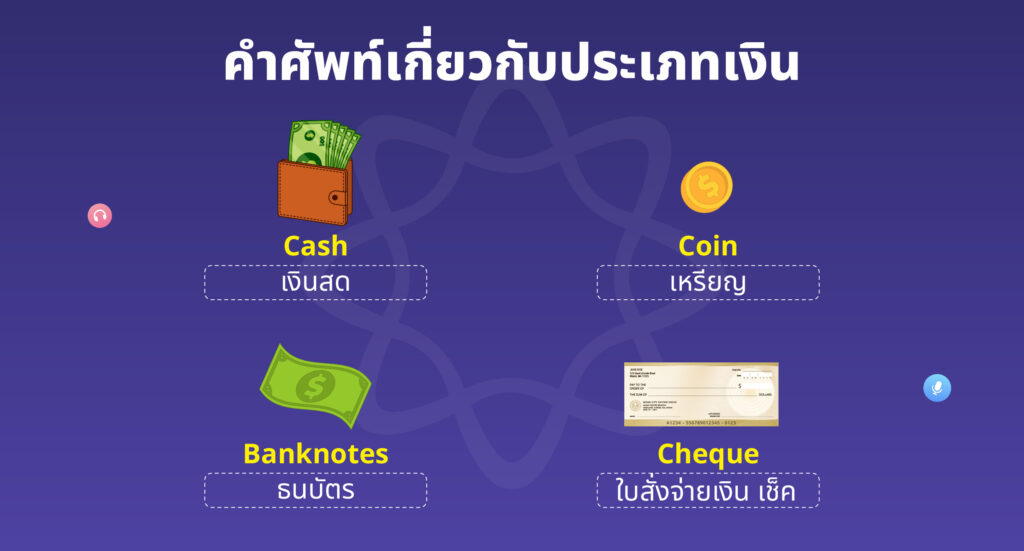
Baht (บาท) เป็นสกุลเงินอย่างเป็นทางการของประเทศไทย ในภาษาอังกฤษเรียกว่า Thai Baht แบ่งออกเป็นสองหน่วยหลัก: สตางค์ (หน่วยเล็ก) และบาท (หน่วยหลัก) เงินไทยแบ่งออกเป็น 3 ประเภทหลัก ได้แก่ เหรียญ (สตางค์) เหรียญ (บาท) และธนบัตร (บาท)
| ประเภทเงิน | หน่วยเงิน | ตัวอย่าง |
| เหรียญสตางค์ | 25 สตางค์ 50 สตางค์ | One hundred satang is equal to one baht. (หนึ่งร้อยสตางค์ เท่ากับ หนึ่งบาท) |
| เหรียญบาท | 1 บาท 2 บาท 5 บาท 10 บาท | One baht coin is made out of steel or aluminum. (เหรียญหนึ่งบาททำด้วยเหล็กหรืออลูมิเนียม) |
| ธนบัตร (บาท) | 20 บาท 50 บาท 100 บาท 500 บาท 1,000 บาท | The 100 Baht note is one of the most commonly used banknotes in Thailand. (ธนบัตร 100 บาท ถือเป็นธนบัตรที่ใช้กันมากที่สุดในประเทศไทย) |

คำศัพท์เกี่ยวกับเงินเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ
ประเภทเงิน
| คำศัพท์ | วิธีอ่าน | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| Money (ˈmʌn.i) | /ˈmʌn.i/ | เงิน | How much money do you earn? (คุณมีรายได้เท่าไร?) |
| Cash (kæʃ) | /kæʃ/ | เงินสด | Will you pay by credit card or in cash? (คุณจะชำระด้วยบัตรเครดิตหรือเงินสด?) |
| Coin (kɔɪn) | /kɔɪn/ | เหรียญ | The date on the coin is 1755. (วันที่บนเหรียญคือปี 1755) |
| Banknotes (ˈbæŋk.noʊts) | /ˈbæŋk.noʊts/ | ธนบัตร | Hidden in the suitcase were wads of banknotes. (กระเป๋าเดินทางมีธนบัตรจำนวนหนึ่งซ่อนอยู่) |
| Bucks (bʌks) | /bʌks/ | คำสแลงของสกุลเงินดอลลาร์ (dollar) | Can I borrow a couple of bucks? (ฉันขอยืมเงินสักสองสามเหรียญได้ไหม?) |
| Salary (ˈsæləri) | /ˈsæləri/ | เงินเดือน | Her net monthly salary is ฿120,000. (เงินเดือนสุทธิของเธอคือ 120,000 บาทต่อเดือน) |
| Profit (ˈprɑfət) | /ˈprɑfət/ | กำไร | The company made a profit of ฿1 million this year. (ปีนี้บริษัททำกำไรได้ 1 ล้านบาท) |
| Pension (ˈpɛnʃn) | /ˈpɛnʃn/ | เงินเลี้ยงชีพ เงินบำนาญ | Ten won’t be able to draw his pension until he’s 65. (เท็นจะไม่สามารถเบิกเงินบำนาญได้จนกว่าเขาจะอายุ 65 ปี) |
| Pocket money (ˈpɑkɪt ˌmʌni) | /ˈpɑkɪt ˌmʌni/ | เงินติดตัว, เงินติดกระเป๋า | My mom gives me ฿400 a week pocket money. (แม่ฉันให้เงินไว้ติดตัวสัปดาห์ละ 400 บาท) |
| Compensation (ˌkɑmpənˈseɪʃn) | /ˌkɑmpənˈseɪʃn/ | ค่าชดเชย ชดเชย | Linda received ฿2,200,000 in compensation for a lost eye. (ลินดารับเงินชดเชย 2,200,000 บาท จากการสูญเสียดวงตา) |
| Commission (kəˈmɪʃn) | /kəˈmɪʃn/ | ค่านายหน้า | Bi gets a 20 percent commission on every machine he sells. (บีได้รับค่าคอมมิชชั่น 20 เปอร์เซ็นต์จากการขายเครื่องจักร) |
| Penny (ˈpen.i) | /ˈpen.i/ | เหรียญเพนนีของอังกฤษมีค่าเท่ากับ 1/12 ชิลลิง | He has calculated the costs down to the last penny. (เขาคำนวณต้นทุนจนเหลือเพนนีสุดท้ายแล้ว) |
| Bonus (ˈboʊnəs) | /ˈboʊnəs/ | เงินโบนัส | The salary was set at ฿600,000, plus a bonus if the company had a good year. (เงินเดือนเริ่มต้น อยู่ที่ 600,000 บาท พร้อมโบนัสหากบริษัทมีผลงานดีตลอดปี) |
| Cheque (tʃek) | /tʃek/ | เช็ค | I wrote her a cheque for ฿4,000. (ฉันเขียนเช็คให้เธอ 4,000 บาท) |
| Grant (ɡrænt) | /ɡrænt/ | เงินช่วยเหลือ | Students receive a grant equal to ฿10,000 per month. (นักศึกษาจะได้รับทุนสนับสนุนเดือนละ 10,000 บาท) |
| Foreign currency (ˈfɔrən ˈkɜrənsi) | /ˈfɔrən ˈkɜrənsi/ | เงินตราต่างประเทศ | You can exchange foreign currency at the bank. (คุณสามารถแลกเปลี่ยนเงินตราต่างประเทศได้ที่ธนาคาร) |
| Currency (ˈkɜrənsi) | /ˈkɜrənsi/ | สกุลเงินตรา | The currency in Thailand is the Baht. (สกุลเงินของประเทศไทยคือบาท) |
| Monetary (ˈmɑnɪteri) | /ˈmɑnɪteri/ | เกี่ยวกับเงินตรา | The monetary policy affects inflation rates. (นโยบายการเงินส่งผลต่ออัตราเงินเฟ้อ) |
| Revenue (ˈrɛvənuː) | /ˈrɛvənuː/ | รายได้ | The government collects revenue through taxes. (รัฐบาลจัดเก็บรายได้ผ่านทางภาษี) |
| Cash check (kæʃ tʃek) | /kæʃ tʃek/ | เช็คเงินสด | She went to the store to cash her check. (เธอไปที่ร้านเพื่อนำเช็คไปขึ้นเงิน) |
| Deposit (dɪˈpɑzɪt) | /dɪˈpɑzɪt/ | เงินฝาก | I made a deposit of ฿10,000 into my savings account. (ฉันฝากเงิน 10,000 บาท เข้าบัญชีออมทรัพย์ของฉัน) |
| Bank Deposit (bæŋk dɪˈpɑzɪt) | /bæŋk dɪˈpɑzɪt/ | เงินฝากธนาคาร | The bank deposit was processed without any issues. (การฝากเงินผ่านธนาคารได้รับการดำเนินการโดยไม่มีปัญหาใดๆ) |
| Fixed Deposit Account (fɪkst dɪˈpɑzɪt əˈkaʊnt) | /fɪkst dɪˈpɑzɪt əˈkaʊnt/ | บัญชีเงินฝากประจำ | She opened a fixed deposit account to save for her future. (เธอเปิดบัญชีเงินฝากประจำเพื่อออมเงินสำหรับอนาคตของเธอ) |
| Savings Account (ˈseɪvɪŋz əˈkaʊnt) | /ˈseɪvɪŋz əˈkaʊnt/ | บัญชีเงินฝากออมทรัพย์ | The bank offers high interest rates for savings accounts. (ธนาคารเสนออัตราดอกเบี้ยสูงสำหรับบัญชีออมทรัพย์) |
| Balance (ˈbæləns) | /ˈbæləns/ | เงินค้าง ยอดเงิน ยอดคงเหลือ | You can check your account balance online. (คุณสามารถตรวจสอบยอดเงินในบัญชีของคุณได้ทางออนไลน์) |
| Credit (ˈkrɛdɪt) | /ˈkrɛdɪt/ | เครดิต | She has a good credit score. (เธอมีคะแนนเครดิตดี) |
| Loan (loʊn) | /loʊn/ | เงินกู้ | I took out a loan to buy a new car. (ฉันกู้เงินเพื่อซื้อรถคันใหม่) |
| Principal (ˈprɪnsəpl) | /ˈprɪnsəpl/ | ต้นทุน | The loan principal must be paid off within 5 years. (เงินกู้ต้องชำระคืนภายใน 5 ปี) |
| Interest (ˈɪntrəst) | /ˈɪntrəst/ | ดอกเบี้ย | The interest rate on this loan is 5%. (อัตราดอกเบี้ยสินเชื่อนี้คือ 5%) |
| Change (tʃeɪndʒ) | /tʃeɪndʒ/ | เงินทอน | He paid with a 500 baht note and received 100 baht in change. (เขาจ่ายด้วยธนบัตร 500 บาท และได้รับเงินทอน 100 บาท) |
| Transfer fee (ˈtrænsfɜːr fiː) | /ˈtrænsfɜːr fiː/ | ค่าธรรมเนียมการโอน | There is a 50 baht transfer fee for international payments. (ค่าธรรมเนียมการโอนระหว่างประเทศ 50 บาท) |
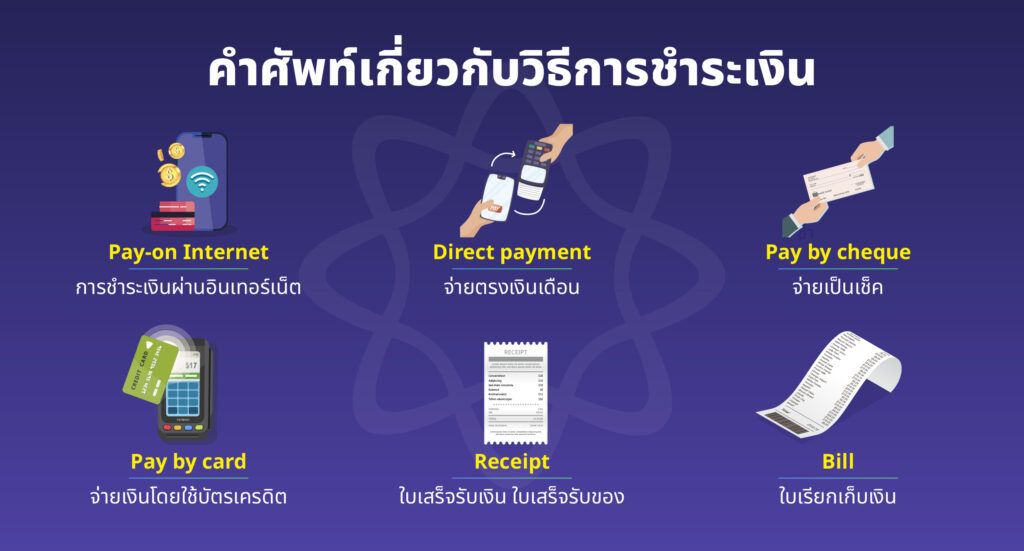
วิธีการชำระเงิน
| คำศัพท์ | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง |
| Mode of payment (moʊd əv ˈpeɪmənt) | วิธีการชำระเงิน | They were only accepting credit or debit cards as the mode of payment. (พวกเขารับเฉพาะบัตรเครดิตหรือบัตรเดบิตในการชำระเงินเท่านั้น) |
| Pay-on Internet (peɪ ɒn ˈɪntərnɛt) | การชำระเงินผ่านอินเทอร์เน็ต | PayPal is the best pay-on Internet app. (PayPal เป็นแอปชำระเงินทางอินเตอร์เน็ตที่ดีที่สุด) |
| Direct payment (dəˈrɛkt ˈpeɪmənt) | ระบบจ่ายตรงเงินเดือน หรือที่เรียกว่า การชำระเงินโดยตรง | Direct payments allow you to receive cash payments from your local authority instead of care services. (การชำระเงินโดยตรงทำให้คุณสามารถรับการชำระเงินด้วยเงินสดจากหน่วยงานท้องถิ่นของคุณ แทนบริการการรับฝาก) |
| Pay by cheque (peɪ baɪ tʃɛk) | จ่ายเป็นเช็ค | When you pay by cheque, you instruct your financial institution to give money from your account to the person that is depositing the cheque. (เมื่อคุณชำระเงินด้วยเช็ค คือคุณขอให้สถาบันการเงินของคุณโอนเงินจากบัญชีของคุณไปยังผู้รับเช็ค) |
| Pay by card (peɪ baɪ kɑːrd) | จ่ายเงินโดยใช้บัตรเครดิต | Don’t tell me guys pay you by credit card. (อย่าบอกนะว่าพวกจ่ายเงินให้คุณด้วยบัตรเครดิต) |
| Receipt (rɪˈsiːt) | ใบเสร็จรับเงิน ใบเสร็จรับของ | Make sure you are given a receipt for everything you buy. (ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าคุณได้รับใบเสร็จทุกใบเกี่ยวกับสิ่งที่คุณซื้อ) |
| Bill (bɪl) | ใบเรียกเก็บเงิน | Could we have the bill, please? (เราขอบิลหน่อยได้มั้ย?) |
กิจกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้อง
| คำศัพท์ | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง |
| Discount / Sale (ˈdɪskaʊnt / seɪl) | ลดราคา ลดส่วน | There is a 40% discount on all electrical goods until the end of the week. (เครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้าทุกชนิดลด 40% ถึงสุดสัปดาห์นี้) |
| Order (ˈɔːrdər) | สั่ง | Can I take your order now? said the waiter. (ฉันรับออเดอร์ของคุณตอนนี้ได้ไหม? พนักงานเสิร์ฟกล่าว) |
| Online shopping (ˈɒnlaɪn ˈʃɒpɪŋ) | การซื้อของหรือสินค้าผ่านช่องทางอินเทอร์เน็ต | The greatest benefit of online shopping is its convenience. (ประโยชน์ที่ยิ่งใหญ่ที่สุดของการช้อปปิ้งออนไลน์คือความสะดวกสบาย) |
| Deposit money (dɪˈpɒzɪt ˈmʌni) | เงินมัดจำ | Apart from lending deposit money, parents can also act as mortgage guarantors. (นอกจากเงินฝากให้กู้ยืมแล้ว ผู้ปกครองยังสามารถเป็นผู้ค้ำประกันได้อีกด้วย) |
| Withdraw money (wɪðˈdrɔː ˈmʌni) | ถอนเงิน | I have to withdraw some money from an ATM machine. (ฉันต้องถอนเงินจากตู้ ATM) |
| Transfer money (trænsˈfɜːr ˈmʌni) | การโอนเงิน | How can I online transfer money? (ฉันสามารถโอนเงินออนไลน์ได้อย่างไร?) |
| Owe money (oʊ ˈmʌni) | ติดเงิน เป็นหนี้ | He claims the firm owes him money. (เขาอ้างว่าบริษัทเป็นหนี้เงินเขา) |
| Invest (ɪnˈvɛst) | ลงทุน ใช้จ่าย | The institute will invest 5 million in the project. (สถาบันจะลงทุน 5 ล้านบาทในโครงการนี้ ) |
| Save money (seɪv ˈmʌni) | ประหยัดเงิน | Try to save some money for your holiday. (พยายามเก็บเงินไว้สำหรับวันหยุดของคุณ) |
| Waste money (weɪst ˈmʌni) | สิ้นเปลือง ฟุ่มเฟือย | We waste money on plants and decorations that we could be spending on salaries. (เราเสียเงินไปกับต้นไม้และของประดับตกแต่งที่เราสามารถนำมาใช้เป็นเงินเดือนได้) |
| Earn money (ɜːrn ˈmʌni) | ทำงานได้เงินมา | Publishers earn money from their content. (ผู้จัดพิมพ์สร้างรายได้จากเนื้อหาของตนเอง) |
คำศัพท์อื่นๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
| คำศัพท์ | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง |
| Currency (/ˈkʌr.ən.si/) | สกุลเงินตรา | The local currency in Thailand is the Bath. (สกุลเงินท้องถิ่นของประเทศไทยคือบาท) |
| Credit card (/ˈkrɛd.ɪt kɑːrd/) | บัตรเครดิต | She used her credit card to book the hotel. (เธอใช้บัตรเครดิตของเธอจองโรงแรม) |
| Debit card (/ˈdɛb.ɪt kɑːrd/) | บัตรเดบิต | I prefer using a debit card for everyday expenses. (ฉันชอบใช้บัตรเดบิตใช้จ่ายในชีวิตประจำวัน) |
| Exchange rate (/ɪksˈʧeɪndʒ reɪt/) | อัตราการแลกเปลี่ยนเงินตราระหว่างประเทศ | The exchange rate between USD and EUR has gone up. (อัตราแลกเปลี่ยนระหว่าง USD และ EUR เพิ่มขึ้น) |
| Inflation (/ɪnˈfleɪ.ʃən/) | เงินเฟ้อ | Inflation has caused prices to rise significantly. (เงินเฟ้อทำให้ราคาเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมาก) |
| Interest rate (/ˈɪn.trəst reɪt/) | อัตราดอกเบี้ย | The bank offers a low-interest rate for home loans. (ธนาคารเสนออัตราดอกเบี้ยต่ำสำหรับสินเชื่อบ้าน) |
| Bank account (/bæŋk əˈkaʊnt/) | บัญชีเงินฝากกับธนาคาร | You need to open a bank account to receive your salary. (คุณต้องเปิดบัญชีธนาคารเพื่อรับเงินเดือนของคุณ) |
| Savings account (/ˈseɪ.vɪŋz əˈkaʊnt/) | บัญชีเงินฝากออมทรัพย์ | I deposited $500 into my savings account. (ฉันฝากเงิน 500 เหรียญเข้าบัญชีออมทรัพย์ของฉัน) |
| Checking account (/ˈʧɛk.ɪŋ əˈkaʊnt/) | บัญชีเงินฝากกระแสรายวัน | Most of my transactions go through my checking account. (ธุรกรรมส่วนใหญ่ของฉันจะผ่านบัญชีเงินฝากกระแสรายวันของฉัน) |
| Loan (/ləʊn/) | เงินกู้ | He took out a loan to buy a new car. (เขากู้เงินมาซื้อรถใหม่) |
| Mortgage (/ˈmɔː.ɡɪdʒ/) | การจำนอง สัญญาจำนอง | They are paying off their mortgage on the house. (พวกเขากำลังชำระเงินจำนองบ้านอยู่) |
| Debt (/dɛt/) | หนี้ หนี้สิน | She is trying to pay off her student debt. (เธอกำลังพยายามชำระหนี้ค่าเล่าเรียนของเธอ) |
| Deposit (/dɪˈpɒz.ɪt/) | เงินฝาก | You need to pay a deposit before signing the contract. (คุณจะต้องชำระเงินมัดจำก่อนลงนามในสัญญา) |
| Withdrawal (/wɪðˈdrɔː.əl/) | การถอนออก การเอากลับ | I made a withdrawal of $200 from the ATM. (ฉันถอนเงิน 200 เหรียญจากตู้ ATM) |
| Transfer (/ˈtræns.fɜːr/) | ถ่ายโอน โอน | She transferred money to her sister’s account. (เธอโอนเงินเข้าบัญชีน้องสาวของเธอ) |
| ATM (/ˌeɪ.tiːˈɛm/) | เครื่องจ่ายเงินอัตโนมัติ เอทีเอ็ม | The ATM is out of service right now. (ขณะนี้ตู้ ATM ไม่สามารถใช้งานได้) |
สกุลเงินที่ได้รับความนิยมมากที่สุด

| สกุลเงินตรา | สัญลักษณ์สกุลเงิน | วิธีเขียน | การสะกดคำ | ความหมาย |
| USD | $ | US dollar | /juː.ɛs ˈdɑː.lɚ/ | ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ |
| EUR | € | Euro | /ˈjʊə.rəʊ/ | ยูโร |
| JPY | ¥ | Japanese yen | /jɛn jɛn/ | เยนญี่ปุ่น |
| GBP | £ | British pound | /brɪtɪʃ paʊnd/ | ปอนด์สเตอร์ลิง |
| AUD | $ | Australian dollar | /ɔːˈstreɪ.li.ən ˈdɒlə(r)/ | ดอลลาร์ออสเตรเลีย |
| CAD | $ | Canadian dollar | /ˈkænədiən ˈdɒlə(r)/ | ดอลลาร์แคนาดา |
| CHF | Fr | Swiss franc | /swɪs fræŋk/ | ฟรังก์สวิส |
| VND | ₫ | Vietnamese Dong | /viˌɛtnəˈmis ˈdɒŋ/ | เวียดนามดอง |
| CNY | ¥ | Chinese yuan | /tʃaɪˈniːz juːˈɑːn/ | หยวนจีน |
ตัวอย่างประโยคที่ใช้คำศัพท์เกี่ยวกับเงิน
ตัวอย่างประโยคการสื่อสารเมื่อต้องชำระเงิน

| ตัวอย่างประโยค | ความหมาย |
| Excuse me, we’d like the bill. | ขอโทษนะคะ/นะครับ เราต้องการบิลค่ะ/ครับ |
| We’re ready to pay. | เราพร้อมที่จะจ่ายเงินแล้วค่ะ/ครับ |
| Can I have my bill? | ฉันขอบิลได้ไหม? |
| Do you accept credit cards? | คุณรับบัตรเครดิตไหม? |
| Are you using any coupons today? | วันนี้คุณต้องการใช้คูปองไหม? |
| I am sorry we do not accept checks. | ฉันขออภัยเราไม่รับเช็ค |
| Would you like to use another form of payment? | คุณต้องการชำระเงินด้วยวิธีอื่นไหม? |
| Are you interested in taking part in our promotion? | คุณสนใจที่จะเข้าร่วมโปรโมชั่นของเราไหม? |
| Would you like your receipt? | คุณต้องการใบเสร็จไหม? |
| Would you like any cashback? | คุณต้องการเงินคืนไหม? |
>>> Read more: ตัวอย่างประโยค บทสนทนาขายของภาษาอังกฤษ สั้นๆ ที่ใช้บ่อย
ตัวอย่างการถามราคาเมื่อซื้อของเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ

| ตัวอย่างประโยค | ความหมาย |
| I will give you + ราคา | ฉันจะจ่ายเงินให้คุณ (จำนวน) ของ… |
| I will buy it for + ราคา | ฉันจ่ายได้ในราคา (จำนวน) ของ… |
| Can you lower the price? | ลดราคาได้ไหม? |
| That’s too expensive. How about $… ? | แพงไปนะ แล้วราคา….ละ ? |
| Is that the best price you can give me? How about + ค่า? That’s my last offer. | นั่นคือราคาที่ดีที่สุดที่คุณให้ฉันได้ใช่ไหม แล้ว + ราคา ล่ะ? นั่นคือราคาสุดท้ายของฉัน |
| How much is this and this all together? | อันนี้กับอันนี้รวมกันเท่าไร? |
| Can I get a discount? | ฉันจะได้รับส่วนลดได้ไหม? |
| Is that your best price? | นั่นคือราคาที่ดีที่สุดของคุณใช่ไหม? |
| I saw a similar item for $… | ฉันเห็นสินค้าที่คล้ายกันราคา $… |
| Please give me a… percent discount. | ลดส่วนลดสัก…เปอร์เซ็นต์นะ |

>>> Read more: ลดราคาภาษาอังกฤษว่าอย่างไร รวบรวมคําศัพท์ ประโยคคําตอบพื้นฐานและสุภาพที่สุด
วิธีเขียนสกุลเงินไทยเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ
| วิธีเขียน | ตัวอย่าง |
| เครื่องหมายจุลภาคคั่นหลักพัน หลักแสน และหลักล้าน | 3,000,000 THB (3 ล้านบาท) |
| จุดจะแยกส่วนทั้งหมดและเศษส่วนของจำนวนได้ | 1,50 THB (1 บาทและ 50 สตางค์) |
| จุดหรือลูกน้ำสามารถแยกส่วนทั้งหมดและเศษส่วนของจำนวนได้ | 99,95 THB หรือ 99.99 THB (99 บาทและ 95 สตางค์) |
| เครื่องหมายจุลภาคแยกส่วนทั้งหมดและเศษส่วนของจำนวนได้ | 23,56 THB (23 บาทและ 56 สตางค์) |
| จุดหรือเครื่องหมายจุลภาคอาจใช้เป็นสกุลเงินต่างประเทศได้ | 1 THB (1 บาท) |

ประโยคเกี่ยวกับสกุลเงินเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ
| ประโยค | ความหมาย |
| Money can’t buy happiness, but it can buy comfort. | เงินซื้อความสุขไม่ได้ แต่ซื้อความสะดวกสบายได้ |
| A penny saved is a penny earned. | การประหยัดเพนนีคือการสร้างกำไรจากเพนนี |
| Time is money. | เวลาเป็นเงินเป็นทอง |
| The lack of money is the root of all evil. | การขาดแคลนเงินเป็นต้นตอของความหายนะทั้งหมด |
| Money talks, wealth whispers. | เงินพูดได้ แต่ความมั่งคั่งได้แค่กระซิบเท่านั้นแหละ |
| Don’t spend money you don’t have to impress people you don’t like. | อย่าใช้เงินที่คุณไม่มีไปสร้างความประทับใจให้กับคนที่คุณไม่ชอบ |
| Too many people spend money they haven’t earned, to buy things they don’t want, to impress people they don’t like. | ผู้คนจำนวนมากใช้เงินที่ตนเองไม่ได้หามา เพื่อซื้อสิ่งของที่ไม่ได้ต้องการ เพื่อสร้างความประทับใจให้กับคนที่ตนไม่ชอบ |
| Money is a terrible master but an excellent servant. | เงินเป็นเจ้านายที่เลวร้าย แต่เป็นผู้รับใช้ที่ดีเยี่ยม |
| It’s not about having a lot of money, it’s about knowing how to manage it. | ไม่ใช่เรื่องการมีเงินมากมาย แต่เป็นเรื่องของการรู้จักบริหารมัน |
| Wealth consists not in having great possessions, but in having few wants. | ความร่ำรวยไม่ได้หมายถึงการมีทรัพย์สมบัติมากมาย แต่หมายถึงการมีสิ่งที่ต้องการเพียงเล็กน้อย |
| If you want to know what a man values, watch where he spends his money. | หากคุณอยากรู้ว่าผู้ชายให้ความสำคัญกับอะไร ให้ดูว่าเขาใช้เงินที่ไหน |
| Bring home the bacon. | หาเลี้ยงครอบครัว |
| Swimming in money. | อยู่อย่างมั่งคั่ง มีเงินทองมากมาย |
| Money to burn. | มีเงินมากจนล้น |
| Tighten your belt. | อดออมเข้าไว้ |
| Nest egg. | จำนวนเงินที่เก็บไว้ใช้ในอนาคต |
| Money doesn’t grow on trees. | เงินไม่ได้งอกขึ้นมาจากต้นไม้ |
| Cook the books. | ดัดแปลงข้อมูลในบัญชีเพื่อฉ้อโกง |
| Go Dutch. | แบ่งกันจ่ายคนละครึ่ง |
| Live from hand to mouth. | ชักหน้าไม่ถึงหลัง ไม่มีเงินเหลือเก็บ |
| On a shoestring. | การดำเนินชีวิตหรือทำกิจกรรมอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งโดยใช้จ่ายเงินน้อย |
| Golden handshake. | เงินบำเหน็จหรือเงินก้อนเมื่อเกษียณอายุการทำงาน |
| Balance the books. | งบดุลบัญชีลงตัว |
| Penny pincher. | คนขี้เหนียว คนขี้ตืด คนตระหนี่ |
| Gravy train. | อาชีพหรืองานที่เบา |
| Saving for a rainy day. | เก็บเงินเพื่อใช้ในวันที่ลำบาก |

คำถามที่พบบ่อย
เหรียญ ภาษาอังกฤษ คืออะไร?
Coin.
รายได้ ภาษาอังกฤษ คืออะไร?
Income.
การโอนเงิน ภาษาอังกฤษ
Transfer money.
หลังจากอ่านบทความนี้ คุณได้ค้นพบความรู้ที่เป็นประโยชน์เกี่ยวกับเงินภาษาอังกฤษ รวมถึงประเภทของสกุลเงินและคำศัพท์ที่เกี่ยวข้องในภาษาอังกฤษ นอกจากนี้ เพื่อให้การเรียนภาษาอังกฤษของคุณใช้งานได้จริงมากขึ้น เราขอแนะนำให้คุณติดตั้งแอปการเรียนรู้การสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษออนไลน์ที่นักเรียนจำนวนมากทั่วโลกชื่นชอบ – ELSA Speak ลงในโทรศัพท์ของคุณดูนะ
การเขียนอีเมล สมัครงาน ภาษาอังกฤษ เป็นทักษะสำคัญที่ช่วยให้คุณสร้างความประทับใจแก่นายจ้างต่างชาติ บทความนี้มีคำแนะนำทีละขั้นตอน พร้อมตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษอย่างมืออาชีพ มาเรียนรู้ไปด้วยกันเพื่อเพิ่มโอกาสความสำเร็จในการสมัครงาน!
การสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษเรียกว่าอะไร?
เมื่อพูดถึงการสมัครงานในภาษาอังกฤษ คำที่มักใช้คือ apply for a job ซึ่งเป็นวลีที่ใช้กันทั่วไปเมื่อคุณต้องการบอกว่ากำลังยื่นใบสมัครหรือต้องการหางาน นอกจากนี้ ยังมีวลีที่เกี่ยวข้อง เช่น be a candidate for (เป็นผู้สมัครสำหรับตำแหน่งหนึ่ง) ที่มักใช้ในบริบทคล้ายกัน
เพื่อให้เข้าใจดีขึ้น มาดูตัวอย่างกัน:
- I want to apply for a job at your company.
(ฉันต้องการสมัครงานที่บริษัทของคุณ) - She decided to be a candidate for the manager position.
(เธอตัดสินใจสมัครเป็นผู้จัดการ)
นอกจากวลีนี้แล้ว ภาษาอังกฤษยังมีวิธีการพูดเกี่ยวกับการสมัครงานอื่น ๆ เช่น:
- Submit a job application: ยื่นใบสมัครงาน
- Job hunting: หางาน
หากคุณกำลังเตรียมสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษ อย่าลืมใช้วลีที่ถูกต้องเพื่อสร้างความประทับใจที่ดีให้แก่นายจ้าง!

โครงสร้างและวิธีเขียนแต่ละส่วนของอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษ
หมายเหตุ: เมื่อเขียน email สมัครงาน ภาษาอังกฤษ ผู้สมัครควรใช้ภาษาทางการและหลีกเลี่ยงการใช้คำย่อ เช่น แทนที่จะเขียน I’m ควรเขียนเป็น I am
การตั้งหัวข้ออีเมลให้ชัดเจน
หัวข้ออีเมลควรกระชับและมีข้อมูลครบถ้วนเพื่อให้นายจ้างเข้าใจจุดประสงค์ของคุณได้ทันที
Apply for [ชื่อตำแหน่ง] Position – [ชื่อ-นามสกุล]
Job Application: [ชื่อตำแหน่ง] – [ชื่อ-นามสกุล]
ตัวอย่าง:
- Apply for Marketing Specialist Position – John Smith
- Job Application: Software Engineer – Emily Johnson
ระบุชื่อผู้รับ ตำแหน่ง และบริษัทให้ถูกต้อง
การใส่รายละเอียดเหล่านี้แสดงถึงความเคารพและความเป็นมืออาชีพในวิธีการสื่อสาร
ตัวอย่าง:
- Mr./Mrs./Ms. [ชื่อ-นามสกุลผู้รับ]
- Human Resources Manager (ผู้จัดการฝ่ายทรัพยากรบุคคล)
- XYZ Company (บริษัท XYZ)
| การใช้ ms mrs ให้ถูกต้องเมื่อต้องพูดถึงตำแหน่ง มาศึกษากับ ELSA Speak เกี่ยวกับวิธีอ่าน และข้อผิดพลาดในการใช้คำนำหน้าชื่ออื่น ๆ ที่คุณควรรู้ |
เริ่มต้นอีเมลด้วยคำทักทายที่สุภาพ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการเขียนอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาไทยหรือภาษาอังกฤษ การเริ่มต้นด้วยคำทักทายและการเรียกชื่อผู้รับอย่างเหมาะสมเป็นสิ่งสำคัญมาก เพราะนอกจากจะแสดงถึงความเป็นมืออาชีพแล้วยังสร้างความประทับใจที่ดีต่อนายจ้าง
เริ่มต้นด้วยการทักทายให้เหมาะสมกับชื่อหรือตำแหน่งของผู้รับ
- Dear Mr./Mrs. [ชื่อผู้รับ]: (เรียน คุณ…)
- Dear Hiring Manager: (เรียน ผู้จัดการฝ่ายสรรหา)
- Dear Human Resources Manager: (เรียน ผู้จัดการฝ่ายทรัพยากรบุคคล)
- To Whom It May Concern: (เรียน ทุกท่านที่เกี่ยวข้อง)
ตัวอย่าง: Dear Hiring Manager,
I am writing to express my interest in the Marketing Specialist position advertised on your company website.
หมายเหตุ: หลีกเลี่ยงการใช้คำทักทายที่ไม่เป็นทางการ เช่น Hello, Hi, หรือ Good Morning
>>> Read more: วิธีเขียนอีเมลภาษาอังกฤษแบบมืออาชีพและเหมาะสำหรับทุกสถานการณ์

แนะนำตัวอย่างกระชับและน่าประทับใจ
ในการเขียนอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษ สิ่งที่สำคัญที่สุดคือเนื้อหาของอีเมล คุณจะต้องชี้แจงให้ชัดเจนว่าคุณต้องการสมัครตำแหน่งใด (คุณสามารถเพิ่มตำแหน่งที่คุณเห็นประกาศรับสมัครงานได้อีกด้วย) นอกจากนี้ ให้อธิบายสั้น ๆ ว่าเหตุใดคุณจึงสนใจและเหมาะสมกับตำแหน่งนี้
เทมเพลตอีเมลแนะนำสั้นๆ พร้อมคำแปลเพื่อช่วยให้คุณสร้างความประทับใจให้กับนายจ้าง:
| รูปแบบอีเมลแนะนำตัว | ความหมาย |
| I am applying for the [ชื่อตำแหน่ง] position at [ชื่อบริษัท] Company. | ฉันกำลังสมัครตำแหน่ง [ชื่อตำแหน่ง] ที่บริษัท [ชื่อบริษัท] |
| I would like to submit my application for the [ชื่อตำแหน่ง] position that [ชื่อบริษัท] posted on Jobsdb. | ฉันต้องการส่งใบสมัครสำหรับตำแหน่ง [ชื่อตำแหน่ง] ที่บริษัท [ชื่อบริษัท] ได้ประกาศไว้บน Jobsdb |
| For the past two years I have been working as an/a [อาชีพ/ตำแหน่งงาน]. | ในช่วงสองปีที่ผ่านมา ฉันได้ทำงานในตำแหน่ง [อาชีพ/ตำแหน่งงาน] |
| My skillset and expertise makes me a valuable asset to your company. | ทักษะและความเชี่ยวชาญของฉันทำให้ฉันเป็นทรัพยากรที่มีคุณค่าสำหรับบริษัทของคุณ |
| I recently graduated with a degree in [สาขาวิชา]. | ฉันเพิ่งจบการศึกษาพร้อมปริญญาในสาขา [สาขาวิชา] |
>>> Read more: 16 วิธี แนะนําตัวภาษาอังกฤษ สัมภาษณ์งาน
คำถามและตัวอย่างแนวคิดสำหรับการตอบในอีเมลสมัครงานของคุณ:
| หัวข้อหลัก | แนวคิดตัวอย่าง | ตัวอย่าง |
| ทำไมนายจ้างควรเลือกคุณ? | Highlight your unique skills or qualities. | I possess strong analytical skills that can drive results. (ฉันมีทักษะการวิเคราะห์ที่แข็งแกร่งซึ่งสามารถสร้างผลลัพธ์ได้ ) |
| ประสบการณ์ที่เกี่ยวข้อง | Link your past experiences to the job requirements. | In my previous role, I successfully managed projects similar to those outlined in this position. (ในบทบาทก่อนหน้านี้ ฉันสามารถจัดการโครงการที่คล้ายกับที่ระบุไว้ในตำแหน่งนี้ได้สำเร็จ) |
| ทำไมคุณถึงอยากทำงานในตำแหน่งนี้? | Explain your passion for the industry or job function. | I am passionate about innovative technology and want to contribute to a forward-thinking company. (ฉันหลงใหลในเทคโนโลยีที่ล้ำสมัยและต้องการมีส่วนร่วมกับบริษัทที่มีวิสัยทัศน์ก้าวหน้า) |
ให้ข้อมูลการติดต่อ
อย่าลืมระบุอีเมลและเบอร์โทรศัพท์เพื่อให้นายจ้างติดต่อคุณได้ง่าย
ข้อมูลการติดต่อ
โทรศัพท์
อีเมล
ตัวอย่าง: I can be reached anytime via email at example@gmail.com or my cell phone, 099-123-4567.
ปิดท้ายอีเมลด้วยคำลงท้ายที่เหมาะสม
คำลงท้ายอีเมลควรแสดงถึงความเป็นมืออาชีพและความเคารพ
Best regards,
Yours sincerely,
ลงชื่อเต็มด้านล่าง
>>> Read more: คําลงท้ายจดหมาย ภาษาอังกฤษทางการ ใช้ได้ทุกกรณีที่ไม่ควรพลาด

ตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษ
ด้านล่างนี้คือตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษสำหรับผู้ที่กำลังมองหางาน อีเมลแต่ละฉบับถูกปรับให้เหมาะกับสายงานและตำแหน่งเฉพาะ เพื่อช่วยให้คุณสร้างความประทับใจให้นายจ้าง คุณสามารถใช้ตัวอย่างนี้และปรับแต่งให้เหมาะสมกับความต้องการส่วนตัวเพื่อแสดงถึงความเป็นมืออาชีพและทักษะของคุณ

ตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานทั่วไป
หัวข้ออีเมล: [ตำแหน่งที่สมัคร] – [ชื่อของคุณ]
เนื้อหาอีเมล:
| Dear Mr./Ms. [ชื่อผู้ว่าจ้าง] หรือ Dear Hiring Manager/HR Department, This is in reference to the job posting by you on the Internet dated [วันที่โพสต์ตำแหน่งงาน]. I have read the job description and find that my work experience as well as my skills and the job requirements may be a perfect match. I have been working for the past five years as a [ชื่องาน] in X Company. During that time, I have gained a significant amount of experience and such skills as [ระบุทักษะบางอย่าง] needed for [ตำแหน่งงานที่สมัคร]. I have attached my CV to this email. I hope you will learn more about my background, education, achievements, and awards through my CV. Please let me know if I can provide you with any further information. I am looking forward to hearing from you. Yours Sincerely, [ลายเซ็น] |
ความหมาย:
หัวข้ออีเมล: [ตำแหน่งที่สมัคร] – [ชื่อของคุณ]
เนื้อหาอีเมล:
เรียนคุณ [ชื่อผู้ว่าจ้าง] หรือ เรียนแผนกทรัพยากรบุคคล/ผู้จัดการฝ่ายสรรหา
ฉันเขียนอีเมลฉบับนี้เพื่อตอบรับตำแหน่งงานที่คุณได้โพสต์ไว้บนอินเทอร์เน็ตเมื่อวันที่ [วันที่โพสต์ตำแหน่งงาน] ฉันได้อ่านคำอธิบายงานแล้วพบว่าประสบการณ์การทำงานและทักษะของฉันเข้ากันได้อย่างสมบูรณ์แบบกับความต้องการของตำแหน่งนี้
ในช่วงห้าปีที่ผ่านมา ฉันได้ทำงานในตำแหน่ง [ชื่องาน] ที่บริษัท X ในช่วงเวลานั้น ฉันได้สะสมประสบการณ์และทักษะที่สำคัญ เช่น [ระบุทักษะบางอย่าง] ซึ่งจำเป็นสำหรับ [ตำแหน่งงานที่สมัคร]
ฉันได้แนบ CV ของฉันมาพร้อมกับอีเมลฉบับนี้ หวังว่าคุณจะได้ทราบเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับประวัติส่วนตัว การศึกษา ความสำเร็จ และรางวัลของฉันผ่าน CV นี้
โปรดแจ้งให้ฉันทราบหากคุณต้องการข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม ฉันหวังว่าจะได้รับการติดต่อกลับจากคุณ
ด้วยความเคารพ
[ลายเซ็น]
ตัวอย่างคำศัพท์:
Reference: การอ้างอิง เกี่ยวข้องกับ (เช่น ประกาศรับสมัครงาน)
Perfect match: ความเหมาะสมอย่างสมบูรณ์
Skills: ทักษะ
Attached: แนบมาด้วย
Background: พื้นฐาน (เช่น การศึกษา ประสบการณ์ของผู้สมัคร)
>>> Read more: วิธีเขียน CV เป็นภาษาอังกฤษอย่างมืออาชีพและน่าประทับใจที่สุด
ตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษสำหรับนักศึกษาจบใหม่
หัวข้ออีเมล: Application for HR Internship_Christine Charlo
เนื้อหาอีเมล:
| Dear Mr. Tim, My name is Christine Charlo – a graduate from the Foreign Trade University with a Bachelor’s degree in International Business. I have been seeking an internship program where I can gain more in-depth knowledge in Human Resource Management. Knowing that Pledge Camp is looking for an HR intern, I’m confident that I’ll be the right fit for this role. Please kindly check out my CV and let me know if you have any questions. I await your response and thank you for your consideration! Sincerely,Christine Charlochristine_charlo@cakeresume.com0900-123-456 linkedin.com/in/christine_charlo |
ความหมาย
หัวข้ออีเมล: ใบสมัครฝึกงานในตำแหน่ง HR_Christine Charlo
เรียน คุณทิม
ฉันชื่อ Christine Charlo – บัณฑิตจากมหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา สาขาปริญญาตรีธุรกิจระหว่างประเทศ ฉันกำลังมองหาโปรแกรมฝึกงานที่สามารถเพิ่มพูนความรู้เชิงลึกเกี่ยวกับการจัดการทรัพยากรบุคคล เมื่อทราบว่า Pledge Camp กำลังมองหานักศึกษาฝึกงานในตำแหน่ง HR ฉันมั่นใจว่าตัวเองเหมาะสมกับตำแหน่งนี้
กรุณาตรวจสอบ CV ของฉัน และโปรดแจ้งให้ฉันทราบหากคุณมีคำถามใด ๆ ฉันรอคอยการตอบกลับของคุณ และขอขอบคุณสำหรับการพิจารณาของคุณ!
ด้วยความเคารพ
Christine Charlo
christine_charlo@cakeresume.com
0900-123-456
linkedin.com/in/christine_charlo
คำศัพท์บางคำในตัวอย่าง:
Graduate: สำเร็จการศึกษา
Internship: การฝึกงาน
In-depth knowledge: ความรู้เชิงลึก
Consideration: การพิจารณา
Response: การตอบกลับ
ตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษสำหรับตำแหน่งครู
หัวข้ออีเมล: Application for Mathematics Teacher_[ชื่อเต็มของคุณ]
เนื้อหาอีเมล:
| Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name], My name is [Your Name] and I am writing to apply for the Mathematics Teacher position at your esteemed institution. I learned about this opportunity through your job posting on [Job Posting Site]. I am confident that my qualifications, skills, and passion for education make me an ideal candidate for this role. I hold a Master’s degree in Mathematics Education from [Your University Name] and have been teaching in [Previous School’s Name] for the past [Number of Years of Experience] years. My experience ranges from teaching foundational mathematics to more complex topics in calculus and trigonometry. Over the years, I have developed effective teaching strategies that adapt to each student’s individual learning style, helping them grasp complex mathematical concepts with greater ease. One of the key aspects of my teaching style is incorporating technology to enhance the learning process. I regularly use digital tools and interactive software to engage students and facilitate understanding of mathematical concepts. I believe that an innovative approach to teaching mathematics helps students see its relevance in everyday life and sparks their interest in the subject. Thank you for considering my application. I am eager to bring my teaching expertise, passion for mathematics, and dedication to student success to [School’s Name]. I would be happy to provide any additional information or attend an interview at a time that is convenient for you. Please find my resume attached to this email for further details about my experiences and qualifications. I am looking forward to the opportunity to discuss how my skills and experiences align with the needs of your school. Thank you again for your time and consideration. Best Regards, [Your Full Name] [Your Contact Information] |
ความหมาย
หัวข้ออีเมล: ใบสมัครตำแหน่งครูสอนคณิตศาสตร์_[ชื่อเต็มของคุณ]
เรียน [ชื่อผู้จัดการฝ่ายสรรหา]
ฉันชื่อ [ชื่อของคุณ] และเขียนอีเมลนี้เพื่อสมัครตำแหน่งครูสอนคณิตศาสตร์ในสถาบันที่น่าเคารพของคุณ ฉันได้ทราบโอกาสนี้ผ่านประกาศรับสมัครงานใน [เว็บไซต์ที่ประกาศ] ฉันมั่นใจว่าคุณสมบัติ ทักษะ และความหลงใหลในการสอนของฉันทำให้ฉันเป็นผู้สมัครที่เหมาะสมสำหรับตำแหน่งนี้
ฉันสำเร็จการศึกษาปริญญาโทด้านการศึกษาคณิตศาสตร์จาก [ชื่อมหาวิทยาลัยของคุณ] และได้สอนใน [ชื่อโรงเรียนที่เคยสอน] มาแล้วเป็นเวลา [จำนวนปีประสบการณ์] ปี ประสบการณ์ของฉันครอบคลุมตั้งแต่การสอนคณิตศาสตร์พื้นฐานไปจนถึงหัวข้อที่ซับซ้อน เช่น แคลคูลัสและตรีโกณมิติ ตลอดหลายปีที่ผ่านมา ฉันได้พัฒนากลยุทธ์การสอนที่มีประสิทธิภาพเพื่อให้สอดคล้องกับสไตล์การเรียนรู้ของนักเรียนแต่ละคน ซึ่งช่วยให้นักเรียนเข้าใจแนวคิดทางคณิตศาสตร์ที่ซับซ้อนได้ง่ายขึ้น
หนึ่งในจุดเด่นของวิธีการสอนของฉันคือการผสมผสานเทคโนโลยีเข้ากับกระบวนการเรียนรู้ ฉันใช้เครื่องมือดิจิทัลและซอฟต์แวร์เชิงโต้ตอบเป็นประจำเพื่อดึงดูดนักเรียนและช่วยอำนวยความสะดวกในการเข้าใจแนวคิดทางคณิตศาสตร์ ฉันเชื่อว่าวิธีการสอนคณิตศาสตร์ที่สร้างสรรค์ช่วยให้นักเรียนมองเห็นความเชื่อมโยงของวิชานี้ในชีวิตประจำวันและกระตุ้นความสนใจของพวกเขา
ขอบคุณสำหรับการพิจารณาใบสมัครของฉัน ฉันหวังว่าจะได้นำความเชี่ยวชาญด้านการสอน ความหลงใหลในคณิตศาสตร์ และความมุ่งมั่นต่อความสำเร็จของนักเรียนมาสู่ [ชื่อโรงเรียน] ฉันยินดีที่จะให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมหรือเข้าร่วมการสัมภาษณ์ในเวลาที่สะดวกสำหรับคุณ
โปรดดูประวัติส่วนตัวของฉันที่แนบมาในอีเมลนี้เพื่อทราบรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับประสบการณ์และคุณสมบัติของฉัน ฉันตั้งตารอโอกาสในการพูดคุยเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่ทักษะและประสบการณ์ของฉันสอดคล้องกับความต้องการของโรงเรียนของคุณ
ขอบคุณอีกครั้งสำหรับเวลาและการพิจารณาของคุณ
ขอแสดงความนับถือ
[ชื่อเต็มของคุณ]
[ข้อมูลการติดต่อของคุณ]
คำศัพท์ในตัวอย่าง:
Esteemed: น่าเคารพ
Qualifications: คุณสมบัติ
Adapt: ปรับให้เหมาะสม
Interactive: เชิงโต้ตอบ
Dedication: ความทุ่มเท
ตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษในสายงาน IT
หัวข้ออีเมล: John Doe – Application for Software Developer Position
เนื้อหาอีเมล:
| Dear Hiring Manager, My name is John Doe, and I am writing to express my interest in the Software Developer position advertised on your website. I am confident that my qualifications and experience make me a strong candidate for this role. Over the past 5 years, I have honed my skills in multiple programming languages including Python, JavaScript, and C#. I have also gained valuable experience in front-end and back-end development, Agile methodologies, and cloud computing. These technical skills, combined with my problem-solving abilities and keen attention to detail, have enabled me to deliver high-quality software solutions in my previous roles. During my tenure as a Junior Developer at XYZ Software, I was part of a dynamic team where we developed a range of innovative applications that led to a significant increase in user retention and growth. This experience has reinforced my passion for software development, and I am excited to bring this passion, experience, and talent to your team. Please find attached my resume and a few samples of my work. You may also view my portfolio on my personal website [Name of website], which showcases some of the projects I have completed and their impacts. I would be happy to provide further details or answer any questions on these examples. Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to the possibility of discussing my candidacy further and how I can contribute to your team. Please feel free to reach me at [Your email] or [Your phone]. Best regards, John Doe |
ความหมาย
หัวข้ออีเมล: John Doe – ใบสมัครตำแหน่งนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
เรียน ผู้จัดการฝ่ายสรรหา
ฉันชื่อ John Doe และเขียนอีเมลฉบับนี้เพื่อแสดงความสนใจในตำแหน่งนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ที่โฆษณาไว้บนเว็บไซต์ของคุณ ฉันมั่นใจว่าคุณสมบัติและประสบการณ์ของฉันทำให้ฉันเป็นผู้สมัครที่แข็งแกร่งสำหรับตำแหน่งนี้
ตลอดระยะเวลา 5 ปีที่ผ่านมา ฉันได้พัฒนาทักษะของตัวเองในหลายภาษาโปรแกรม เช่น Python, JavaScript และ C# ฉันยังได้สั่งสมประสบการณ์ที่มีค่าในการพัฒนา front-end และ back-end การทำงานในรูปแบบ Agile และการใช้ระบบ cloud computing ทักษะทางเทคนิคเหล่านี้เมื่อรวมกับความสามารถในการแก้ปัญหาและความใส่ใจในรายละเอียดช่วยให้ฉันสามารถนำเสนอวิธีแก้ปัญหาซอฟต์แวร์คุณภาพสูงในบทบาทก่อนหน้านี้
ในช่วงเวลาที่ฉันทำงานเป็นนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ระดับ Junior ที่ XYZ Software ฉันเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของทีมที่มีพลังซึ่งพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชันที่เป็นนวัตกรรมใหม่ๆ นำไปสู่การเพิ่มอัตราการคงผู้ใช้งานและการเติบโตอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ ประสบการณ์นี้เสริมสร้างความหลงใหลในพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ของฉัน และฉันตื่นเต้นที่จะนำความหลงใหล ประสบการณ์ และความสามารถนี้มาสู่ทีมของคุณ
โปรดดูเอกสารแนบที่ฉันส่งมาด้วย ซึ่งรวมถึงประวัติย่อและตัวอย่างงานบางส่วนของฉัน คุณสามารถเยี่ยมชมพอร์ตโฟลิโอของฉันได้ที่เว็บไซต์ส่วนตัว [ชื่อเว็บไซต์] ซึ่งจะแสดงโครงการบางส่วนที่ฉันได้ทำและผลกระทบของมัน ฉันยินดีที่จะให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมหรือคำตอบสำหรับคำถามเกี่ยวกับตัวอย่างเหล่านี้
ขอขอบคุณที่พิจารณาใบสมัครของฉัน ฉันตั้งตารอที่จะได้พูดคุยเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับความสามารถของฉันและวิธีที่ฉันสามารถมีส่วนร่วมกับทีมของคุณ โปรดติดต่อฉันได้ที่ [อีเมลของคุณ] หรือ [หมายเลขโทรศัพท์ของคุณ]
ขอแสดงความนับถือ
John Doe
คำศัพท์ในตัวอย่าง:
Express: แสดงออก
Programming languages: ภาษาโปรแกรม
Cloud computing: การประมวลผลแบบคลาวด์
Portfolio: พอร์ตโฟลิโอ
Possibility: ความเป็นไปได้
ตัวอย่างอีเมลสมัครงานในสายงาน Marketing
หัวข้ออีเมล: Application for Copywriter Position – [Your full name]
เนื้อหาอีเมล:
| Dear Hiring Manager, I am delighted to submit my application for the Copywriter position at your esteemed organization. I came across the job posting on your official website, and I believe that my unique blend of skills, experience, and creativity makes me a perfect candidate for the role. For the past three years, I have been serving as a Copywriter at a highly reputed digital marketing agency. Throughout my tenure, I honed my ability to write compelling and persuasive copy that elevates brand voices, engages target audiences, and drives conversion. In my current role, I’ve successfully produced and edited a broad spectrum of content, including digital articles, web content, promotional emails, social media posts, and press releases. My work has spanned various industries ranging from technology to healthcare, showcasing my versatility and adaptability to different sectors and target markets.I hold a Bachelor’s Degree in English, which has solidified my foundation in writing, grammar, and attention to detail. However, real-world experience has taught me that great copywriting involves more than just impeccable grammar and spelling—it requires creativity, an understanding of the audience’s psyche, and a data-driven approach. As such, I’ve developed my skills in areas such as Search Engine Optimization (SEO), Content Management Systems (like WordPress), and the use of Google Drive and Microsoft Office Suite. One of my most notable achievements was leading a website copywriting project that resulted in a 47% increase in brand awareness and a 20% increase in website traffic over six months. I believe this kind of result demonstrates my capacity to make a significant contribution to your organization. I am eager to bring my creativity, strategic thinking, and proven track record to your team. I am confident that I can help amplify your brand’s voice, engage your audience more effectively, and drive marketing results. Thank you for considering my application. I would like to discuss my qualifications further in an interview. Please find my resume attached for more information about my experience and achievements. Sincerely, [Your Name] [Your Contact Information] |
ความหมาย:
หัวข้ออีเมล: Application for Copywriter Position – [ชื่อเต็มของคุณ]
เรียน ผู้จัดการฝ่ายสรรหา
ฉันรู้สึกยินดีอย่างยิ่งที่ได้ยื่นใบสมัครสำหรับตำแหน่ง Copywriter ในองค์กรอันทรงเกียรติของคุณ ดิฉันพบประกาศรับสมัครงานในเว็บไซต์อย่างเป็นทางการของคุณ และเชื่อว่าการผสมผสานทักษะ ประสบการณ์ และความคิดสร้างสรรค์ของดิฉันทำให้ดิฉันเหมาะสมกับตำแหน่งนี้เป็นอย่างยิ่ง
ในช่วง 3 ปีที่ผ่านมา ดิฉันทำงานในตำแหน่ง Copywriter ที่บริษัทเอเจนซี่การตลาดดิจิทัลชั้นนำ ตลอดระยะเวลาการทำงาน ดิฉันได้พัฒนาทักษะการเขียนเนื้อหาที่น่าสนใจและโน้มน้าวใจ ซึ่งช่วยเสริมสร้างภาพลักษณ์ของแบรนด์ ดึงดูดกลุ่มเป้าหมาย และเพิ่มอัตราการเปลี่ยนแปลง
ในบทบาทปัจจุบัน ดิฉันประสบความสำเร็จในการสร้างและแก้ไขเนื้อหาหลากหลายประเภท เช่น บทความดิจิทัล เนื้อหาเว็บไซต์ อีเมลประชาสัมพันธ์ โพสต์ในสื่อสังคมออนไลน์ และข่าวประชาสัมพันธ์ งานของดิฉันครอบคลุมหลายอุตสาหกรรม ตั้งแต่เทคโนโลยีไปจนถึงการดูแลสุขภาพ ซึ่งแสดงถึงความหลากหลายและความสามารถในการปรับตัวให้เข้ากับกลุ่มเป้าหมายและตลาดที่แตกต่างกัน
ดิฉันสำเร็จการศึกษาระดับปริญญาตรีสาขาภาษาอังกฤษ ซึ่งช่วยเสริมสร้างพื้นฐานด้านการเขียน ไวยากรณ์ และความใส่ใจในรายละเอียด อย่างไรก็ตาม ประสบการณ์จริงสอนให้ดิฉันเข้าใจว่าการเขียนที่ยอดเยี่ยมไม่ใช่แค่ไวยากรณ์หรือการสะกดคำที่ถูกต้องเท่านั้น แต่ยังต้องอาศัยความคิดสร้างสรรค์ ความเข้าใจในจิตวิทยาของกลุ่มเป้าหมาย และการใช้ข้อมูลมาวิเคราะห์ ด้วยเหตุนี้ ดิฉันจึงพัฒนาทักษะในด้านการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเครื่องมือค้นหา (SEO) การใช้ระบบจัดการเนื้อหา (เช่น WordPress) และการใช้งาน Google Drive รวมถึง Microsoft Office
หนึ่งในความสำเร็จที่น่าภาคภูมิใจที่สุดของดิฉันคือการเป็นหัวหน้าโครงการเขียนเนื้อหาเว็บไซต์ ซึ่งส่งผลให้การรับรู้แบรนด์เพิ่มขึ้น 47% และการเข้าชมเว็บไซต์เพิ่มขึ้น 20% ภายในหกเดือน ดิฉันเชื่อว่าผลลัพธ์นี้แสดงให้เห็นถึงความสามารถของดิฉันในการสร้างผลงานที่มีคุณค่าให้แก่องค์กรของคุณ
ดิฉันกระตือรือร้นที่จะนำความคิดสร้างสรรค์ ความคิดเชิงกลยุทธ์ และประวัติการทำงานที่พิสูจน์แล้วของดิฉันมาสู่ทีมของคุณ ดิฉันมั่นใจว่าสามารถช่วยเสริมเสียงของแบรนด์ ดึงดูดกลุ่มเป้าหมายได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ และขับเคลื่อนผลลัพธ์ทางการตลาดให้กับองค์กรของคุณ
ขอขอบคุณที่พิจารณาใบสมัครของดิฉัน ดิฉันหวังว่าจะได้พูดคุยเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับคุณสมบัติของดิฉันในการสัมภาษณ์ โปรดดูประวัติส่วนตัวของดิฉันที่แนบมานี้เพื่อข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับประสบการณ์และความสำเร็จของฉัน
ด้วยความนับถือ
[ชื่อของคุณ]
[ข้อมูลติดต่อของคุณ]
คำศัพท์ในตัวอย่าง:
Delighted: ยินดี/ดีใจ
Blend: การผสมผสาน
Persuasive copy: เนื้อหาที่โน้มน้าวใจ
SEO (Search Engine Optimization): การปรับแต่งเว็บไซต์ให้ติดอันดับในเครื่องมือค้นหา
Strategic thinking: ความคิดเชิงกลยุทธ์
>>> Read more: การตอบ email confirm สัมภาษณ์งานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษอย่างน่าประทับใจ

หมายเหตุเกี่ยวกับการเขียนอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ
ผู้สมัครหลายคน แม้ว่าจะมีความสามารถและประสบการณ์มากมาย ก็ยังถูกนายจ้างปฏิเสธเนื่องจากข้อผิดพลาดร้ายแรงในการเขียนอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ ด้านล่างนี้คือข้อควรระวังสำคัญที่ผู้สมัครควรรู้เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงข้อผิดพลาดเหล่านี้:
เกี่ยวกับเนื้อหา
เนื้อหาของอีเมลถือเป็นหัวใจสำคัญ ดังนั้นผู้สมัครควรใส่ใจและนำเสนอข้อมูลให้ครบถ้วน ไม่ควรละเว้นข้อมูลสำคัญใดๆ เช่น:
หัวข้ออีเมล: แม้จะดูเล็กน้อย แต่มีความสำคัญมาก ผู้สมัครควรระบุชื่อและตำแหน่งงานที่สมัครให้ชัดเจนเพื่อไม่ให้นายจ้างมองข้าม
เนื้อหาของจดหมาย: ควรเขียนให้กระชับและสั้น ไม่ควรทำซ้ำข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ในเรซูเม่ที่แนบไป
ไฟล์แนบ: นอกจากเนื้อหาหลักในอีเมลแล้ว ควรมีเรซูเม่แนบไปด้วย ผู้สมัครสามารถใช้ประโยค “I attached my CV to this email” เพื่อแจ้งให้นายจ้างทราบ ช่วยให้มั่นใจว่าเรซูเม่จะไม่ถูกมองข้าม
ตรวจสอบการสะกดและไวยากรณ์: หากไม่มั่นใจในเนื้อหาของอีเมล ผู้สมัครสามารถขอให้ญาติหรือเพื่อนที่มีความเชี่ยวชาญด้านภาษาอังกฤษช่วยตรวจสอบ หรือใช้เครื่องมือออนไลน์เพื่อตรวจสอบไวยากรณ์และการสะกดคำ
การใช้คำ: ควรเลือกใช้คำนามและประโยคที่เป็นรูปแบบคำกริยาช่องถูกเพื่อเพิ่มความสุภาพและทางการ นอกจากนี้ ควรใช้กลุ่มคำกริยาและคุณศัพท์ที่แสดงถึงทัศนคติที่ดีและความกระตือรือร้นต่อตำแหน่งงาน
โครงสร้างของประโยค: หลีกเลี่ยงการเขียนประโยคสั้นเกินไปหรือยาวเกินไป ควรแบ่งเนื้อหาในแต่ละส่วนให้มีความยาวไม่เกิน 2 บรรทัด เพื่อให้เนื้อหาชัดเจนและเข้าใจง่าย
รูปแบบ
เมื่อเขียนอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ ผู้สมัครควรใส่ใจในรูปแบบบางประการดังนี้:
ใช้ฟอนต์ที่มีเชิง (serif) เช่น Times New Roman
ตั้งขนาดฟอนต์ที่ 13-14 และจัดย่อหน้าซ้ายหรือจัดย่อหน้าทั้งสองข้าง
ความยาวของอีเมลควรอยู่ในขนาดประมาณ 1 หน้ากระดาษ A4
ใช้ที่อยู่อีเมลที่ประกอบด้วยชื่อและนามสกุล หรือสามารถเพิ่มวันเกิดเพื่อความเป็นมืออาชีพในการส่งอีเมลสมัครงาน

คำศัพท์และวลีภาษาอังกฤษที่ควรรู้เมื่อสมัครงาน
| คำศัพท์ | การสะกดคำ | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง |
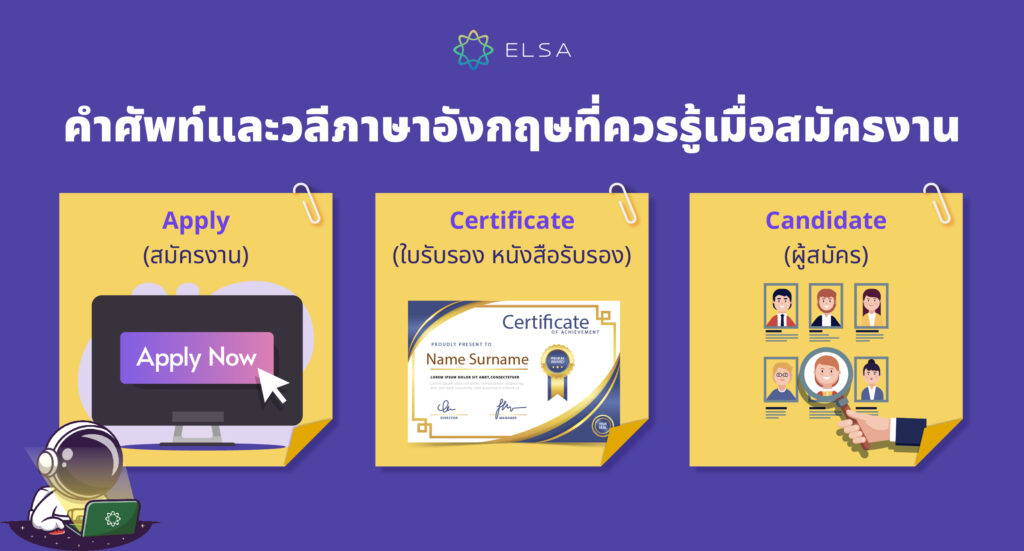
| Apply | /əˈplaɪ/ | สมัครงาน | You should apply for this position. (คุณควรสมัครตำแหน่งนี้) |
| Application | /ˌæplɪˈkeɪʃən/ | ใบสมัครงาน การสมัคร | Your application has been approved. (ใบสมัครของคุณได้รับการอนุมัติแล้ว) |
| Certificate | /sərˈtɪfɪkət/ | ใบรับรอง หนังสือรับรอง | He received a certificate in teaching. (เขาได้รับหนังสือรับรองการสอน) |
| Candidate | /ˈkændədət/ | ผู้สมัคร | There are many candidates for this job. (มีผู้สมัครหลายคนสำหรับงานนี้) |
| Marital Status | /ˈmærɪtl ˈsteɪtəs/ | สถานภาพการแต่งงาน | Please fill in your marital status. (กรุณากรอกสถานภาพสมรสของคุณ) |
| Educational Background | /ˌɛdʒuˈkeɪʃənl ˈbækɡraʊnd/ | พื้นฐานการศึกษา | His educational background is impressive. (พื้นฐานการศึกษาของเขาน่าประทับใจมาก) |
| Employee | /ɪmˈplɔɪiː/ | พนักงาน | The company hired a new employee. (บริษัทได้จ้างพนักงานใหม่แล้ว) |
| Employer | /ɪmˈplɔɪər/ | นายจ้าง | She is a fair employer. (เธอเป็นนายจ้างที่ยุติธรรม) |
| Expertise | /ˌɛkspərˈtiːz/ | ความเชี่ยวชาญ | He has expertise in finance. (เขามีความเชี่ยวชาญในด้านการเงิน) |
| Professional Experience | /prəˈfɛʃənl ɪkˈspɪəriəns/ | ประสบการณ์ทำงาน | She has 5 years of professional experience. (เธอมีประสบการณ์การทำงาน 5 ปี) |
| Perk | /pɜrk/ | สิทธิประโยชน์ | Free lunches are one of the perks. (อาหารกลางวันฟรีเป็นหนึ่งในสิทธิประโยชน์) |
| Notify | /ˈnoʊtɪfaɪ/ | แจ้งให้ทราบ | Please notify me of any changes. (กรุณาแจ้งฉันหากมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดๆ) |
| Relevant | /ˈrɛləvənt/ | เกี่ยวข้อง | This document is relevant to our work. (เอกสารนี้เกี่ยวข้องกับงานของเรา) |
| Occupation | /ˌɑkjuˈpeɪʃən/ | อาชีพ | His occupation is a teacher. (อาชีพของเขาคือครู) |
| Salary | /ˈsæləri/ | เงินเดือน | She earns a high salary. (เธอได้รับเงินเดือนสูง) |
| Skill | /skɪl/ | ทักษะ | Communication is an important skill. (การสื่อสารเป็นทักษะที่สำคัญ) |
| Cover letter | /ˈkʌvər ˈlɛtər/ | จดหมายสมัครงาน | I attached my cover letter to the application. (ฉันได้แนบจดหมายสมัครงานไปกับใบสมัคร) |
| Dear | /dɪr/ | เรียน | Dear Mr. Smith, (เรียนคุณสมิธ) |
| Sincerely | /sɪnˈsɪrli/ | ขอบคุณ | Sincerely, (ขอแสดงความนับถือ) |
| Interview | /ˈɪntərvjuː/ | สัมภาษณ์ | I have an interview scheduled for next week. (ฉันมีกำหนดสัมภาษณ์สัปดาห์หน้า) |
| Strengths | /strɛŋθs/ | จุดแข็ง | My strengths include teamwork and communication. (จุดแข็งของฉันรวมถึงการทำงานเป็นทีมและการสื่อสาร) |
| Human resource department | /ˈhjuːmən rɪˈsɔːrs dɪˈpɑːtmənt/ | แผนกทรัพยากรบุคคล | I sent my application to the human resource department. (ฉันได้ส่งใบสมัครไปยังแผนกทรัพยากรบุคคล) |
| Fresh graduate | /frɛʃ ˈɡrædʒuət/ | นักศึกษาจบใหม่ | As a fresh graduate, I am eager to start my career. (เป็นนักศึกษาจบใหม่ ฉันตื่นเต้นที่จะเริ่มต้นอาชีพของตัวเอง) |
| Senior | /ˈsiːniər/ | ผู้สูงอายุในงาน | I am applying for a senior position in your company. (ฉันกำลังสมัครตำแหน่งระดับสูงในบริษัทของคุณ) |
| Job description | /dʒɑb dɪskrɪpˈʃən/ | คำอธิบายงาน | The job description outlines the responsibilities. (คำอธิบายงานระบุถึงความรับผิดชอบ) |
| Career objective | /kəˈrɪr əbˈdʒɛktɪv/ | เป้าหมายในอาชีพ | My career objective is to become a project manager. (วัตถุประสงค์ในอาชีพของฉันคือการเป็นผู้จัดการโครงการ) |
| Thrilled | /θrɪld/ | ตื่นเต้น | I am thrilled to receive this job offer. (ฉันตื่นเต้นที่ได้รับข้อเสนอจากงานนี้) |
| Motivate | /ˈmoʊtɪveɪt/ | กระตุ้น | I aim to motivate my team to achieve our goals. (ฉันตั้งเป้าหมายที่จะกระตุ้นทีมงานของฉันเพื่อบรรลุเป้าหมาย) |
| Passionate | /ˈpæʃənət/ | มีความหลงใหล | I am passionate about working in marketing. (ฉันหลงใหลในการทำงานในด้านการตลาด) |
| experience | /ɪkˈspɪəriənsiːz/ | ประสบการณ์ | I have gained valuable experiences in my previous jobs. (ฉันได้สะสมประสบการณ์ที่มีค่าในงานก่อนหน้านี้) |
| Development | /dɪˈvɛləpmənt/ | การพัฒนา | Continuous development is key to success. (การพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องเป็นกุญแจสำคัญสู่ความสำเร็จ) |
| Undertake | /ˌʌndərˈteɪk/ | รับผิดชอบ | I will undertake the new project starting next month. (ฉันจะรับผิดชอบโครงการใหม่ที่จะเริ่มต้นในเดือนหน้า) |
| Position | /pəˈzɪʃən/ | ตำแหน่ง | She applied for the marketing position. (เธอสมัครตำแหน่งในด้านการตลาด) |
| Performance | /pərˈfɔrməns/ | ผลการดำเนินงาน | The performance of the team was outstanding. (ผลการทำงานของทีมยอดเยี่ยมมาก) |
| Skills | /skɪlz/ | ทักษะ | You need to develop your skills in this area. (คุณต้องพัฒนาทักษะของคุณในด้านนี้) |
| Level | /ˈlɛvəl/ | ระดับ | He is at the senior level in the company. (เขาอยู่ในระดับสูงในบริษัท) |
| Work for | /wɜrk fɔr/ | ทำงานให้ | I work for a multinational company. (ฉันทำงานให้กับบริษัทข้ามชาติ) |
| Professional | /prəˈfɛʃənl/ | มืออาชีพ | He is a professional in his field. (เขาคือผู้เชี่ยวชาญในสาขาของเขา) |
| Believed in | /bɪˈliːvd ɪn/ | เชื่อมั่นใน | I have always believed in my abilities. (ฉันเชื่อในความสามารถของตัวเองเสมอ) |
| Confident | /ˈkɒnfɪdənt/ | มั่นใจ | She is confident in her skills. (เธอมั่นใจในทักษะของเธอ) |
| Business trip | /ˈbɪznəs trɪp/ | การเดินทางไปทำงาน | I have a business trip scheduled for next week. (ฉันมีกำหนดการเดินทางไปทำธุรกิจในสัปดาห์หน้า) |
| Recruitment | /rɪˈkruːtmənt/ | การสรรหาบุคลากร | Recruitment is essential for company growth. (การสรรหาบุคลากรเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นสำหรับการเติบโตของบริษัท) |
| Recruiter | /rɪˈkruːtər/ | ผู้สรรหา | The recruiter reached out to me for this position. (ผู้สรรหา/ผู้รับสมัครติดต่อมาหาฉันเกี่ยวกับตำแหน่งนี้) |
| Recruit | /rɪˈkruːt/ | การสรรหาพนักงาน | They plan to recruit new employees next quarter. (พวกเขาวางแผนที่จะสรรหาพนักงานใหม่ในไตรมาสถัดไป) |
| Working style | /ˈwɜrkɪŋ staɪl/ | สไตล์การทำงาน | His working style is very collaborative. (สไตล์การทำงานของเขาเป็นแบบร่วมมือกันอย่างมาก) |
| Competitor | /kəmˈpɛtɪtər/ | คู่แข่ง | Our main competitor is launching a new product. (คู่แข่งหลักของเรากำลังเปิดตัวผลิตภัณฑ์ใหม่) |
| Deadline | /ˈdɛdlaɪn/ | กำหนดส่งงาน | The deadline for the project is next Friday. (กำหนดส่งโครงการคือวันศุกร์หน้า) |
| Look forward | /lʊk ˈfɔːrwərd/ | การตั้งตารอ | I look forward to meeting you. (ฉันตั้งตารอที่จะพบคุณ) |
| Welcome | /ˈwɛlkəm/ | การต้อนรับ | Welcome to our team! (ยินดีต้อนรับสู่ทีมของเรา!) |
| Improve | /ɪmˈpruːv/ | การพัฒนา การเจริญเติบโต | I want to improve my communication skills. (ฉันต้องการพัฒนาทักษะการสื่อสารของฉัน) |
| Acquire | /əˈkwaɪər/ | การได้รับ | You can acquire new skills through practice. (คุณสามารถพัฒนาทักษะใหม่ ๆ ได้ผ่านการฝึกฝน) |
| Accomplish | /əˈkɑmplɪʃ/ | การบรรลุ | I hope to accomplish my goals this year. (ฉันหวังว่าจะบรรลุเป้าหมายของฉันในปีนี้) |
| Interested | /ˈɪntrəstɪd/ | สนใจ ใส่ใจ | I am interested in this job opportunity. (ฉันสนใจในโอกาสงานนี้) |
| Application letter | /ˌæplɪˈkeɪʃən ˈlɛtər/ | จดหมายสมัครงาน/จดหมายแนะนำตัว | I submitted my application letter yesterday. (ฉันได้ยื่นจดหมายสมัครงานเมื่อวานนี้) |
| CV (Curriculum vitae) | /siːˈviː/ | ประวัติย่อ | Please attach your CV with the application. (โปรดแนบประวัติย่อของคุณกับใบสมัครงาน) |
| Supervisor | /ˈsuːpərvaɪzər/ | หัวหน้า ผู้ดูแล | My supervisor gave me helpful feedback. (หัวหน้าของฉันให้ความคิดเห็นที่มีประโยชน์) |
| Weakness | /ˈwiːk.nəs/ | จุดอ่อน | Identify your weaknesses to improve. (ระบุจุดอ่อนของคุณเพื่อพัฒนา) |
| Working environment | /ˈwɜrkɪŋ ɪnˈvaɪrənmənt/ | สภาพแวดล้อมการทำงาน | A supportive working environment boosts productivity. (สภาพแวดล้อมการทำงานที่สนับสนุนจะช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงาน) |
| Personal objectives | /ˈpɜrsənl əbˈdʒɛktɪvz/ | เป้าหมายส่วนบุคคล | Set personal objectives for your career growth. (ตั้งเป้าหมายส่วนบุคคลสำหรับการเติบโตในอาชีพของคุณ) |
| Colleague | /ˈkɒliːɡ/ | เพื่อนร่วมงาน | I have a great relationship with my colleagues. (ฉันมีความสัมพันธ์ที่ดีเยี่ยมกับเพื่อนร่วมงานของฉัน) |
| Motivation | /ˌmoʊtɪˈveɪʃən/ | แรงจูงใจ | Finding motivation is essential for success. (การหามูลเหตุจูงใจเป็นสิ่งสำคัญสำหรับความสำเร็จ) |
| Effort | /ˈɛfərt/ | ความพยายาม | Your effort will be rewarded. (ความพยายามของคุณจะได้รับการตอบแทน) |
| Challenge | /ˈtʃælɪndʒ/ | ความท้าทาย | I enjoy taking on new challenges. (ฉันชอบรับมือกับความท้าทายใหม่ ๆ) |
| Working performance | /ˈwɜrkɪŋ pərˈfɔrməns/ | ความสามารถในการทำงาน | Her working performance has improved significantly. (ประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของเธอได้พัฒนาไปอย่างมาก) |
| Responsibility | /rɪˌspɒnsəˈbɪlɪti/ | ความรับผิดชอบ | You have a responsibility to meet deadlines. (คุณมีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบในการทำงานให้ทันเวลา) |
| Delegate | /ˈdɛlɪɡeɪt/ | การมอบหมาย การมอบอำนาจ | I will delegate tasks to my team members. (ฉันจะมอบหมายงานให้กับสมาชิกในทีมของฉัน) |
| Promotion | /prəˈmoʊʃən/ | การเลื่อนตำแหน่ง | She received a promotion after her excellent performance. (เธอได้รับการเลื่อนตำแหน่งหลังจากผลงานที่ยอดเยี่ยม) |
| Division | /dɪˈvɪʒən/ | แผนก | I work in the marketing division. (ฉันทำงานในแผนกการตลาด) |
| Pro-active, self starter | /ˈproʊˌæktɪv ˈsɛlf ˈstɑrtər/ | ผู้กระตือรือร้น | A pro–active approach can lead to success. (วิธีการที่มีความกระตือรือร้นสามารถนำไปสู่ความสำเร็จ) |
| Propose | /prəˈpoʊz/ | ข้อเสนอ | I propose we meet next week to discuss this. (ฉันขอเสนอให้เราพบกันในสัปดาห์หน้าเพื่อหารือเกี่ยวกับเรื่องนี้) |
>>> Read more: 50+ คำศัพท์ควรรู้ในหัวข้อ ประกาศรับสมัครงาน ภาษาอังกฤษ
คำถามที่พบบ่อยเมื่อเขียน email สมัครงาน ภาษาอังกฤษ
การส่งอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษจำเป็นต้องแนบ Cover Letter หรือไม่?
อาจจำเป็นต้องแนบ อ่านคำขอจากผู้จ้างงานอย่างละเอียดและสอบถามกับแผนกทรัพยากรบุคคลหากจำเป็น
รูปแบบไฟล์ที่ดีที่สุดเมื่อส่ง CV พร้อมอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษคืออะไร?
PDF หรือ Word หากไม่มีคำขอเฉพาะ ควรเลือก PDF เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาฟอนต์
ควรแนบเอกสารอะไรบ้างในอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ?
CV, Cover Letter, Portfolio, ประกาศนียบัตรทางภาษา ควรตั้งชื่อเอกสารให้ชัดเจนตามโครงสร้าง: ชื่อเอกสาร – ชื่อ-นามสกุลผู้สมัคร – ตำแหน่งที่สมัคร
หากไม่ได้รับการตอบกลับ ควรส่งอีเมลสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษซ้ำอีกครั้งหรือไม่?
ควรส่งอีกครั้ง หลังจากอย่างน้อย 2-3 สัปดาห์เพื่อเตือนผู้จ้างงานเกี่ยวกับความสนใจของคุณ
เอกสารสมัครงานภาษาอังกฤษคืออะไร?
เอกสารการสมัครงานเป็นภาษาอังกฤษเรียกว่า Job Application Document ซึ่งประกอบด้วยเอกสารเช่น CV ภาษาอังกฤษ (ประวัติชีวิต), Cover Letter (จดหมายสมัครงาน), Reference Letter (จดหมายแนะนำตัว) และใบประกาศอื่น ๆ เอกสารเหล่านี้ช่วยให้คุณแนะนำความสามารถ ประสบการณ์ และเหตุผลที่เหมาะสมกับตำแหน่งที่สมัคร
ตำแหน่งงานที่เปิดรับสมัครงาน ภาษาอังกฤษคืออะไร?
ตำแหน่งงานที่ประกาศมักจะเรียกเป็นภาษาอังกฤษดังนี้:
| ภาษาอังกฤษ | ตำแหน่ง |
| Chief Executive Officer (CEO) | ประธานเจ้าหน้าที่บริหาร (CEO) |
| Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | ประธานเจ้าหน้าที่ฝ่ายการเงิน (CFO) |
| Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) | ประธานเจ้าหน้าที่ฝ่ายการตลาด (CMO) |
| Human Resources Manager | ผู้จัดการฝ่ายทรัพยากรบุคคล |
| Software Engineer | วิศวกรซอฟต์แวร์ |
| Web Developer | นักพัฒนาเว็บ |
| Sales Representative | ตัวแทนฝ่ายขาย |
| Technical Support Specialist | ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านการสนับสนุนทางเทคนิค |
| Accountant | นักบัญชี |
| Data Analyst | นักวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล |
| Project Manager | ผู้จัดการโครงการ |
| Customer Service Representative | ตัวแทนบริการลูกค้า |
| Marketing Associate | ผู้ช่วยฝ่ายการตลาด |
| Graphic Designer | นักออกแบบกราฟิก |
| Application Developer | นักพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชัน |
| Product Manager | ผู้จัดการผลิตภัณฑ์ |
| Logistics Coordinator | ผู้ประสานงานด้านโลจิสติกส์ |
| SEO Specialist | ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเว็บไซต์ SEO |
| Network Engineer | วิศวกรเครือข่าย |
| Content Specialist | ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านเนื้อหา |
| Chief Technology Officer (CTO) | ประธานเจ้าหน้าที่ฝ่ายเทคโนโลยี (CTO) |
| Chief Operating Officer (COO) | ประธานเจ้าหน้าที่ฝ่ายปฏิบัติการ (COO) |
| Business Development Representative | ตัวแทนพัฒนาธุรกิจ |
| Business Analyst | นักวิเคราะห์ธุรกิจ |
| Brand Manager | ผู้จัดการแบรนด์ |
| Legal Associate | ผู้ช่วยฝ่ายกฎหมาย |
| Market Research Analyst | นักวิเคราะห์วิจัยตลาด |
| Public Relations Specialist | ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านประชาสัมพันธ์ |
| Event Manager | ผู้จัดการงานอีเว้นต์ |
| Interior Designer | นักออกแบบภายใน |
| Electrical Engineer | วิศวกรไฟฟ้า |
| Health Care Assistant | ผู้ช่วยดูแลสุขภาพ |
| Purchasing Agent | ตัวแทนฝ่ายจัดซื้อ |
| Maintenance Technician | ช่างเทคนิคซ่อมบำรุง |
| Training Specialist | ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านการฝึกอบรม |
| Auditor | ผู้ตรวจสอบบัญชี |
| Product Developer | นักพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์ |
| Supply Chain Manager | ผู้จัดการห่วงโซ่อุปทาน |
| Information Security Specialist | ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านความปลอดภัยข้อมูล |
Job Application แปลว่าอะไร?
Job Application คือคำศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษที่ใช้ในการอธิบายกระบวนการหรือใบสมัครงานที่ผู้สมัครส่งให้กับนายจ้าง อาจประกอบด้วยแบบฟอร์มทางการ, ประวัติย่อ หรือชุดเอกสารที่รวมทั้ง CV และ Cover Letter
ทํางาน ภาษาอังกฤษเขียนยังไง?
คำว่า “ทำงาน” ในภาษาอังกฤษเขียนว่า work ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาที่ใช้บ่อยเพื่อบอกถึงการทำงาน, ปฏิบัติภารกิจ หรือทำงานในสภาพแวดล้อมที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
นอกจากนี้ ในบางกรณีอาจใช้คำว่า working (รูปแบบกริยาที่กำลังทำ) หรือ to work (รูปแบบคำกริยาต้น) ขึ้นอยู่กับหลักไวยากรณ์
จากคำแนะนำข้างต้นนี้ คุณก็สามารถเขียนอีเมล สมัครงาน ภาษาอังกฤษ ที่น่าประทับใจและเป็นมืออาชีพได้ง่ายขึ้นแล้ว แต่หากคุณต้องการฝึกฝนและเตรียมตัวสำหรับการสัมภาษณ์หลังจากที่ผ่านการคัดเลือกจาก CV แล้ว ลองพัฒนาคำศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษในชีวิตประจำวันกับแอปพลิเคชัน ELSA Speak กันนะ!
คติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษมีความสำคัญมากสำหรับการฝึกทักษะการเรียนภาษาอังกฤษ ทั้ง 4 ทักษะ ถ้าคุณรู้จักคติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษอย่างลึกซึ้งคุณก็จะสามารถพัฒนาคำศัพท์และเข้าใจวัฒนธรรมของชาวอังกฤษได้…แล้วคติประจําใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ ใช้ยังไง ในบทความนี้ ELSA Speak จะแนะนำวิธีใช้และรวบรวม 150+ คติประจําใจภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆ เกี่ยวกับหัวข้อต่างๆมากมายเพื่อให้คุณเรียนรู้ เรามาดูไปพร้อมกันนะ
คติประจําใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ คืออะไร?

ตามพจนานุกรมของเคมบริดจ์ คำคติประจําใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ (English proverb) คือคำพูดสั้นๆ ที่กระชับและสื่อถึงข้อความหรือบทเรียนเกี่ยวกับจริยธรรมและวิถีชีวิต คติประจำใจเหล่านี้มักปรากฏทั้งในภาษาพูดและภาษาเขียน ช่วยในการแสดงความคิด หรือเพื่อเตือนสติและแนะนำผู้อื่น
คติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษใช้ได้อย่างยืดหยุ่นในหลายบริบท ตั้งแต่การสนทนาในชีวิตประจำวันไปจนถึงการเขียน จากการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวันไปจนถึงการสอนและการค้นคว้า มันไม่เพียงแต่ขยายความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับโลกรอบตัวเราเท่านั้น แต่ยังช่วยให้เรามองเห็นตัวเองและเข้าใจผู้อื่นดีขึ้นอีกด้วย
รวบรวมคติประจําใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ สั้นๆ และมีความหมายดีๆ
คติประจําใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ สั้นๆ ที่ถูกใช้บ่อยที่สุด
หากคุณกำลังหาคติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษสั้นๆ ที่มักใช้ทั่วไปในชีวิตประจำวันลองศึกษาคติประจำใจด้านล่างนี้
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| The only way to do great work is to love what you do. | วิธีเดียวที่จะทำงานในฝันของคุณได้คือการรักในสิ่งที่คุณทำ |
| Success is not final, failure is not fatal: It is the courage to continue that counts. | ความสำเร็จไม่ใช่จุดสิ้นสุด ความล้มเหลวไม่ใช่ความตาย: สิ่งที่สำคัญคือความกล้าที่จะดำเนินต่อไป |
| In the middle of every difficulty lies opportunity. | ท่ามกลางความยากลำบากทุกอย่าง มีโอกาสซ่อนอยู่ |
| The secret to getting ahead is getting started. | เคล็ดลับเพื่อจะก้าวหน้าต่อไปคือต้องเริ่มต้น |
| The future depends on what you do today. | อนาคตขึ้นอยู่กับสิ่งที่คุณทำในวันนี้ |
| Don’t watch the clock; do what it does. Keep going. | อย่ามองแต่นาฬิกาจงทำเหมือนที่มันทำ คือเดินหน้าต่อไป |
| Believe you can and you’re halfway there. | เชื่อว่าตัวเองทำได้ และตัวเองก็มาครึ่งทางแล้ว |
| The biggest risk is not taking any risk. | อันตรายที่ใหญ่ที่สุดคือการไม่กล้าที่จะเสี่ยง |
| Happiness is not something ready-made. It comes from your own actions. | ความสุขไม่ได้เกิดขึ้นเอง มันมาจากการกระทำของคุณ |
| If you want to achieve greatness, stop asking for permission. | ถ้าคุณต้องการบรรลุความยิ่งใหญ่ อย่ามัวแต่ขออนุญาตจากใคร |
| The best way to predict the future is to create it. | วิธีที่ดีที่สุดในการทำนายอนาคตคือการสร้างมันขึ้นมา |
| The only limit to our realization of tomorrow will be our doubts of today. | อุปสรรคเพียงอย่างเดียวต่อความเป็นจริงของเราในวันพรุ่งนี้คือความสงสัยของวันนี้ |
| Don’t cry because it’s over, smile because it happened. ― Dr. Seuss | อย่าร้องไห้เพราะสิ่งนั้นจบลงแต่จงยิ้มเพราะสิ่งนั้นเกิดขึ้นต่างหาก |
| You only live once, but if you do it right, once is enough. ― Mae West | คุณใช้ชีวิตได้เพียงแค่ครั้งเดียว แต่ถ้าใช้อย่างถูกต้อง ครั้งเดียวก็เพียงพอ |
| Life is 10% what happens to us and 90% how we react to it. – Dennis P. Kimbro. | ชีวิตคือ 10% ของสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นกับเรา ในขณะที่อีก 90% คือวิธีการที่เรารับมือกับมัน |
| Good friends, good books, and a sleepy conscience: this is the ideal life. ― Mark Twain | เพื่อนที่ดี หนังสือที่ดี และจิตใจที่สงบ นี่คือชีวิตในอุดมคติ |
| Sometimes the questions are complicated and the answers are simple. ― Dr. Seuss | บางครั้งคำถามอาจซับซ้อน แต่คำตอบกลับง่ายดาย |
| I am thankful to all who said no to me. It is because of them that I’m doing it myself. — Albert Einstein | ฉันขอบคุณทุกคนที่ปฏิเสธฉัน เพราะพวกเขา ฉันจึงลงมือทำด้วยตัวเอง |
| Life is either a daring adventure or nothing at all. | ถ้าชีวิตไม่ใช่การผจญภัย มันก็เป็นเพียงความว่างเปล่าเท่านั้น |
| In the end, we only regret the chances we didn’t take. | สุดท้ายแล้ว เรามักจะเสียดายกับโอกาสที่เราไม่ได้ใช้ |
| Where there is a will, there is a way. | ที่ไหนมีความตั้งใจ ที่นั่นย่อมมีหนทางเสมอ |
| Genius is one percent inspiration and ninety-nine percent perspiration. | อัจฉริยะเกิดจาก แรงบันดาลใจ 1 % และอีก 99 % เกิดจากหยาดเหงื่อที่ลงมือทำ |
| Strive not to be a success, but rather to be of value. – Albert Einstein | อย่าพยายามสร้างแต่ความสำเร็จ แต่จงสร้างคุณค่าจะเป็นเรื่องที่ดีกว่า |
| No one can make you feel inferior without your consent. – Eleanor Roosevelt | ไม่มีใครทำให้คุณรู้สึกต่ำต้อยได้หากไม่ได้รับความยินยอมจากคุณ |

เรียนรู้ คําอวยพรปีใหม่ ภาษาอังกฤษ เพื่อส่งความสุขและความหมายดี ๆ ให้คนสำคัญในช่วงปีใหม่
คติประจําใจในภาษาอังกฤษตลกๆ
ด้านล่างนี้คือตารางคติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษตลกๆ
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| I’m going to stand outside. So if anyone asks, I am outstanding. | ฉันจะยืนข้างนอก เพราะเวลาใครถามฉันก็จะเป็นคนที่โดดเด่นที่สุด |
| Do not argue with an idiot. He will drag you down to his level and beat you with experience. | อย่าไปเถียงกับคนโง่ เพราะเขาจะลากคุณลงไปในระดับเดียวกับเขาและเอาชนะคุณด้วยประสบการณ์ของเขาเอง |
| Death is life’s way of telling you you’ve been fired. | ความตายเป็นสัญญาณแห่งชีวิตว่าคุณถูกไล่ออก |
| The future depends on your dreams. So don’t hesitate to sleep. | อนาคตขึ้นอยู่กับความฝันของคุณ เพราะฉะนั้นอย่าลังเลอีกต่อไป ไปนอนต่อกันเถอะ |
| Don’t get older. I level up. | ฉันไม่ได้แก่ขึ้น ฉันกำลังพัฒนาขั้น |
| I’m not clumsy. The floor just hates me, the table and chair are bullies, and the walls get in my way. | ฉันไม่ได้ซุ่มซ่ามนะ พื้นเกลียดฉัน โต๊ะกับเก้าอี้ก็ชอบแกล้ง ส่วนกำแพงก็มาขวางทางตลอด |
| I’m not procrastinating. I’m doing intensive research on the art of doing nothing. | ฉันไม่ได้ผัดวันประกันพรุ่งนะ ฉันกำลังทำวิจัยเชิงลึกเกี่ยวกับศิลปะแห่งการไม่ทำอะไรเลยต่างหาก |
| I may not be perfect, but at least I’m not fake. | ฉันอาจจะไม่สมบูรณ์แบบ แต่อย่างน้อยฉันก็ไม่เสแสร้ง |
| I don’t need hairstylists, my pillow gives me a new hairstyle every morning. | ฉันไม่ต้องการช่างทำผมเพราะทุกเช้าหมอนก็จะเปลี่ยนทรงผมใหม่ให้ฉันเอง |
| Behind every successful person is a substantial amount of coffee. | เบื้องหลังความสำเร็จของทุกคน คือปริมาณกาแฟที่มากมาย |
| I am on a seafood diet. I see food, and I eat it. | ฉันกำลังอยู่ในโปรแกรมไดเอทแบบ see food เห็นอาหารเมื่อไหร่ก็กินเมื่อนั้น |
| Age is of no importance unless you’re a cheese. | อายุไม่สำคัญ เว้นแต่คุณจะเป็นชีสชิ้นหนึ่ง |
| If you think nobody cares if you’re alive, try missing a couple of car payments. | ถ้าคุณคิดว่าไม่มีใครสนใจว่าคุณยังมีชีวิตอยู่ ลองไม่จ่ายค่าผ่อนรถสักสองงวดดูสิ |
| Life is short. Smile while you still have teeth. | ชีวิตนั้นสั้น ยิ้มในขณะที่ยังมีฟันอยู่ |
| The best way to teach your kids about taxes is by eating 30 percent of their ice cream. | วิธีที่ดีที่สุดในการสอนลูกๆ เกี่ยวกับเรื่องภาษี คือการกินไอศกรีมของพวกเขาไป 30% |
| Always borrow money from a pessimist. He won’t expect it back. | ยืมเงินจากคนที่มองโลกในแง่ร้ายเสมอ เขาจะไม่คาดหวังว่าคุณจะคืนมัน |
| I wish I were a unicorn so I could stab idiots with my head. | ฉันอยากเป็นยูนิคอร์นเพื่อที่จะได้แทงคนโง่ด้วยหัวของฉัน |
| Whoever said, “It’s not whether you win or lose that counts,” probably lost. | ใครก็ตามที่พูดว่า “ชนะหรือแพ้ไม่สำคัญ” แสดงว่าคนๆนั้นขี้แพ้อย่างแน่นอน |
| I wake up every morning at nine and grab the morning paper. Then I look at the obituary page. If my name is not on it, I get up. — Benjamin Franklin | ฉันตื่นนอนตอนเก้าโมงเช้าและหยิบหนังสือพิมพ์ขึ้นมาอ่าน จากนั้นฉันก็ดูข่าวเกี่ยวกับคนตาย ถ้าไม่มีชื่อฉัน ฉันก็จะยอมลุกขึ้น |
| People often say that motivation doesn’t last. Well, neither does bathing – that’s why we recommend it daily. — Zig Ziglar | คนมักจะพูดว่าแรงจูงใจไม่คงอยู่ตลอดไป ก็เหมือนกับการอาบน้ำ – นั่นคือเหตุผลที่เราแนะนำให้อาบน้ำทุกวัน |

คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษดีๆเกี่ยวกับความพยายาม
ความพยายามไม่เคยทำร้ายใคร หากเราทำอย่างจริงจังและเต็มที่ ต่อไปนี้เป็นคติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษดีๆเกี่ยวกับความพยายามที่จะเป็นประโยชน์กับคุณ
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| The purpose of life is not to be happy. It is to be useful, to be honorable, to be compassionate, to have it make some difference that you have lived and lived well. | จุดประสงค์ของชีวิตไม่ใช่เพื่อให้มีความสุข แต่เพื่อให้มีประโยชน์ มีความเคารพ มีความเห็นอกเห็นใจ และสร้างความแตกต่างระหว่างการใช้ชีวิตและการดำเนินชีวิตได้เป็นอย่างดี |
| Life isn’t about waiting for the storm to pass. It’s about learning to dance in the rain. | ชีวิตไม่ใช่การนั่งรอพายุผ่านไป มันเกี่ยวกับการเรียนรู้วิธีเต้นรำท่ามกลางสายฝนต่างหาก |
| Life is a journey that must be traveled no matter how bad the roads and accommodations. | ชีวิตคือการเดินทางไกลที่คุณต้องทำไม่ว่าสถานการณ์จะเลวร้ายแค่ไหนก็ตาม |
| In three words I can sum up everything I’ve learned about life: it goes on. | ฉันสามารถสรุปทุกสิ่งที่ฉันได้เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับชีวิตมาเพียงสามคำคือทำต่อไป |
| Life is too short to be anything but happy. | ชีวิตนั้นสั้นเกินกว่าจะเป็นอย่างอื่นได้นอกจากความสุข |
| Life is really simple, but we insist on making it complicated. | ชีวิตมันง่ายมาก แต่เรากลับทำให้มันซับซ้อน |
| The good life is one inspired by love and guided by knowledge. | ชีวิตที่ดีคือชีวิตที่ได้รับแรงบันดาลใจจากความรักและได้รับการชี้นำด้วยความรู้ |
| Live each day as if it were your last. | ใช้ชีวิตในแต่ละวันราวกับว่ามันจะเป็นวันสุดท้ายของคุณ |
| Success is not the key to happiness. Happiness is the key to success. If you love what you are doing, you will be successful. | ความสำเร็จไม่ใช่กุญแจสู่ความสุข แต่ความสุขคือกุญแจสู่ความสำเร็จ คุณจะประสบความสำเร็จได้ ถ้าคุณรักในสิ่งที่คุณทำ |
| Life is a journey, not a destination. | ชีวิตคือการเดินทางไม่ใช่จุดหมายปลายทาง |
| I love those who can smile in trouble. – Leonardo da Vinci | ฉันชอบคนที่หัวเราะได้แม้ในช่วงเวลาที่ยากลำบาก |
| Believe that life is worth living and your belief will help create the fact. – William James | เชื่อว่าชีวิตนี้คุ้มค่าที่จะมีชีวิตอยู่ และความเชื่อนั้นจะกลายเป็นความจริง |
| The trick in life is learning how to deal with it. — Helen Mirren | เคล็ดลับในชีวิตคือการเรียนรู้วิธีรับมือกับมัน |
| Life always offers you a second chance. It’s called tomorrow. – Dylan Thomas | ชีวิตมักจะให้โอกาสครั้งที่สองกับคุณเสมอมันเรียกว่าวันพรุ่งนี้ |
| I can accept failure, everyone fails at something. But I can’t accept not trying. – Michael Jordan | ฉันยอมรับความล้มเหลวได้ ทุกคนล้มเหลวในบางครั้งแต่ฉันรับไม่ได้กับการไม่พยายาม |
| If you want to live a happy life, tie it to a goal, not to people or things. — Albert Einstein | หากคุณต้องการมีชีวิตที่มีความสุข จงผูกชีวิตไว้กับเป้าหมาย ไม่ใช่กับคนหรือสิ่งของ |
| It’s OK to not be OK, as long as you don’t stay that way. — Anonymous | ไม่โอเคบ้างก็ไม่เป็นไรตราบใดที่คุณไม่ได้อยู่ในสภาพนั้นตลอดไป |
| Life is like riding a bicycle. To keep your balance, you must keep moving. ― Albert Einstein | ชีวิตก็เหมือนการปั่นจักรยาน เพื่อรักษาสมดุล คุณต้องเคลื่อนไหวต่อไป |
| Believe you can and you’re halfway there. — T. Roosevelt | แค่เชื่อว่าคุณทำได้ คุณก็จะไปถึงครึ่งทางแล้ว |
| Everything you can imagine is real. ― Pablo Picasso | ทุกสิ่งที่คุณจินตนาการนั้นมีจริง |
| When life changes to be harder, change yourself to be stronger. – Edwin Mamerto | เมื่อชีวิตเปลี่ยนไปและยากขึ้น จงเปลี่ยนตัวเองให้แข็งแกร่งขึ้น |
>>> Read more: 100+ คําให้กําลังใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ สั้นๆ ช่วยให้คุณรู้สึกมองโลกในแง่ดีมากขึ้น
คติประจำใจ ภาษาอังกฤษเกี่ยวกับความรัก

บางครั้งเราหลงทางและไม่เชื่อในความรัก ต่อไปนี้เป็นคติประจำใจ ภาษาอังกฤษดีๆ หรือคติพจน์ภาษาอังกฤษเกี่ยวกับความรัก ที่คุณอาจสนใจ
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| Love is not about how many days, months, or years you have been together. It’s all about how much you love each other every single day. | ความรักไม่ได้วัดจากจำนวนวัน เดือน หรือปีที่คุณอยู่ด้วยกัน แต่มันวัดจากความรักที่คุณมีให้กันในทุกๆ วัน |
| The best and most beautiful things in the world cannot be seen or even touched – they must be felt with the heart. | สิ่งที่ดีที่สุดและสวยงามที่สุดในโลกไม่สามารถมองเห็นหรือสัมผัสได้ – มันต้องรู้สึกด้วยหัวใจ |
| Love is when the other person’s happiness is more important than your own. | ความรักคือการที่ความสุขของอีกฝ่ายสำคัญกว่าความสุขของตัวเอง |
| To love and be loved is to feel the sun from both sides. | การรักและได้รับความรักคือการรู้สึกถึงแสงแดดจากทั้งสองด้าน |
| The best love is the kind that awakens the soul and makes us reach for more, that plants a fire in our hearts and brings peace to our minds. | ความรักที่ดีที่สุดคือความรักที่ปลุกจิตวิญญาณและกระตุ้นให้เราบรรลุเป้าหมายมากขึ้น ความรักที่จุดไฟในใจและนำสันติสุขมาสู่จิตใจ |
| A successful marriage requires falling in love many times, always with the same person. | การแต่งงานที่ประสบความสำเร็จต้องอาศัยการตกหลุมรักคนคนเดิมซ้ำแล้วซ้ำเล่า |
| The best love is the one that makes you a better person, without changing you into someone other than yourself. | ความรักที่แท้จริงคือสิ่งที่ทำให้คุณเป็นคนที่ดีขึ้น โดยไม่เปลี่ยนแปลงตัวตนที่แท้จริงของคุณ |
| Love is the bridge between two hearts. | ความรักคือสะพานเชื่อมหัวใจสองดวง |
| Love isn’t something you find. Love is something that finds you. | ความรักไม่ใช่สิ่งที่คุณพบ ความรักคือสิ่งที่ตามหาคุณ |
| How can you love another if you don’t love yourself? | จะรักคนอื่นได้ยังไงในเมื่อไม่รักตัวเอง? |
| Immature love says: ‘I love you because I need you.’ Mature love says ‘I need you because I love you.’ | ความรักแบบเด็กๆพูดว่า ‘ผมรักคุณเพราะผมต้องการคุณ’ ส่วนความแบบผู้ใหญ่พูดว่า ‘ผมต้องการคุณเพราะผมรักคุณ |
| A man falls in love through his eyes, a woman through her ears. | ผู้หญิงรักด้วยหู ผู้ชายรักด้วยตา |
| Hate has a reason for everything but love is unreasonable. | ความเกลียดมีเหตุผลสำหรับทุกสิ่ง แต่ความรักไม่มีเหตุผล |
| Life is the flower for which love is the honey. | ชีวิตคือดอกไม้ส่วนความรักคือน้ำผึ้ง |
| Love is like a beautiful flower that I may not touch, but whose fragrance makes the garden a place of delight just the same. | ความรักก็เหมือนดอกไม้ที่สวยงามที่ฉันอาจแตะต้องไม่ได้ แต่กลิ่นหอมหวานทำให้สวนทั้งสวนเป็นสถานที่ที่สวยงาม |
| To the world, you may be one person, but to one person you may be the world. | คุณอาจเป็นเพียงคนคนหนึ่งในโลกนี้ แต่สำหรับบางคน คุณอาจเป็นโลกทั้งใบของเขา |
| It only takes a second to say I love you, but it will take a lifetime to show you how much. | ใช้เวลาเพียงไม่กี่วินาทีในการพูดว่า “ฉันรักคุณ” แต่ต้องใช้เวลาทั้งชีวิตในการพิสูจน์ |
| A great lover is not one who loves many, but one who loves one woman for life. | ความรักที่ยิ่งใหญ่ไม่ใช่การมีคนให้รักมากมาย แต่รักคนเดียวไปตลอดชีวิต |
| Don’t stop giving love even if you don’t receive it. Smile and have patience. | อย่ายอมแพ้กับความรัก แม้ว่าคุณจะยังไม่ได้รับมันก็ตาม ยิ้มและอดทน |
| You know when you love someone when you want them to be happy even if their happiness means that you’re not part of it. | คุณตระหนักว่าคุณรักใครสักคนเมื่อคุณอวยพรให้พวกเขามีความสุข แม้ว่าคุณจะไม่ได้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความสุขของพวกเขาก็ตาม |
| Love is the crowning grace of humanity, the holiest right of the soul, and the golden link which binds us. | ความรักคือพระคุณอันยิ่งใหญ่ที่สุดของมนุษยชาติ สิทธิอันศักดิ์สิทธิ์ที่สุดของจิตวิญญาณ และเป็นด้ายสีทองที่รวมเราเป็นหนึ่งเดียวกัน |
| Love is when you give him a piece of your soul that you never knew was missing. | ความรักคือการที่คุณมอบชิ้นส่วนจิตวิญญาณของคุณให้กับเขาโดยที่คุณไม่เคยรู้เลยว่าขาดหายไป |
| Sometimes the heart sees what is invisible to the eye. | บางครั้งใจก็รับรู้ถึงสิ่งที่ไม่สามารถมองเห็นได้ด้วยตาเปล่า |
| Being deeply loved by someone gives you strength while loving someone deeply gives you courage. | การได้รับความรักอย่างลึกซึ้งจากใครสักคนจะทำให้คุณเข้มแข็ง ในขณะที่การรักใครสักคนอย่างลึกซึ้งจะทำให้คุณมีความกล้า |
| A flower cannot blossom without sunshine, and man cannot live without love. | ดอกไม้ไม่สามารถบานสะพรั่งได้หากไม่มีแสงแดด และผู้คนก็อยู่ไม่ได้หากปราศจากความรัก |
| To love and be loved is to feel the sun from both sides. | การรักและถูกรักคือการได้สัมผัสแสงแดดจากทั้งสองฝ่าย |
| Beauty is in the eyes of the beholder. | ความงามไม่ได้อยู่ที่แก้มสีชมพูของหญิงสาว แต่อยู่ในสายตาของคู่รัก |
| Love is not about how much you say ‘I love you’, but how much you prove that it’s true. | ความรักไม่ใช่ว่าคุณพูดว่า “ผมรักคุณ” กี่ครั้ง แต่อยู่ที่ว่าคุณพิสูจน์ได้กี่ครั้ง |
| The best thing to hold onto in life is each other. – Audrey Hepburn | สิ่งที่ดีที่สุดที่ควรยึดมั่นในชีวิตคือกันและกัน |
| Love doesn’t make the world go round. Love is what makes the ride worthwhile. – Franklin P. Jones | ความรักไม่ได้ทำให้โลกหมุนไปเรื่อยๆ ความรักคือสิ่งที่ทำให้การเดินทางมีค่า |
| To love and be loved is to feel the sun from both sides. – David Viscott | การรักและถูกรักคือการได้สัมผัสแสงแดดจากทั้งสองฝ่าย |
| Love is composed of a single soul inhabiting two bodies. – Aristotle | ความรักประกอบด้วยจิตวิญญาณเดียวที่อาศัยอยู่ในสองร่าง |
| We love because it’s the only true adventure. – Nikki Giovanni | เรารักเพราะมันคือการผจญภัยที่แท้จริงเพียงอย่างเดียว |
| Love is when you meet someone who tells you something new about yourself. – Andre Breton | ความรักคือการที่คุณพบกับใครสักคนที่สามารถบอกคุณถึงสิ่งใหม่ๆ เกี่ยวกับตัวคุณ |
>>> Read more: 90+ คําคมความรักภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมาย สั้นๆ และโรแมนติกที่สุด
คติประจำใจ ภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆ เกี่ยวกับมิตรภาพ

นอกจากครอบครัวแล้ว เพื่อนแท้จะช่วยให้เราเติบโต ปกป้อง และพัฒนาไปพร้อมกับเราในอนาคต ด้านล่างนี้คือคติประจำใจ ภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆ เกี่ยวกับมิตรภาพที่คุณควรอ่าน
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| A true friend is someone who is always there for you, even when the whole world walks away. | เพื่อนแท้คือคนที่อยู่เคียงข้างคุณเสมอ แม้ว่าโลกทั้งใบจะจากไปแล้วก็ตาม |
| A true friend is one who overlooks your failures and tolerates your success. | เพื่อนที่แท้จริงคือคนที่มองข้ามความล้มเหลวของคุณและอดทนต่อความสำเร็จของคุณ |
| A true friend is someone who is always there during the ups and downs of life. | เพื่อนแท้คือคนที่มีอยู่ในทุกแง่มุมของชีวิตของคุณ |
| Friendship is not about who you have known the longest, it’s about who came and never left your side. | มิตรภาพไม่ได้เกี่ยวกับคนที่คุณรู้จักมานานที่สุด แต่เกี่ยวกับผู้ที่ผ่านเข้ามาและไม่เคยทิ้งคุณไป |
| A friend is someone who knows all about you and still loves you. | เพื่อนที่ดีจะรู้ทุกอย่างเกี่ยวกับคุณแต่ก็ยังรักคุณ |
| A true friend is the one who walks in when others walk out. | เพื่อนแท้คือคนที่เดินเข้ามาเมื่อมีคนอื่นที่เดินออกไป |
| Friendship is the only cement that will hold the world together. | มิตรภาพคือกาวที่ยึดโลกไว้ด้วยกัน |
| A true friend is someone you can disagree with and still remain friends. | เพื่อนแท้คือคนที่คุณไม่เห็นด้วยแต่ยังคงเป็นเพื่อนกันได้ |
| Friendship is born when two people discover they have similar crazy minds. | มิตรภาพเกิดขึ้นเมื่อคนสองคนตระหนักว่าพวกเขามีความคิดที่บ้าคลั่งเหมือนกัน |
| Friends are the family you choose for yourself. | เพื่อนคือครอบครัวที่คุณเลือกเอง |
| A good friend knows all your best stories. A best friend has lived them with you. | เพื่อนที่ดีเป็นคนรู้เรื่องราวที่ดีที่สุดของคุณทั้งหมด ส่วนเพื่อนสนิทเป็นคนเคยผ่านเรื่องราวเหล่านั้นกับคุณ |
| Friendship is not a big thing, it’s a million little things. | มิตรภาพไม่ใช่เรื่องใหญ่ แต่มีสิ่งเล็กๆ น้อยๆ มากมาย |
| A true friend is someone who accepts your past, supports your present, and encourages your future. | เพื่อนแท้คือคนที่เข้าใจอดีตของคุณ เคียงข้างคุณในปัจจุบัน และสนับสนุนอนาคตของคุณ |
| A true friend is someone who can make you laugh even when you feel like crying. | เพื่อนแท้คือคนที่ทำให้คุณหัวเราะได้แม้ในเวลาที่คุณต้องการร้องไห้ |
| Friends show their love in times of trouble, not in happiness. | เพื่อนจะแสดงความรักในยามที่คุณเผชิญปัญหา ไม่ใช่ในยามที่คุณมีความสุข |
| Count your age by friends, not years Count your life by smiles, not tears. – John Lennon. | นับอายุของคุณด้วยจำนวนเพื่อน ไม่ใช่จำนวนปี นับชีวิตของคุณด้วยรอยยิ้ม ไม่ใช่น้ำตา |
| A friendship can weather most things and thrive in thin soil; but it needs a little mulch of letters and phone calls and small, silly presents every so often – just to save it from drying out completely. – Pam Brown | มิตรภาพสามารถทนทานต่อสิ่งต่างๆ ได้และเติบโตได้แม้ในดินที่ไม่ดี แต่ก็ต้องการความใส่ใจเล็กน้อย เช่น การเขียนจดหมาย โทรศัพท์ หรือของขวัญเล็กๆ น้อยๆ เป็นครั้งคราว เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้มันแห้งเหือดไปหมด |
| Friendship is the only cement that will ever hold the world together. – Woodrow Wilson | มิตรภาพคือซีเมนต์เพียงอย่างเดียวที่จะยึดโลกไว้ด้วยกัน |
| Friendship is the purest love. | มิตรภาพคือความรู้สึกที่บริสุทธิ์ที่สุด |
| Wishing to be friends is quick work, but friendship is a slow-ripening fruit. – Aristotle | ความปรารถนาที่จะเป็นเพื่อนนั้นเป็นเรื่องเร่งรีบ แต่มิตรภาพนั้นเป็นผลไม้ที่สุกอย่างช้าๆ |
| Friendship improves happiness, and abates misery, by doubling our joys and dividing our grief. – Marcus Tullius Cicero | มิตรภาพเพิ่มความสุขและลดความทุกข์ โดยเพิ่มความสุขเป็นสองเท่าและแบ่งปันความเศร้า |
| Friendship is like a glass ornament, once it is broken it can rarely be put back together exactly the same way. – Charles Kingsley | มิตรภาพก็เหมือนเครื่องประดับแก้ว เมื่อมันแตกแล้วมักจะไม่สามารถนำกลับมาประกอบได้เหมือนเดิม |
| True friendship is like sound health; the value of it is seldom known until it is lost. – Charles Caleb Colton | มิตรภาพที่แท้จริงก็เหมือนสุขภาพที่ดี มักจะไม่รู้คุณค่าจนกระทั่งสูญเสียมันไป |
| Friendship without self-interest is one of the rare and beautiful things in life. – James Francis Byrnes | มิตรภาพที่ไม่มีความสนใจในตัวเองเป็นหนึ่งในสิ่งที่หายากและสวยงามที่สุดในชีวิต |
| A snowball in the face is surely the perfect beginning to a lasting friendship. – Markus Zusak | หิมะที่โดนหน้าเป็นการเริ่มต้นที่สมบูรณ์แบบสำหรับมิตรภาพที่ยั่งยืน |
| Friends are people you can talk to without words when you have to. | เพื่อนคือคนที่คุณสามารถพูดคุยได้โดยไม่ต้องใช้คำพูด เมื่อจำเป็น |
| For the friendship of two, the patience of one is required. | สำหรับมิตรภาพของสองคน ความอดทนจากหนึ่งคนเป็นสิ่งที่จำเป็น |
| We are all travelers in the wilderness of the world, and the best we can find in our travels is an honest friend. – Robert L. Stevenson | เราทุกคนต่างเป็นนักเดินทางในป่าของโลก และสิ่งที่ดีที่สุดที่เราจะพบในการเดินทางคือเพื่อนที่ซื่อสัตย์ |
| When friendship is once rooted fast, it is a plant no storm can blast. | เมื่อมิตรภาพถูกปลูกฝังอย่างมั่นคงแล้ว มันก็จะเป็นต้นไม้ที่พายุใดๆ ก็ไม่สามารถทำลายได้ |
| Friendship is born at that moment when one person says to another, ‘What! You too? I thought I was the only one.’ – C.S. Lewis | มิตรภาพเกิดขึ้นในช่วงเวลาที่คนหนึ่งพูดกับอีกคนว่า ‘อะไรนะ! คุณด้วยเหรอ? ฉันนึกว่าฉันเป็นคนเดียว |
| A real friend is one who walks in when the rest of the world walks out. – Walter Winchell | เพื่อนที่แท้จริงคือคนที่เดินเข้ามาเมื่อคนอื่นๆ ในโลกเดินออกไป |
| Friendship is the only cement that will ever hold the world together. – Woodrow Wilson | มิตรภาพเป็นเพียงกาวเดียวที่สามารถยึดโลกไว้ด้วยกัน |
| A friend is someone who understands your past, believes in your future, and accepts you just the way you are. – Unknown | เพื่อนคือคนที่เข้าใจอดีตของคุณ เชื่อในอนาคตของคุณ และยอมรับคุณในสิ่งที่คุณเป็น |
| Good friends are like stars. You don’t always see them, but you know they’re always there. – Unknown | เพื่อนที่ดีก็เหมือนดวงดาว คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นพวกเขาเสมอไป แต่คุณรู้ว่าพวกเขาอยู่ที่นั่นเสมอ |
| Friendship is not about who you’ve known the longest. It’s about who walked into your life, said ‘I’m here for you,’ and proved it. – Unknown | มิตรภาพไม่ใช่เกี่ยวกับใครที่คุณรู้จักยาวนานที่สุด มิตรภาพมันเกี่ยวกับว่าใครเดินเข้ามาในชีวิตของคุณด้วยความจริงใจ |
| Friends are the family we choose for ourselves. – Edna Buchanan | เพื่อนคือครอบครัวที่เราเลือกเอง |
คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆเกี่ยวกับความพยายามและความแข็งแกร่ง

ความพยายามคือกุญแจสู่ความสำเร็จ ทุกที่ที่มีความพยายาม ความสำเร็จก็จะอยู่ที่นั่น ต่อไปนี้เป็นคติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆ เกี่ยวกับความพยายามความเข้มแข็งที่สามารถสร้างแรงบันดาลใจให้กับคุณได้
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| No pain, no gain. | ไม่มีความเจ็บปวดก็ไม่มีผลลัพธ์ |
| The harder you work, the luckier you get. | ยิ่งทำงานหนักเท่าไหร่ คุณก็ยิ่งโชคดีเท่านั้น |
| It does not matter how slowly you go as long as you do not stop. | ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณจะเดินช้าแค่ไหน ขอแค่คุณอย่าหยุดเดินก็แล้วกัน |
| Strength doesn’t come from what you can do. It comes from overcoming the things you once thought you couldn’t. | ความเข้มแข็งไม่ได้มาจากสิ่งที่คุณทำได้ มันมาจากการเอาชนะสิ่งที่คุณคิดว่าเป็นไปไม่ได้ต่างหาก |
| Believe in yourself and all that you are. Know that there is something inside you that is greater than any obstacle. | เชื่อในตัวเองและทุกสิ่งที่คุณเป็น รู้ไว้ว่ามีบางสิ่งในตัวคุณที่ยิ่งใหญ่กว่าอุปสรรคใดๆ |
| Don’t be afraid to give up the good and go for the great. | ในการแสวงหาสิ่งที่ยิ่งใหญ่ อย่ากลัวที่จะยอมแพ้ |
| The difference between a successful person and others is not a lack of strength, not a lack of knowledge, but will. | ความแตกต่างระหว่างคนที่ประสบความสำเร็จกับคนอื่นๆ ไม่ใช่การขาดความเข้มแข็งหรือความรู้ แต่เป็นการขาดความตั้งใจ |
| Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. | ความสำเร็จคือผลรวมของความพยายามเล็กๆ ที่ทำซ้ำๆ ทุกวัน |
| The only way to do great work is to love what you do. | วิธีเดียวที่จะทำงานที่ยอดเยี่ยมได้คือรักในสิ่งที่คุณทำ |
| Never give up on a dream just because of the time it will take. The time will pass anyway. | อย่าละทิ้งความฝันเพียงเพราะต้องใช้เวลาเพื่อทำให้สำเร็จ ยังไงแล้ว เวลาก็จะผ่านไป |
| The only place where success comes before work is in the dictionary. | ที่เดียวที่ความสำเร็จมาก่อนการลงมือทำ คืออยู่ในพจนานุกรมเท่านั้น |
| You have the power to change your life. Don’t wait for it to happen. Take action now. | คุณมีพลังที่จะเปลี่ยนแปลงชีวิตของคุณได้อย่างแน่นอน อย่ารอช้าลงมือทำเลย |
| The harder you work for something, the greater you’ll feel when you achieve it. | ยิ่งคุณทำงานหนักเพื่อสิ่งใดสิ่งหนึ่ง คุณจะรู้สึกยิ่งใหญ่ขึ้นเมื่อบรรลุเป้าหมายนั้น |
| Believe in yourself and all that you are. Know there is something greater inside you than any obstacle. | เชื่อในตัวเองและทุกสิ่งที่คุณเป็น รู้ไว้ว่ามีบางสิ่งที่ยิ่งใหญ่กว่าทุกอุปสรรคในตัวคุณ |
| Don’t watch the clock; do what it does. Keep going. | อย่ามองแต่นาฬิกา จงทำเหมือนมันทำคือเดินหน้าต่อไป |
| Strength does not come from winning. Your struggles develop your strengths. | ความเข้มแข็งไม่ได้มาจากชัยชนะ การต่อสู้ของคุณต่างหากทำให้ความแข็งแกร่งของคุณเพิ่มขึ้น |
| You are stronger than you think. | คุณแข็งแกร่งกว่าที่คุณคิด |
| Success is measured not by what you accomplish but by the opposition encountered, and courage against odds. | ความสำเร็จไม่ได้วัดจากสิ่งที่คุณทำได้ แต่จะวัดจากอุปสรรคที่เผชิญ และความกล้าหาญที่ต่อสู้กับมัน |
| A river cuts through rock, not because of power, but persistence. | แม่น้ำกัดกร่อนหินไม่ได้เพราะพลัง แต่เพราะความต่อเนื่อง |
| Pain is temporary. Quitting lasts forever. | ความเจ็บปวดเป็นเพียงชั่วคราว การยอมแพ้จะคงอยู่ตลอดไป |
| Dream big and dare to fail. | ฝันให้ใหญ่และกล้าที่จะล้มเหลว |
| Strength grows in moments you think you can’t go on but keep going. | ความแข็งแกร่งเกิดขึ้นในช่วงเวลาที่คุณคิดว่าคุณไปต่อไม่ได้ แต่คุณยังคงก้าวต่อไป |
| Success is what happens after surviving all mistakes. | ความสำเร็จคือสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นหลังจากรอดพ้นจากความผิดพลาดทั้งหมด |
| Life’s difficulties are meant to make us better, not bitter. | ความยากลำบากในชีวิตมีไว้เพื่อทำให้เราดีขึ้น ไม่ใช่ขมขื่น |
| The struggle today develops tomorrow’s strength. | การต่อสู้ที่คุณกำลังประสบในวันนี้คือการพัฒนาความแข็งแกร่งที่คุณต้องการสำหรับวันพรุ่งนี้ |
| Stay strong, stand up, and have a voice. | จงเข้มแข็ง ยืนหยัด และเชื่อในเสียงของตัวเอง |
| What lies behind us and before us are tiny matters compared to what lies within us. | สิ่งที่ผ่านไปแล้วและสิ่งที่จะเกิดขึ้นนั้นเป็นเรื่องเล็กๆ น้อยๆ เมื่อเทียบกับสิ่งที่อยู่ภายในตัวเรา |
| Success is not for the lazy. | ความสำเร็จไม่ได้มีไว้สำหรับคนขี้เกียจ |
| Never let failures define you. Let them teach you. | อย่าให้ความล้มเหลวกำหนดตัวคุณ ให้มันเป็นบทเรียนสอนคุณ |
| You were given this life because you are strong enough to live it. | คุณได้รับชีวิตนี้เพราะคุณเข้มแข็งพอที่จะใช้ชีวิตนี้ |
| Your time is limited, don’t waste it living someone else’s life. | เวลาของคุณมีจำกัด อย่าเสียเวลาไปใช้ชีวิตแบบคนอื่น |
| The only limit to our realization of tomorrow is our doubts of today. – Franklin D. Roosevelt | ข้อจำกัดเพียงอย่างเดียวในการบรรลุสิ่งที่เราหวังในวันพรุ่งนี้ คือความสงสัยในวันนี้ |
คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษเกี่ยวกับครอบครัว

ครอบครัวคือที่ของเรา ตารางด้านล่างนี้คือคติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษดีๆ เกี่ยวกับครอบครัวที่คุณสามารถเรียนรู้ได้
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| Family is not an important thing. It’s everything. – Michael J. Fox | ครอบครัวไม่ใช่สิ่งสำคัญ มันคือทุกสิ่ง |
| The love of a family is life’s greatest blessing. – Unknown | ความรักของครอบครัวเป็นพรที่ยิ่งใหญ่ที่สุดของชีวิต |
| In family life, love is the oil that eases friction. – Friedrich Nietzsche | ในชีวิตครอบครัว ความรักคือน้ำมันที่บรรเทาความขัดแย้งทั้งหมด |
| Family means no one gets left behind or forgotten. – David Ogden Stiers | ครอบครัวหมายถึงไม่มีใครถูกทิ้งไว้ข้างหลังหรือถูกลืม |
| To us, family means putting your arms around each other and being there. – Barbara Bush | สำหรับเรา ครอบครัวหมายถึงการโอบกอดกันและอยู่เคียงข้างกันเสมอ |
| Families are like branches on a tree. We grow in different directions, yet our roots remain as one. – Unknown | ครอบครัวก็เหมือนกิ่งก้านใบบนต้นไม้ เราเติบโตไปในทิศทางที่ต่างกัน แต่รากของเรายังคงเป็นหนึ่งเดียว |
>>> Read more: คำคมเกี่ยวกับครอบครัวในภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดี ๆ ตลก และน่ารักมากกว่า 150 คำ
คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆของคนชื่อดัง
คติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆ ของคนชื่อดัง เช่น: วิทยากร นักลงทุน นักดนตรี ฯลฯ สามารถเรียนรู้ได้ในตารางต่อไปนี้
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| The only impossible journey is the one you never begin. – Tony Robbins, motivational speaker | การเดินทางที่เป็นไปไม่ได้คือการเดินทางที่คุณไม่เคยเริ่มต้น |
| Be yourself; everyone else is already taken. – Oscar Wilde, writer | จงเป็นตัวของตัวเอง เพราะทุกคนที่เหลือก็เป็นของตัวเองแล้ว |
| To live is the rarest thing in the world. Most people exist, that is all. – Oscar Wilde, writer | การใช้ชีวิตอย่างแท้จริงเป็นสิ่งที่หายากที่สุดในโลก คนส่วนใหญ่ก็มีอยู่แค่นั้นเอง |
| I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that won’t work. – Thomas Edison, inventor | ฉันไม่ได้ล้มเหลว ฉันแค่ค้นพบ 10,000 วิธีที่ไม่ได้ผล |
| In three words I can sum up everything I’ve learned about life: it goes on. – Robert Frost, poet | มีสามคำที่ฉันสามารถสรุปสิ่งที่ฉันเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับชีวิตได้ทั้งหมดคือ ชีวิตยังคงดำเนินต่อไป |
| Art is the lie that enables us to realize the truth. – Pablo Picasso, painter | ศิลปะคือลวงตาที่ทำให้เราสามารถตระหนักถึงความจริง |
| Life is what happens when you’re busy making other plans. – John Lennon, musician | ชีวิตคือสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นเมื่อคุณยุ่งอยู่กับการวางแผนอย่างอื่น |

คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษเกี่ยวกับรอยยิ้ม
คติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษเกี่ยวกับการยิ้มที่สร้างแรงบันดาลใจและมีพลัง สรุปได้ในตารางดังต่อไปนี้
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| A warm smile is the universal language of kindness. – William Arthur Ward | รอยยิ้มอันอบอุ่นเป็นภาษาสากลแห่งความเมตตา |
| Life is short. Smile while you still have teeth. – Unknown | ชีวิตนั้นสั้น ยิ้มในขณะที่ยังมีฟันอยู่ |
| Smile, it is the key that fits the lock of everybody’s heart. – Anthony J. D’Angelo | ยิ้ม นั่นคือกุญแจที่ล็อคหัวใจของทุกคน |
| A smile is a curve that sets everything straight. – Phyllis Diller | รอยยิ้มคือเส้นโค้งที่ทำให้ทุกอย่างตรง |
| Smile at strangers and you just might change a life. – Steve Maraboli | ยิ้มให้กับคนแปลกหน้า และคุณอาจจะเปลี่ยนแปลงชีวิตของใครบางคนได้ |
| Wear a smile and have friends; wear a scowl and have wrinkles. – George Eliot | จงยิ้มให้กับเพื่อน หากหน้าบึ้งระวังมีริ้วรอยนะ |
| Smile, it’s free therapy. – Douglas Horton | ยิ้มเถอะ มันคือการบำบัดที่ได้มาฟรีๆ |

คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆ เกี่ยวกับความขอบคุณ
คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายดีๆเกี่ยวกับความขอบคุณที่คุณสามารถเรียนรู้ได้จากด้านล่างนี้
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| Gratitude turns what we have into enough. – Anonymous | ความกตัญญูเปลี่ยนสิ่งที่เรามีให้เพียงพอ |
| Gratitude is not only the greatest of virtues but the parent of all others. – Cicero | ความกตัญญูกตเวทีไม่เพียงแต่เป็นคุณธรรมที่ยิ่งใหญ่ที่สุดเท่านั้น แต่ยังเป็นแหล่งที่มาของคุณธรรมอื่นๆ ทั้งหมดด้วย |
| The more grateful I am, the more beauty I see. – Mary Davis | ยิ่งฉันรู้สึกขอบคุณมากเท่าไหร่ ฉันก็ยิ่งเห็นความสวยงามมากขึ้นเท่านั้น |
| Gratitude can transform common days into thanksgivings, turn routine jobs into joy, and change ordinary opportunities into blessings. – William Arthur Ward | ความกตัญญูสามารถเปลี่ยนวันธรรมดาให้เป็นวันขอบคุณพระเจ้า งานประจำวันให้เป็นความสุข และโอกาสธรรมดาๆ ให้เป็นพร |
| Gratitude is the healthiest of all human emotions. The more you express gratitude for what you have, the more likely you will have even more to express gratitude for. – Zig Ziglar | ความกตัญญูกตเวทีเป็นอารมณ์ที่ดีต่อสุขภาพของมนุษย์ ยิ่งคุณแสดงความขอบคุณต่อสิ่งที่คุณมีมากเท่าไร คุณก็จะยิ่งมีสิ่งที่ต้องแสดงความขอบคุณมากขึ้นเท่านั้น |
| Silent gratitude isn’t very much to anyone. – Gertrude Stein | ความขอบคุณที่เงียบสงบไม่ใช่สิ่งที่มีค่ามากนักสำหรับใครบางคน |
| Gratitude is the fairest blossom that springs from the soul. – Henry Ward Beecher | ความขอบคุณคือดอกไม้ที่สวยงามที่สุดที่เบ่งบานจากจิตวิญญาณ |

คติประจำใจในภาษอังกฤษอันโด่งดังเกี่ยวกับความสำเร็จ
ด้านล่างนี้คือตารางคติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษอันโด่งดังเกี่ยวกับความสำเร็จพร้อมคำแปล
| คติประจำใจ | แปล |
| Success is not the key to happiness. Happiness is the key to success. If you love what you are doing, you will be successful. – Albert Schweitzer | ความสำเร็จไม่ใช่กุญแจสู่ความสุข ความสุขคือกุญแจสู่ความสำเร็จ ถ้าคุณรักสิ่งที่คุณทำ คุณจะประสบความสำเร็จ |
| Success is not how high you have climbed, but how you make a positive difference to the world. – Roy T. Bennett | ความสำเร็จไม่ได้ขึ้นอยู่กับว่าคุณปีนขึ้นไปได้สูงแค่ไหน แต่อยู่ที่ว่าคุณสร้างความแตกต่างเชิงบวกได้มากเพียงใดในโลก |
| Success is not in what you have, but who you are. – Bo Bennett | ความสำเร็จไม่ได้อยู่ที่สิ่งที่คุณมี แต่อยู่ที่สิ่งที่คุณเป็น |
| The road to success and the road to failure are almost exactly the same. – Colin R. Davis | เส้นทางสู่ความสำเร็จและเส้นทางสู่ความล้มเหลวแทบจะเหมือนกันทุกประการ |
| Success is stumbling from failure to failure with no loss of enthusiasm. – Winston Churchill | ความสำเร็จคือการสะดุดจากความล้มเหลวไปยังความล้มเหลวโดยไม่สูญเสียความพยายาม |
| Success is not final; failure is not fatal: It is the courage to continue that counts. – Winston Churchill | ความสำเร็จไม่ใช่จุดสิ้นสุด ความล้มเหลวไม่ใช่เรื่องที่ทำให้ถึงตาย สิ่งที่สำคัญคือความกล้าที่จะเดินหน้าต่อไป |

วิธีเรียนคติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษ
มี 3 วิธีในการเรียนคติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษอย่างรวดเร็วและง่ายดาย
- เริ่มต้นด้วยคติประจำใจที่ง่ายๆ: เริ่มต้นด้วยคติประจำใจง่ายๆ เข้าใจง่าย ผู้เรียนสามารถค้นหาคติประจำใจง่ายๆ ได้ในหนังสือเรียน เว็บไซต์ หรือแอปพลิเคชันการเรียนรู้ภาษาอังกฤษ
- เรียนคำศัพท์และโครงสร้างประโยค: เมื่อผู้เรียนเข้าใจเนื้อหาของคติประจำใจแล้ว ให้เริ่มเรียนรู้คำและโครงสร้างประโยคของคติประจำใจนั้น ช่วยพัฒนาคำศัพท์และความสามารถในการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษของคุณ
- ฝึกการใช้คติประจำใจ: หลังจากที่คุณเข้าใจเนื้อหาและเรียนรู้คำศัพท์และโครงสร้างประโยคของคติประจำใจแล้ว ให้เริ่มฝึกใช้คติประจำใจนั้น ใช้ในการเขียน การพูด หรือการสนทนาในชีวิตประจำวัน การฝึกใช้คติประจำใจจะช่วยให้คุณจำคติประจำใจได้นานขึ้น
สาเหตุที่ควรอ่านคติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษ
มีเหตุผลหลายประการที่ผู้เรียนควรอ่านคติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษ ต่อไปนี้คือสาเหตุหลักบางประการ
- พัฒนาคำศัพท์และความสามารถในการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษ: โครงสร้างประโยคที่หลากหลาย การอ่านคติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษช่วยให้คุณเรียนรู้คำศัพท์และโครงสร้างประโยคใหม่ๆ พัฒนาคำศัพท์และความสามารถในการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษ
- เข้าใจวัฒนธรรมและผู้คนต่างชาติได้ดีขึ้น: คติประจำใจ ภาษาอังกฤษเป็นส่วนสำคัญของวัฒนธรรมและผู้คนในอังกฤษ การเรียนรู้คติประจำใจจะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจวัฒนธรรมและผู้คนของประเทศอังกฤษได้ดีขึ้น สื่อสารและบูรณาการกับเจ้าของภาษาได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
- เข้าถึงบทเรียนอันลึกซึ้งเกี่ยวกับชีวิต คติประจำใจภาษาอังกฤษประกอบด้วยบทเรียนอันลึกซึ้งเกี่ยวกับชีวิต ความรัก ความสำเร็จ ความล้มเหลว… การอ่านคติประจำใจจะช่วยให้ผู้อ่านได้รับความรู้และประสบการณ์อันทรงคุณค่าในการใช้ชีวิตที่ดีขึ้น
- ค้นหาแรงจูงใจและแรงบันดาลใจ: คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษสามารถสร้างแรงบันดาลใจและจูงใจผู้อ่านในชีวิตได้ เมื่อเผชิญกับความยากลำบากหรือความล้มเหลว การอ่านคติประจำใจที่ดีจะช่วยให้ผู้อ่านมีแรงบันดาลใจ

พัฒนาทักษะภาษาอังกฤษมาตรฐานที่ครอบคลุมกับ ELSA
การใช้คติประจำใจไม่เพียงช่วยให้คุณทำคะแนนในการสอบเช่น IELTS ได้เท่านั้น แต่ยังสร้างความประทับใจที่ดีให้กับผู้ฟังอีก ด้วย ELSA Speak คุณไม่เพียงพัฒนาความสามารถในการพูดภาษาอังกฤษของคุณเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังสามารถใช้คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อยกระดับการสื่อสารของคุณได้อีกด้วย
โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งแพ็คเกจ ELSA Premium เพียงอย่างเดียวที่รวมคุณสมบัติ AI ที่ทันสมัยซึ่งจะช่วยช่วย:
- การใช้หลักการที่ยืดหยุ่น: ELSA AI จะนำเสนอสถานการณ์ในชีวิตจริงและช่วยให้คุณฝึกฝนวิธีใช้คติประจำใจที่เหมาะสมในประโยค
- ตรวจจับและแก้ไขข้อผิดพลาดในการออกเสียงโดยละเอียด: ระบบ AI วิเคราะห์การออกเสียงและให้คำแนะนำเฉพาะเจาะจงเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการฝึกฝน
- ฝึกฝนได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา: คุณสามารถปรับปรุงความสามารถในการสื่อสารของคุณได้อย่างชัดเจนในเวลาเพียงไม่กี่นาทีต่อวันด้วยโทรศัพท์ แล็ปท็อป แท็บเล็ต…
ด้วยคุณสมบัติพิเศษของ ELSA AI ที่รวมอยู่ในแพ็คเกจ ELSA Premium นี้คุณสามารถสนทนากับ AI ได้โดยตรงหรือฝึกการออกเสียงเป็นประจำและใช้คติประจำใจในภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อการสื่อสารในชีวิตประจำวัน สร้างความประทับใจให้กับผู้ฟังของคุณ ลงทะเบียนตอนนี้เลยเพื่อรับแพ็คเกจ ELSA Premium เพื่อสำรวจฟีเจอร์ AI ทั้งหมดและอัปเกรดระดับภาษาอังกฤษของคุณอย่างสมบูรณ์!
ในบทความนี้ เราได้เรียนรู้ 150+ คติประจําใจ ภาษาอังกฤษ ที่ดีที่สุดเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อต่างๆ มากมาย เช่น ความรัก ชีวิต ความพยายาม ฯลฯ ที่ช่วยให้คุณพัฒนาทักษะภาษาอังกฤษของตัวเอง หากคุณอยากปรับปรุงทักษะภาษาอังกฤษเพิ่มเติม โปรดติดตาม ELSA Speak เพื่อติดตามบทความที่มีประโยชน์มากขึ้นและพัฒนาความสามารถในการพูดภาษาอังกฤษของคุณนะ
ในชีวิตประจำวัน บางครั้งเราไม่สามารถหลีกเลี่ยงคำถามกวนๆ จากผู้ใหญ่ เพื่อน หรือเพื่อนร่วมงาน และไม่รู้ว่าจะตอบอย่างไร ไม่ต้องกังวลเพราะในบทความนี้ของ ELSA Speak คุณจะได้ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ คำถามกวนๆ และวิธีตอบสนองที่เหมาะสมในทุกสถานการณ์
คําถามกวนๆ ที่พบบ่อย

วิธีตอบคำถามกวนๆ อย่างมีไหวพริบและชาญฉลาดที่คุณอาจพบในชีวิตครอบครัวและชีวิตการทำงาน
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| If Manchester United plays Chelsea, which side will you cheer for? | ถ้าแมนเชสเตอร์ ยูไนเต็ด เจอกับเชลซี คุณจะเชียร์ทีมไหน? | The sidelines because you can’t cheer inside. (ข้างสนาม เพราะคุณไม่สามารถเชียร์ข้างในได้) |
| What happens to a pair of green shoes thrown into the Red Sea? | มีชายคนหนึ่งไปที่ทะเลแดงและโยนรองเท้าสีเขียวคู่หนึ่งลงไป จะเกิดอะไรขึ้นกับรองเท้า? | They will be wet. (รองเท้าจะเปียก) |
| Why do some people have a sore scalp? | ทำไมบางคนถึงมีอาการเจ็บหนังศีรษะ? | Because their hair is being pulled. (เพราะผมของพวกเขาถูกดึง) |
| Which number comes before 1, 2, 3? | ตัวเลขใดมาก่อน 1, 2, 3? | Well, it’s the number 1, 2, 2. (มันคือตัวเลข 1, 2, 2) |
| What shoes are rare? | รองเท้าแบบไหนที่หายาก? | The missing shoes. (รองเท้าที่หายไป) |
| How do you wash dishes without getting your hands wet? | คุณล้างจานโดยไม่ให้มือเปียกได้อย่างไร? | Eat and let your mother wash them. (กินแล้วปล่อยให้แม่ล้างให้) |
| What is only done to measure? | สิ่งที่ทำได้แค่การวัดคืออะไร? | A ruler (ไม้บรรทัด) |
| Suppose you own a restaurant with 4 tables, tables 1 and 2 have ordered, table 3 has paid, but table 4 has run away; what will you do? | สมมติว่าคุณเป็นเจ้าของร้านอาหารที่มีโต๊ะ 4 ตัว โต๊ะ 1 และ 2 ได้สั่งอาหารแล้ว โต๊ะ 3 ได้ชำระเงินแล้ว แต่โต๊ะ 4 หนีไป คุณจะทำอย่างไร? | Organize it correctly. (จัดระเบียบมันให้ถูกต้อง) |
| Why does Snow White not have a runny nose? | ทำไมสโนว์ไวท์ถึงไม่มีน้ำมูกไหล? | Because she has all seven dwarfs. (เพราะเธอมีคนแคระทั้งเจ็ด) |

รวบรวมคำถามตลกๆ ที่ดีที่สุด
คําถามกวนๆ พร้อมเฉลยด้วยหัวข้อต่างๆ ช่วยให้คุณแสดงตัวตนในการสนทนาต่างๆ
คำถามตลกๆ เกี่ยวกับอาหาร
คำถามฮาๆ เกี่ยวกับอาหาร เหมาะสำหรับถามเด็กๆ และผู้สูงอายุในครอบครัว
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| Which soup has the most nutrients? | ซุปแบบไหนที่มีสารอาหารมากที่สุด? | ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ต วิธีอ่าน /ˈsuː.pəˌmɑː.kɪt/ (เล่นคำจากคำที่ออกเสียงเหมือนกัน /suːp/). |
| Why should you open the medicine cabinet gently? | ทำไมคุณถึงควรเปิดตู้ยาเบาๆ? | Because you’re afraid of waking the sleeping medicine. (เพราะกลัวจะทำให้ยาที่หลับอยู่ตื่น) |
| Which pig does not get full? | หมูตัวไหนที่กินไม่อิ่ม? | Little Pig. (หมูน้อย) |
| Which pig gets full? | หมูตัวไหนที่กินอิ่ม? | Little pigs, lots of rice. (หมูน้อย ข้าวเยอะ) |
| How do you fry a pig without it sticking to the pan? | คุณจะทอดหมูอย่างไรไม่ให้มันติดกระทะ? | Fry in a pot. (ทอดในหม้อ) |
| Which lemon is the sourest? | มะนาวลูกไหนที่เปรี้ยวที่สุด? | Every lemon is sour, is there any lemon that is not sour?( มะนาวทุกลูกเปรี้ยว มีมะนาวลูกไหนที่ไม่เปรี้ยวบ้างไหม?) |
| What is red on the outside and yellow on the inside? | อะไรที่มีสีแดงข้างนอกและสีเหลืองข้างใน? | Where is it? (มีอะไรบ้าง?) |
>>> Read more:
- 200+ คำศัพท์อังกฤษที่ต้องรู้ หมวด เมนูอาหารภาษาอังกฤษ
- รวบรวม 100+ คำศัพท์ และ Idiom เกี่ยวกับหัวข้อรสชาติในภาษาอังกฤษ
- รวบรวม 100 คำถามกวนๆ และคำถามฮาๆ พร้อมเฉลย
คำถามเกี่ยวกับประเทศ ประเภทจังหวัด

ตอบทุกคำถามฮาๆ เกี่ยวกับชาติ ประเภทจังหวัดอยู่ที่ไทยทุกครั้งที่เข้าร่วมการอภิปรายกับผู้อื่น
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| Which country has na in the middle? | ประเทศไหนที่มี ‘na’ อยู่ตรงกลาง? | Canada and Panama with Na in the middle of the name. (Canada และ Panama มี ‘na’ อยู่ตรงกลางชื่อ) |
คำถามฮาๆ เกี่ยวกับสัตว์

สรุปคำตอบคำถามตลกๆเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อสัตว์ทั่วไปในประเทศไทยเมื่อสนทนากับคนแปลกหน้า
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| If a cat and a giraffe mate, what will happen? | ถ้าแมวกับยีราฟผสมพันธุ์กัน จะเกิดอะไรขึ้น? | It’s a hypothetical situation. (มันเป็นสถานการณ์สมมุติ) |
| How to put a hippo in the fridge? | จะใส่ฮิปโปโปเตมัสในตู้เย็นได้อย่างไร? | Open the fridge, put the hippo in, and close it. (เปิดตู้เย็น, ใส่ฮิปโปโปเตมัสเข้าไป, แล้วปิดมัน) |
| Which ant is larger than ant X? | มดตัวไหนที่ใหญ่กว่ามด X? | Ant XL. (มดไซส์ XL) |
| Which ant can dive underwater? | มดตัวไหนที่สามารถดำน้ำได้? | Black ants. (มดดำ) |
| Which crab has 4 legs? | ปูตัวไหนที่มีขา 4 ขา? | Mat crab lying with two friends. (ปูกำลังนอนอยู่กับเพื่อนสองตัว) |
| What fish eats its own young? | ปลาตัวไหนที่กินลูกของตัวเอง? | Mean fish. (ปลาใจร้าย) |
>>> Read more: คำศัพท์สัตว์ภาษาอังกฤษที่พบบ่อยที่สุด
คําถามกวนๆ เพื่อนเล่นคำแบบสุ่ม
คำถามกวนๆ พร้อมคำตอบเมื่อเพื่อนและเพื่อนร่วมงานในที่ทำงานถามคุณ
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| In which room do I see you? | ในห้องไหนที่ฉันจะเห็นคุณ? | ICU – I See You. (ฉันเห็นคุณ) |
| Which ant bites the hardest? | มดตัวไหนที่กัดแรงที่สุด? | Traitor ant (betraying friend). มิตรทรยศ (หักหลังเพื่อน). |
| What is used all the time? | อะไรที่ถูกใช้ตลอดเวลา? | A mother because she uses it regularly. (คุณแม่ เพราะใช้ท่านเป็นประจำ) |
| What is the saddest thing in the bathroom? | สิ่งที่น่าเศร้าที่สุดในห้องน้ำคืออะไร? | The toilet bowl. (โถส้วม) |
เรื่องตลกสั้น ๆ คำถามกวน ๆ เกี่ยวกับความรู้ทั่วไป

รายการคําถามกวนๆ พร้อมเฉลยที่คุณควรใช้ที่ต้องการสร้างความประทับใจให้ใครสักคน
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| What shoes are hardly ever seen? | รองเท้าแบบไหนที่แทบไม่เคยเห็น? | Lost shoes. (รองเท้าที่หายแล้ว) |
| What does the door fear? | ประตูกลัวอะไร? | It fears fire because there is a fire escape door. (กลัวไฟเพราะมันเป็นประตูหนีไฟ) |
| What is it that hangs when sitting and hangs when standing, and is always associated with men? | อะไรที่แขวนเมื่อนั่ง ยืนก็แขวนและเกี่ยวข้องกับผู้ชายเสมอ? | A necktie.(เนกไท) |
| What number comes before 1, 2, 3, 4? | หมายเลขใดที่มาก่อน 1, 2, 3, 4? | It’s 1, 2, 3, 3. (คือเลขที่ 1, 2, 3, 3.) |
| In the story of Cinderella, how many dwarfs are there? | ในเรื่องซินเดอเรลล่า คนแคระมีกี่คน? | There are none because it’s not the story of Snow White. (ไม่มีคนแคระใดเลย เพราะเรื่องนี้ไม่ใช่เรื่องของสโนว์ไวท์) |
| Which months have 28 days? | เดือนไหนบ้างที่มี 28 วัน? | Every month has 28 days. (ทุกเดือนมี 28 วัน) |
| What is the smallest Toyota model? | รุ่นของโตโยต้าที่เล็กที่สุดคือรุ่นไหน? | It’s a tiny Toyota. (มันคือตัวโตโยต้าขนาดเล็ก) |
| What leg is in your mouth? | ขาไหนที่อยู่ในปากของคุณ? | The jaw. (ขากรรไกร) |
| What fish has two twenty? | ปลาตัวไหนที่มีสองยี่สิบ? | Fish costing ten each. (ปลาที่มีราคา 10 ต่อหนึ่งตัว) |
| Which fish does not know manners? | ปลาตัวไหนที่ไม่รู้มารยาท? | A dead fish – it doesn’t bow.. (ปลาตาย – มันไม่ก้มหัว) |

คำถามตลกๆ เบี่ยงเบนปัญหา
มุกฮาๆ บางอย่างที่คุณสามารถรวบรวมและถามเพื่อนและเพื่อนร่วมงานของคุณเมื่อคุณพบพวกเขาในที่ทำงาน งานปาร์ตี้ หรือร้านกาแฟ เพื่อสร้างบรรยากาศที่สนุกสนานและสบายใจ
| คำถามภาษาอังกฤษ | แปล | คำตอบภาษาอังกฤษ |
| Paula jumps into the water, so why is my hair not wet? | พอลล่ากระโดดลงน้ำ แล้วทำไมผมของฉันถึงไม่เปียก? | Because I was standing and watching Paula from above, not jumping in. (เพราะฉันยืนอยู่และมองพอลล่าจากข้างบน ไม่ได้กระโดดลงไป) |
| Suppose has a bicycle, Mr. A sits in the front. Mr. B sits in the middle. Who owns the bicycle? | สมมติว่ามีจักรยาน, คุณ A นั่งข้างหน้า, คุณ B นั่งตรงกลาง. ใครเป็นเจ้าของจักรยาน? | It’s Suppose. (มันคือตัวอย่าง) |
| There are three birds perched on a tree branch. The hunter shoots, and one falls. One has flown away. But the other is still there. Why? | มีนกสามตัวเกาะอยู่บนกิ่งไม้ นายพรานยิงนกและนกตัวหนึ่งตกลงมา อีกตัวบินไปแล้ว แต่ตัวที่เหลือยังอยู่ ทำไม? | One died and the other went to the police. The one on the branch stood as a witness. (ตัวหนึ่งตายและอีกตัวไปแจ้งตำรวจ ส่วนตัวที่เหลืออยู่บนกิ่งเป็นพยาน) |
| Which bird speaks under your feet? Its wings are under your feet. | นกตัวไหนที่พูดอยู่ใต้เท้าของคุณ? ปีกอยู่ใต้เท้าของคุณ | The bird was stepped on. (นกที่ถูกเหยียบ) |
| What is thrown away but costs a lot? | อะไรที่ถูกทิ้งไปแต่มีราคามาก? | Not throwing trash in the bin: Fine of 2000 baht. (ไม่ทิ้งขยะลงถัง: ปรับ 2,000 บาท) |
| If 30 cm equals 1 foot, how many inches are in 2 feet? | ถ้า 30 เซนติเมตรเท่ากับ 1 ฟุต 2 ฟุตมีจำนวนกี่นิ้ว | 2 feet has 10 inches because feet means feet. (2 ฟุตมี 10 นิ้ว เพราะฟุตหมายถึงเท้า) |

สรุปว่า คำถามกวนๆ อาจเกิดขึ้นโดยไม่คาดคิดในชีวิตประจำวัน แต่คุณสามารถเผชิญหน้าได้อย่างมั่นใจและมีไหวพริบ เช่น คุณสามารถถามคำถามตลกๆ เพื่อเปลี่ยนหัวข้อการสนทนาได้ ด้วยบทความนี้ ELSA Speak ได้แบ่งปันเคล็ดลับที่จะช่วยให้คุณ “ได้รับคะแนน” ในสถานการณ์ที่น่าอึดอัดใจที่สุด