Author: Bao Ngan Nguyen
Preposition of place (คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่) ถือเป็นหลักไวยากรณ์ที่พบได้ทั่วไปในชีวิตประจำวัน เช่นเดียวกับการสอบมัธยมปลาย TOEIC..บทเขียนนี้จะให้ผู้อ่านทราบถึงคำนิยาม วิธีใช้คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ และแบบฝึกหัดพร้อมคำตอบโดยละเอียด
Prepositions of place คืออะไร
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ (Prepositions of Place) เป็นคำบุพบทที่ใช้อธิบายสถานที่ พื้นที่เพื่อให้ข้อมูลและกำหนดตำแหน่งของวัตถุหรือเหตุการณ์ดังกล่าวโดยเฉพาะ คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่จะรวมกับคำนามของสถานที่โดยตรง
ตัวอย่าง
- The dog is lying in the kitchen. (สุนัขกำลังนอนอยู่ในครัว)
- Ana and I are studying at school. (อานากับฉันกำลังเรียนอยู่ที่โรงเรียน)
หลักการใช้ In, On, At
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in”
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in” มีความหมายว่า “ใน ข้างใน” ใช้กับความหมายว่าวัตถุหรือเหตุการณ์บางอย่างอยู่ในพื้นที่ขนาดใหญ่และล้อมรอบด้วยพื้นที่นั้น
| หลักการใช้คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in” | ตัวอย่าง |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in” อธิบายสถานที่ในพื้นที่ปิด เช่น ภายในวัตถุ ห้อง หรืออาคาร | Martin is in the kitchen. (มาร์ตินอยู่ในครัว) There are 18 apples in the box. (ในกล่องมีแอปเปิ้ล 18 ผล) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in” อธิบายตำแหน่งในพื้นที่เปิดโล่งขนาดใหญ่ | Sara lives in London. (ซาร่าอาศัยอยู่ในลอนดอน) There are several planets in the universe. (ดาวเคราะห์มีหลายดาวในจักรวาล) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in”ใช้เพื่อแสดงทิศทางหรือวลีแสดงสถานที่: in the south/ north/ east/ west; in the front/ back/ middle… | Anna’s house is in the north of the town. (ร้านอาหารของแอนนาตั้งอยู่ทางตอนเหนือของเมือง) Martin is sitting in the back of the class. (มาร์ตินนั่งอยู่ด้านหลังชั้นเรียน) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “in” ระบุตำแหน่งของวัตถุหรือเหตุการณ์ภายในวัตถุนามธรรมอื่น ๆ ได้แก่ : in a line, in a queue, in a row (ในหนึ่งแถว หนึ่งบรรทัด). | The fans had to stay in a queue for hours to buy tickets for the concert. (แฟนๆ ต้องต่อแถวยาวหลายชั่วโมงเพื่อซื้อตั๋วคอนเสิร์ต) |
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on”
| หลักการใช้คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on” | ตัวอย่าง |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on” ระบุตำแหน่งบนพื้นผิวทางกายภาพ เช่น on the table, on the wall, on the floor… | There are 5 bananas on the table. (มีกล้วย 5 ลูกอยู่บนโต๊ะ) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on” ใช้เพื่ออธิบายตำแหน่งบนถนน | The Bank is on Yellow Street. (ธนาคารตั้งอยู่บนถนน Yellow) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on” อธิบายตำแหน่งบนพื้นของอาคาร | Anna’s apartment is on the fifth floor. (อพาร์ตเมนต์ของแอนนาอยู่บนชั้นห้า) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on” ยังใช้กับวิธีการเดินทาง (ยกเว้นรถยนต์ (car)) | Hanna usually tries to read when she is on the bus. (ฮันนามักจะพยายามอ่านหนังสือเมื่อเธออยู่บนรถเมล์) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “on” ยังใช้กับคำบอกสถานที่ด้วย | The bakery is on the left hand side of the road. (ร้านเบเกอรี่จะอยู่ทางซ้ายมือของถนน) |

คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at”
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at” หมายความว่า “อยู่ที่” ใช้ในกรณีเฉพาะต่อไปนี้
| หลักการใช้คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at” | ตัวอย่าง |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at” ถูกใช้เมื่อผู้พูดต้องการเห็นสถานที่เป็นจุด แทนที่จะเป็นพื้นที่ขนาดใหญ่ที่คลุมวัตถุ (หรือเหตุการณ์) | I am at the hospital to visit Hanna. (ฉันอยู่ที่โรงพยาบาลเพื่อเยี่ยมฮันนา) ไม่ได้ใช้ “I am in hospital” เพราะ “in hospital” หมายถึง “การเข้ารับการรักษาในโรงพยาบาล” |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at” ใช้เพื่ออธิบายที่อยู่เฉพาะของวัตถุหรือเหตุการณ์ | My company is at 991/1 Rama 1 street. (บริษัทของฉันตั้งอยู่ที่ 991/1 ถนนพระรามที่ 1) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at” ใช้เพื่ออธิบายตำแหน่งของกิจกรรมหรือเหตุการณ์ | Sara will have fun at the party tonight. (ซาร่าจะสนุกสนานมากในงานปาร์ตี้คืนนี้) |
| คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ “at” บ่งบอกถึงสถานที่ทำงาน (เรียนหรือทำงาน) ของเรื่องที่กล่าวถึงในประโยค | Jenny is at school, and her dad is at the office now. (เจนนี่อยู่ที่โรงเรียน ส่วนพ่อของเธอตอนนี้อยู่ที่ออฟฟิศ) |

คำบุพบทบางคำอ้างถึงสถานที่อื่น
นอกจากคำบุพบทสามคำของสถานที่ “in on at” ซึ่งมีกรณีการใช้งานที่แตกต่างกันมากมายแล้ว ผู้อ่านยังอาจพบคำบุพบทเกี่ยวกับสถานที่อื่นๆ อีกมากมาย โดยปกติแล้ว คำบุพบทเหล่านี้จะมีกรณีการใช้งานเพียงหนึ่งหรือสองสามกรณีเท่านั้น โดยเฉพาะ
| คำบุพบท บอกสถานที่ | แปล | กรณีการใช้ | ตัวอย่าง |
| Above | ข้างบน | แสดงตำแหน่งเหนือจุดสังเกตเฉพาะ แต่ไม่จำเป็นต้องสัมผัสกับพื้นผิวเหมือนคำบุพบท “on” บรรยายตำแหน่งข้างต้นในรายการ การแข่งขัน | There’s a cupboard above the stove. (มีตู้เก็บของอยู่ข้างบนเตา) I came second because there was a competitor above me. (ฉันจบอันดับที่สองเพราะมีคู่ต่อสู้อยู่ข้างบนฉัน) |
| Among | ในระหว่าง/ ใน | อธิบายตำแหน่งระหว่างวัตถุ 3 ชิ้นขึ้นไป | Tom is the smartest student among us. (ทอมเป็นนักเรียนที่ฉลาดที่สุดในหมู่พวกเรา) |
| Against | วางไว้พึ่งพา | อธิบายตำแหน่งของวัตถุที่วางอยู่บนพื้นผิวอื่น | To use this ladder, you have to put it against the wall. (หากต้องการใช้บันไดนี้ คุณต้องวางไว้กับผนัง) |
| Across | ด้านอื่นๆข้าม | ระบุตำแหน่งที่อยู่อีกด้านหนึ่งของจุดสังเกต โดยคั่นด้วยขอบเขตที่ชัดเจน (แม่น้ำ ถนน) | There’s a bookstore just across the street. (มีร้านหนังสืออยู่ฝั่งตรงข้ามถนน) |
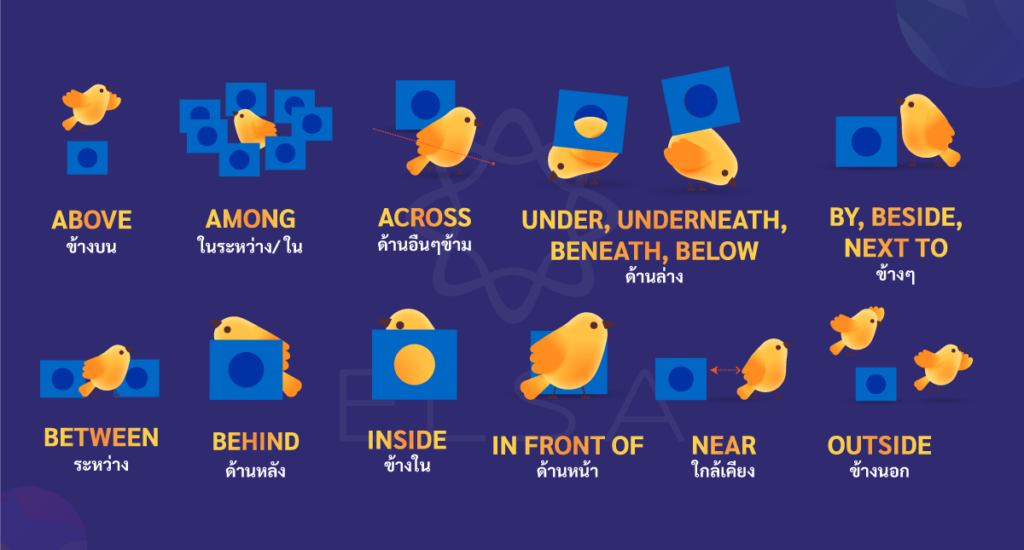
| Under, Underneath, Beneath, Below | ด้านล่าง | อธิบายตำแหน่งด้านล่างวัตถุ โดยเฉพาะ Under มักใช้เพื่อเน้นว่าวัตถุอยู่ในตำแหน่งที่ต่ำกว่า โดยสัมผัสกับวัตถุด้านบน Below มักจะหมายถึงตำแหน่งที่ต่ำกว่า แต่ไม่จำเป็นต้องติดต่อกัน Beneath มีคุณสมบัติเป็น Under และ Below แต่ใช้ในการเขียนอย่างเป็นทางการ Underneath ใช้เมื่อผู้พูดต้องการเน้นความหมายว่าสิ่งด้านล่างถูกสิ่งด้านบนคลุมไว้ | The book is under the pen. (หนังสือเล่มนี้อยู่ใต้ปากกา) The egg sinks below the water surface. (ไข่จะจมอยู่ใต้ผิวน้ำ) The sun is now beneath the horizon. (ขณะนี้ดวงอาทิตย์อยู่ใต้ขอบฟ้าแล้ว) We usually put our unused things underneath the bed. (เรามักจะวางของที่ไม่ได้ใช้ไว้ใต้เตียง) |
| By, beside, next to | ข้างๆ | อธิบายตำแหน่งที่อยู่ติดกับจุดสังเกต | The restaurant is next to/by/beside the post office. (ร้านอาหารตั้งอยู่ข้างๆกับที่ทำการไปรษณีย์) |
| Between | ระหว่าง | อธิบายตำแหน่งระหว่างวัตถุสองชิ้น | The music room is between the art room and the library. (ห้องดนตรีตั้งอยู่ระหว่างห้องรับแขกและห้องสมุด) |
| Behind | ด้านหลัง | ระบุตำแหน่งด้านหลัง โดยมีจุดสังเกตบดบัง | The boy is hiding behind the tree. (เด็กชายซ่อนตัวอยู่หลังต้นไม้) |
| Inside | ข้างใน | อธิบายตำแหน่งภายใน แต่เน้นองค์ประกอบของพื้นที่ปิดล้อม | The children must play inside the house. (เด็กต้องเล่นข้างในบ้าน) |
| In front of | ด้านหน้า | อธิบายตำแหน่งด้านหน้า บดบังจุดสังเกต | The teacher is standing in front of the desk. (ครูยืนอยู่หน้าโต๊ะ) |
| Near | ใกล้เคียง | อธิบายสถานที่ใกล้เคียงแต่ไม่จำเป็นต้องอยู่ข้างๆ เหมือน “ถัดจาก” “next to” | The school is near the bus stop. (โรงเรียนตั้งอยู่ใกล้เคียงกับป้ายรถเมล์) |
| Outside | ข้างนอก | อธิบายตำแหน่งที่อยู่นอกขอบเขตของวัตถุ | At break time, students can play outside the classroom. (ในช่วงพักนักเรียนสามารถเล่นข้างนอกห้องเรียนได้) |
การผกผันกับคำบุพบทบอกสถานที่
นอกเหนือจากการใช้งานตามปกติแล้ว ในภาษาอังกฤษยังมีกรณีของการผกผันกับคำบุพบทบอกสถานที่อีกด้วย ในเวลานั้นเราต้องกลับกริยา/กริยาวลีมาก่อนประธาน อย่ายืมกริยาช่วยในกรณีนี้
Adverb of place + V + S + O…
ตัวอย่าง
- Under the tree was sitting a girl.
(ใต้ต้นไม้มีสาวน้อยนั่งอยู่) - On the bed lay an adorable girl.
(บนเตียง มีสาวน้อยน่ารักอยู่)
หมายเหตุ: ถ้าประธานเป็นสรรพนามส่วนตัว จะไม่มีการใช้การผกผัน
>>> Read more: Inversion คืออะไร? วิธีใช้+ โครงสร้าง+ แบบฝึกหัด+ตัวอย่างที่เข้าใจง่าย
แบบฝึกหัดเรื่องคำบุพบทบอกสถานที่
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1: เติมคำบุพบทว่างในประโยคต่อไปนี้
- Did you learn something ______ school?
- Don’t put all your eggs________ one basket.
- Evan is studying______a university in Brooklyn.
- I live________ 24 Bach Dang Street.
- Is Simpson still ______ bed?
- My mom has been stuck ______ traffic jam for hours.
- She sleeps like a baby ______ the armchair.
- The answer key is_________ page 189.
- The taxi will be waiting_________ the hotel.
- There are many bugs________ the garden.
- We had dinner__________ a Japanese restaurant.
- Winter in England is extremely cold, the temperature has fallen _____ zero.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2: วงกลมคำบุพบทที่ถูกต้องในประโยคต่อไปนี้
- There are 42 students (next/in/on/front) the class.
- The grapes are not in the basket. They are (in/between/next/on) the table.
- My pen is (between/in/on/next) the books and the notebooks.
- The Lamborghini car is (behind/in front/next to/under) my house.
- The teacher stands (from/at/in front of/by) the class.
- There is a clock on the wall just (from/above/before/at) the teacher’s desk.
- August comes (after/before/in/at) July.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3: ดูแผนที่ด้านล่างและกรอกคำบุพบทในประโยคต่อไปนี้
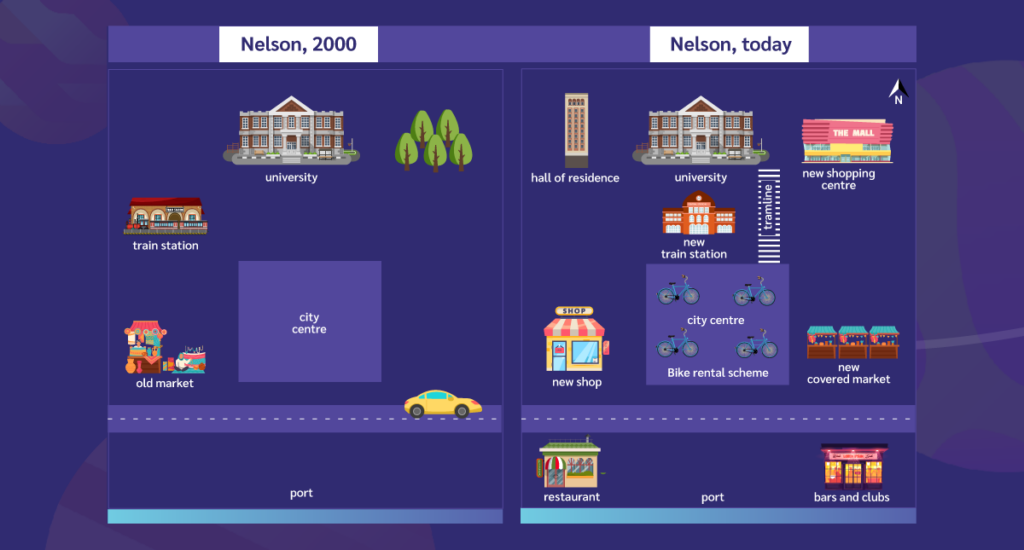
- The university is __________ the hall of residence and the new shopping center.
- The bars and clubs are _________ the restaurant.
- The bike rental scheme is _______ the new covered market.
- The new train station is _________ the bike rental scheme.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 4: กรอกคำบุพบทที่เหมาะสมในย่อหน้าต่อไปนี้
So here we are ______ the entrance_____ the hospital. My name is Ivy, and I’m a receptionist here, and you’ll usually find me _____ the desk just by the main entrance here. So I’d like to tell you a bit about the way the hospital is organized and you should all have a plan __________ you.
คำตอบ
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1:
| 1. at | 2. in | 3. at | 4. on |
| 5. in | 6. in | 7. on | 8. on |
| 9. in front of | 10. in | 11. at | 12. under |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2:
| 1. in | 2. on | 3. between | 4. in |
| 5. in front of | 6. above | 7. after |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 3:
| 1. between | 2. opposite | 3. next to | 4. above |
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 4:
at – to – at – in front of
คำถามที่พบบ่อย
Preposition of place คืออะไร
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ (Prepositions of Place) เป็นคำบุพบทที่ใช้เพื่ออธิบายสถานที่
Preposition of place มีอะไรบ้าง
คำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุดคือ in, on, at และคำบุพบทอื่นๆ ของสถานที่ เช่น above, among, between, behind, in front of, near, inside, outside
บทเขียนข้างต้นได้แนะนำให้ผู้อ่านรู้จัก preposition of place บอกสถานที่ ทั่วไปพร้อมทั้งวิเคราะห์กรณีการใช้งานเฉพาะ ELSA Speak หวังว่าผู้อ่านจะมีความรู้ที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นเกี่ยวกับคำบุพบทบอกสถานที่ เพื่อให้สามารถนำไปใช้ในกิจกรรมภาษาอังกฤษในอนาคตได้อย่างยืดหยุ่น
>>> Read more:
- วิธีการใช้ Subordinating Conjunctions: after, before, although, as soon as,… ในภาษาอังกฤษ
- วิธีการเขียนที่อยู่ภาษาอังกฤษให้ถูกต้องที่สุด
ในการสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษในชีวิตประจำวัน การพูด Of course ได้ใช้บ่อยมาก บทความนี้ ELSA Speak จะให้คำแนะนำโดยละเอียดเกี่ยวกับวิธีการพูด Of course อื่นๆ ในภาษาอังกฤษ มาดูกันเลย!
Of course คืออะไร?
- วิธีการออกเสียง: /əv kɔːrs/
- ประเภทคำ: สำนวน
- ความหมาย: ได้สิ แน่นอน
- วิธีใช้: Of course ใช้เพื่อตอบตกลงหรืออนุญาตให้ใครทำอะไรบางอย่าง แสดงสิ่งที่คุณพูดอย่างชัดเจน แน่นอนหรือแสดงให้เห็นว่าสถานการณ์หรือข้อมูลไม่น่าแปลกใจ
ตัวอย่าง อังกฤษ – ไทย
- The Second World War began, of course, in 1939. (แน่นอน สงครามโลกครั้งที่สองเริ่มต้นขึ้นในปี 1939)
- We arrived at the restaurant 35 minutes late so, of course, our reservation had been canceled. (เรามาถึงร้านอาหารช้าไป 35 นาที แน่นอนว่าที่นั่งที่จองไว้ของเราถูกยกเลิก)
- “Have you written an English essay that the teacher gave us last week yet?” “Of course, I finished it yesterday”. (“คุณได้เขียนเรียงความภาษาอังกฤษที่ครูมอบหมายให้เราเมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้วหรือยัง”-“แน่นอน ฉันทำเสร็จแล้วเมื่อวานนี้”)
- “Can you help me with this luggage?” “Of course. Why not?”. (“คุณช่วยฉันยกกระเป๋าเดินทางใบนี้ได้ไหม” – “ได้สิครับ ทำไมจะไม่ล่ะ”)
- “May I use your smartphone?” “Of course, go right ahead”. (“ฉันขอใช้สมาร์ทโฟนของคุณได้ไหม?” – “ได้สิ โปรดสบายใจเถิด”)
- “Do you love your mother?” “Of course, I do!”. (“คุณรักแม่ของคุณหรือไม่” “แน่นอน ฉันรักแม่”)
- “Can I have one of these colorful pens?” “Of course—help yourself.” (“ฉันขอปากกาหลากสีเหล่านี้สักอันได้ไหม” – “แน่นอน ตามสบาย”)
วลีบางคำที่มีความหมายเหมือนกัน “of course”
| คำวลี | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| naturally | แน่นอน (อย่างที่คุณคาดหวัง ด้วยวิธีปกติและง่ายๆ ) | Naturally, we should arrive early to get the best seats. | แน่นอนว่าเราควรมาถึงก่อนเวลาเพื่อให้ได้ที่นั่งที่ดีที่สุด |
| certainly | โดยแน่นอน แน่ใจ แน่ๆ (ใช้เพื่อตอบอย่างสมบูรณ์หรือเน้นบางสิ่งบางอย่าง และแสดงว่าไม่มีข้อสงสัยเกี่ยวกับเรื่องนี้) | Had you forgotten about our anniversary? Certainly not! I’ve reserved a table at Tiffany’s restaurant for this evening. | พี่ลืมวันครบรอบของเราเหรอ? ไม่แน่นอน พี่จองโต๊ะที่ Tiffany’s สำหรับคืนนี้แล้ว |
| obviously | ชัดเจนและมองเห็นได้ | Obviously, by competing in parliamentary elections, parties compete for office, but that does not mean that their goal is actually to attain office. | เห็นได้ชัดว่า โดยการแข่งขันในการเลือกตั้งรัฐสภา ฝ่ายต่าง ๆ แข่งขันกันเพื่อชิงตำแหน่ง แต่นั่นไม่ได้หมายความว่าเป้าหมายของพวกเขาคือการได้ตำแหน่งจริงๆ |
| by all means | ใช้สำหรับการอนุญาต | May I borrow your book? By all means. | ฉันขอยืมหนังสือของคุณได้ไหม แน่นอน |
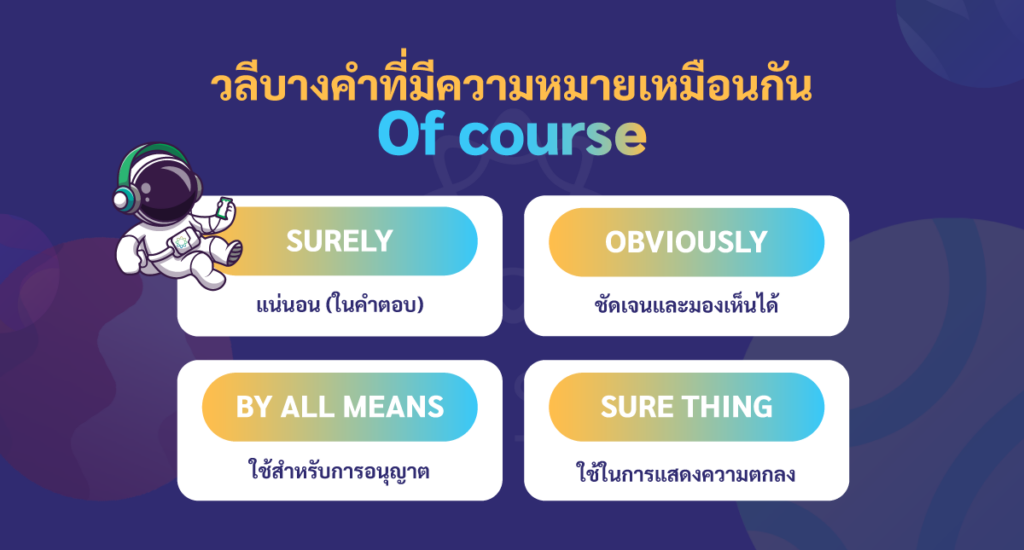
| surely | แน่นอน (ในคำตอบ) | Can I sit here? Surely. | ฉันนั่งตรงนี้ได้ไหม? แน่นอน |
| definitely | แน่นอน ไม่ต้องสงสัยอะไร | Have you definitely decided to go to New Zealand? | คุณตัดสินใจไป New Zealand อย่างแน่นอนหรือไม่ |
| clearly | ใช้เพื่อแสดงว่าคุณคิดว่าบางสิ่งบางอย่างชัดเจนหรือแน่นอน | Clearly, you must tell her the truth. | แน่นอนว่าคุณต้องบอกความจริงกับเธอ |
| undoubtedly | ใช้เพื่อเน้นว่าบางสิ่งเป็นความจริง | Undoubtedly, stress has contributed to his health problems. | ไม่ต้องสงสัยเลยว่าความเครียดส่งผลต่อปัญหาสุขภาพของเขา |
| sure thing | ใช้ในการแสดงความตกลง | Could you give me a ride home tonight, darling? Sure thing! | คืนนี้คุณช่วยพาฉันกลับบ้านหน่อยได้ไหมที่รัก แน่นอนครับ |
| Yes, Yeah, Yep, Yea | แน่นอนว่า การแสดงข้อตกลงย่อมให้ความรู้สึกเป็นมิตรแบบวัยรุ่น | Are you going to Jane’s party tonight? Yep. | คุณจะไปงานปาร์ตี้ของ Jane คืนนี้ไหม แน่นอน |
| Right | มี ใช่ ถูกต้อง เพื่อใช้ในการแสดงข้อตกลง | She’s so nice and generous. That’s right! | เธอใจดีและใจกว้างมาก ใช่ |
| Yes, of course | แน่นอนใช้ในสถานการณ์ที่เป็นทางการ | Could you give me a hand? Yes, of course. | กรุณาช่วยฉันด้วย แน่นอน |
>>> Read more:
- วิธีพูด ไม่เป็นไร ภาษาอังกฤษ ที่เรียบง่ายและจดจำได้ง่าย
- ตัวอย่างประโยคปฏิเสธอย่างสุภาพในภาษาอังกฤษ
- 60+ วิธีบอกว่าใช่ภาษาอังกฤษ นอกจาก Yes No เรียนง่าย จำง่าย จำไม่ลืม
วลีที่เกี่ยวข้องบางส่วน
| คำวลี | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง | ความหมาย |
| of course not | ใช้ในการเน้นว่า คุณไม่เห็นด้วย หรือว่า สิ่งที่ไม่เป็นความจริง | Where did you get that money? Did you steal them? Of course not. I borrowed it from Charlotte. | คุณได้เงินนั้นมาจากไหน? คุณขโมยเหรอ ไม่แน่นอน ฉันยืมมันมาจาก Charlotte (ชาร์ลอตต์) |
| as a matter of course | ถ้ามีอะไรทำเป็นเรื่องแน่นอน มันเป็นเรื่องปกติของวิธีการทำสิ่งต่างๆ และไม่มีอะไรพิเศษ | Safety precautions were observed as a matter of course. | ข้อควรระวังด้านความปลอดภัยเป็นเรื่องที่ทราบกันดีอยู่แล้ว |
| in the course of time | หลังจากช่วงระยะเวลาหนึ่ง | My mother assumes they plan to have children in the course of time. | แม่ของฉันคิดว่าพวกเขาวางแผนที่จะมีลูกเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป |
| in/with the course of time | ค่อยๆ ช้าๆ | With the course of time, he’s learned to live with his disability. | เมื่อเวลาผ่านไป เขาเรียนรู้ที่จะอยู่กับความพิการของเขา |
| pervert the course of justice | กระทำการผิดกฎหมายเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการลงโทษหรือถูกลงโทษจากคนผิดหรือถูกลงโทษผิดคน | The three police officers were charged with perverting the course of justice by fabricating evidence in the trial. | เจ้าหน้าที่ตำรวจทั้งสามนายถูกตั้งข้อหาบิดเบือนกระบวนการยุติธรรมโดยสร้างพยานหลักฐานในระหว่างการพิจารณาคดี |

คำถามที่พบบ่อย
Of course เขียนย่ออย่างไร?
Of course ได้เขียนย่อว่า Ofc
Ofcourse หรือ of course Ofcourse หรือ of course?
ใช้ Of course เป็นการใช้ที่ถูกต้องที่สุด
Of course not คืออะไร?
Of course not หมายความว่าไม่แน่นอน
Of course ออกเสียงอย่างไร?
วิธีออกเสียง: /əv kɔːrs/
ข้างต้นคือความรู้ทั้งหมดเกี่ยวกับว่า Of Course คืออะไร และโครงสร้างของวลี Of Course ในประโยคภาษาอังกฤษที่ ELSA Speak ได้เรียนรู้และสังเคราะห์มาให้ทุกคน ขอให้ทุกคนประสบความสำเร็จในเส้นทางการเรียนรู้และรักภาษาอังกฤษอยู่เสมอ
ประโยคย้อนกลับในภาษาอังกฤษ (Inversion) ใช้เพื่อเน้นความหมายของการกระทำและเพิ่มความแสดงออกของประโยค ประโยคย้อนกลับประกฏบ่อยมากแต่ไม่ใช่ผู้เรียนทุกคนก็รู้วิธีใช้อย่างถูกต้องและได้คะแนนในการทดสอบ มาเรียนรู้ประโยคย้อนกลับกับ ELSA Speak นะ
Inversion คืออะไร
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (Inversion) เป็นโครงสร้างที่คำวิเศษณ์หรือกริยาช่วยไม่อยู่ในตำแหน่งปกติ แต่จะได้นำไว้หน้าประโยคเพื่อเน้นการกระทำของประธาน
แม้ว่าโครงสร้างประโยคทั่วไปในภาษาอังกฤษมีรูปแบบเป็น
Subject (ประธาน) + Verb (กริยา)
แต่โครงสร้างของประโยคย้อนกลับจะตรงกันข้าม:
Verb (คำกริยา) + Subject (ประธาน)
เพราะฉะนั้น เมื่อเรียนโครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ หลายคนมักรู้สึกว่ามันสับสนและยากที่จะเข้าใจได้
ประโยคย้อนกลับมีบทบาทอยังไง
ที่จริงแล้ว เมื่อเริ่มเรียน Tense ในภาษาอังกฤษ ผู้เรียนจะรู้จักรูปแบบของประโยคย้อนกลับแล้ว ซึ่งเป็นโครงสร้างคำถามของ Tense ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างของการสลับในคำถาม
ตัวอย่าง: Is everyone alright?
ตัวอย่างข้างต้นเป็นรูปแบบคำถามหนึ่งของ present simple tense และสามารถเห็นได้ว่าประธานของประโยคนี้คือ “everyone” ถูกวางไว้หลังกริยา “is” เพื่อสร้างโครงสร้างคำถามจากเมื่อก่อนถึงตอนนี้ ผู้เรียนก็ยังใช้อยู่บ่อยๆ
นอกจากหน้าที่ที่สร้างคำถามภาษาอังกฤษแล้ว ไวยากรณ์ของประโยคย้อนกลับนี้ยังได้ใช้เพื่อเน้นข้อมูลที่ได้ถ่ายทอดในประโยค อย่างไรก็ตาม ผู้เรียนต้องจำว่า การสลับใช่เฉพราะในบางกรณีในภาษาอังกฤษเท่านั้น ดังนั้นถ้าอยากใช้ภาษาอังกฤษได้อย่างเป็นธรรมชาติ ผู้เรียนไม่ควรใช้ไวยากรณ์นี้ในทุกประโยคเมื่อพูดหรือเขียน
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับในภาษาอังกฤษ
มีโครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับหลายอย่างที่แตกต่างกันในไวยากรณ์ภาษาอังกฤษ ELSA Speak ขอแนะนำโครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion) ที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุด ตั้งแต่แบบง่ายจนถึงแบบซับซ้อน ดังนี้
ประโยคย้อนกลับด้วยกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่
โดยปกติแล้ว โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วยกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่มักไปพร้อมกับกริยาวิเศษณ์เชิงลบ
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วยกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่
Never/ Rarely/ Hardly/ Seldom/ Little/ Ever + กริยาช่วย + S + V
ตัวอย่าง
• She never goes out with strangers = Never does she go out with strangers.
(เธอไม่เคยออกไปกับคนแปลกหน้า)
• I hardly study English at night = Hardly do I study English at night.
(ฉันไม่ค่อยเรียนภาษาอังกฤษตอนกลางคืน)

ประโยคย้อนกลับด้วย “No” และ “Not any”
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion):
No/Not any + N + กริยาช่วย + S + V
ตัวอย่าง
• No sneakers shall I buy for you = Not any sneakers shall I buy for you.
(ฉันจะไม่ซื้อรองเท้าผ้าให้คุณอีก)
• Not any chances will we work together in the future.
(เราจะไม่มีโอกาสที่ร่วมงานกันอีกในอนาคต)
>>> Read more: วิธีใช้ Some และ Any พร้อมแบบฝึกหัดและเฉลยที่เข้าใจง่ายที่สุด
ประโยคย้อนกลับด้วยวลีเชิงลบ “No”
ถ้าต้องการประยุกต์ใช้โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับในกรณีนี้ คุณต้องจำวลีคำศัพศ์ภาษาอังกฤษที่มีความหมายเชิงลบด้วยคำว่า “No” เช่น
• At no time: ไม่เคย
• In no way: ไม่มีทางอื่น
• On no condition: ไม่อย่างเด็ดขาด
• On no account = For no reasons: ไม่มีเหตุผล
• Under/In no circumstances: ไม่ว่าในกรณีใดก็ตาม
• No longer: Không còn nữa. ไม่…อีกต่อไป
• No where: ไม่มีที่ไหน
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion) ด้วยวลีเชิงลบ “No”
วลีที่มีความหมายเชิงลบ + กริยาช่วย + S + V
• We can’t go to the bus stop in time = In no way can we go to the bus stop in time.
(ไม่มีทางอื่นที่ไปถึงป้ายรถเมล์ตรงเวลาได้)
• She didn’t have to do like that = On no account did you do like that.
( ไม่มีเหตุผลใดที่คุณต้องทำแบบนี้)
• Leaving home is always a bad idea = In no circumstances should you leave home.
(ไม่ควรออกจากบ้านไม่ว่าในกรณีใดก็ตาม)
• She never goes out with strangers = At no time does she go out with strangers.
(เธอไม่เคยออกไปกับคนแปลกหน้า)
• This village grows the best corns = No where can you grow corns as good as in this village.
( ไม่มีที่ไหนจะปลูกข้าวโพดได้ดีเท่าในหมู่บ้านนี้ได้)
| คุณเคยสงสัยไหมว่า have has ใช้ยังไง? ลองอ่านบทความเกี่ยวกับ have และ has เพื่อเข้าใจโครงสร้างและวิธีใช้อย่างถูกต้องในแต่ละกรณี |
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ “No sooner … than”
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วยโครงสร้าง “No sooner…than”
No sooner + กริยาช่วย + S + V + than + S + V (ทันทีที่…ก็…)
ตัวอย่าง
• No sooner did I meet her than she started eating dinner with him.
(ทันที่ที่ฉันพบเธอ เธอก็เริ่มทานอาหารเย็นกับเขา)
• No sooner did we leave home than the letter was delivered.
(ทันที่ที่เราออกจากบ้าน จดหมายก็มาถึง)
ประโยคย้อนกลับด้วย “Such” และ “So…that”
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion) ด้วย “Such” และ “So…that”:
Such + คำวิเศษณ์ + N + that + S + V
So + คำวิเศษณ์/ คำกริยาวิเศษณ์ + กริยาช่วย + N + that + S + V
ตัวอย่าง
Such a beautiful song that I have listened many times = So beautiful is this song that I have listened many times. (เพลงนี้ไฟเราะมาก ฉันฟังมันหลายรอบแล้ว)
>>> Read more: การใช้ Correlative Conjunctions: Either… or, Neither… nor, Such…that,…
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วย “Not only … but also”
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วย “Not only … but also”:
Not only + กริยาช่วย + S + V but S also V (ไม่เพียงแต่…แต่ยัง)
ตัวอย่าง
• Not only is she beautiful but also intelligent.
(เธอไม่เพียงแต่สวยงามเท่านั้น แต่ยังฉลาดอีกด้วย)
• Not only is he nice but he also plays football well.
(เขาไม่เพียงแต่เป็นคนใจดีเท่านั้น แต่ยังเล่นฟุตบอลได้ดีอีกด้วย)
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วย “until/ till”
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion) ด้วยคำบุพบทบอกเวลา until
Not until/ till + (S+V) time + กริยาช่วย + S + V ( จนกระทั่ง )
ตัวอย่าง
• Not until 12pm did I finish my homework.
(จนกระทั่ง 12.00 น ฉันทำการบ้านเสร็จ)
• Not until I helped could she carry the heavy bags.
(จนกระทั่งฉันช่วยเธอจึงถือกระเป๋าหนักๆ นั้น)
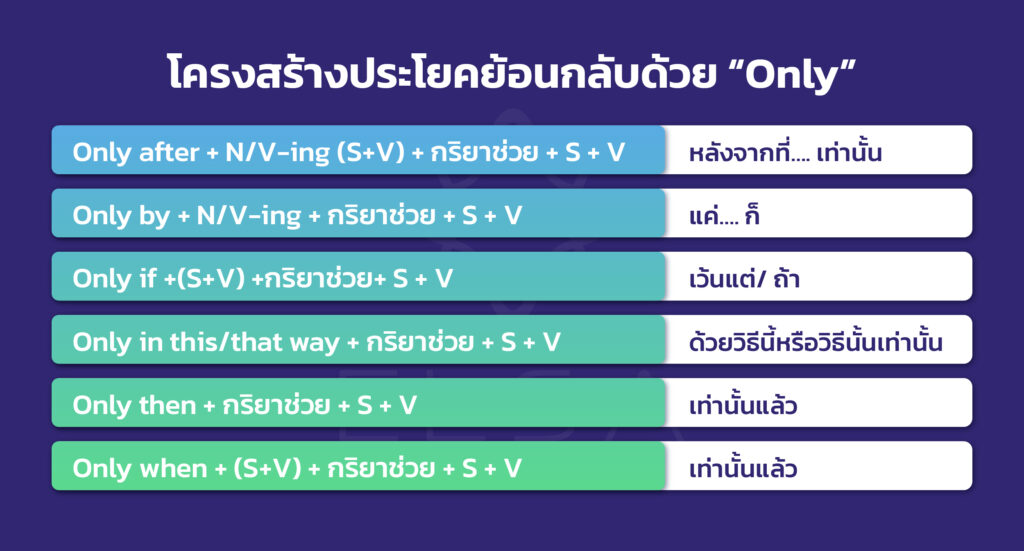
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับด้วย “Only”
| ประโยคย้อนกลับ | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง |
| Only after | Only after + N/V-ing (S+V) + กริยาช่วย + S + V (หลังจากที่…. เท่านั้น) | Only after lunch can we watch TV together. (หลังอาหารกลางวันเท่านั้นที่เราจะดูทีวีด้วยกันได้) Only after eating dinner does he go shopping with his friends.(หลังจากที่กินข้าวเย็นเสร็จเท่านั้นที่เขาจะไปชอปปิ้งกับเพื่อน) |
| Only by | Only by + N/V-ing + กริยาช่วย + S + V (แค่…. ก็) | Only by studying English well can you have a good job. (แค่เรียนภาษาอังกฤษเก่งเท่านั้น คุณก็จะมีงานที่ดีได้) Only by production can a nation satisfy demands. (แค่โดยการผลิตเท่านั้น ประเทศก็สามารถตอบสนองความต้องการได้) |
| Only if | Only if +(S+V) +กริยาช่วย+ S + V (เว้นแต่/ ถ้า) | Only if he agrees would she go with me = She would go with me if he agrees. (ถ้าเขาตกลง เธอจะไปกับฉัน) Only if it isn’t cold can we eat out.(เว้นแต่อากาศไม่หนาว เราก็จะออกไปกินข้าวนอกบ้าน) |
| Only in this/ that way | Only in this/that way + กริยาช่วย + S + V (ด้วยวิธีนี้หรือวิธีนั้นเท่านั้น) | Only in this way can I study English. (ด้วยวิธีนี้เท่านั้นฉันสามารถเรียนภาษาอังกฤษได้) Only in that way will he pass the exam. (ด้วยวิธีนั้นเท่านั้นเขาจะสอบผ่านได้) |
| Only then | Only then + กริยาช่วย + S + V (เท่านั้นแล้ว) | Only then did she receive my money. (เท่านั้นแล้วเธอก็ได้รับเงินของฉัน) |
| Only when | Only when + (S+V) + กริยาช่วย + S + V (เฉพาะเมื่อ) | Only when I met him did he recognize me. (เฉพาะเมื่อฉันเจอเขาเท่านั้นที่เขาจำฉันได้) Only when you study foreign languages will many opportunities happen. (เฉพาะเมื่อคุณเรียนภาษาต่างประเทศเท่านั้นที่จะมีโอกาสมากมายเกิดขึ้น) |
โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับในประโยคเงื่อนไข (if clause inversion)
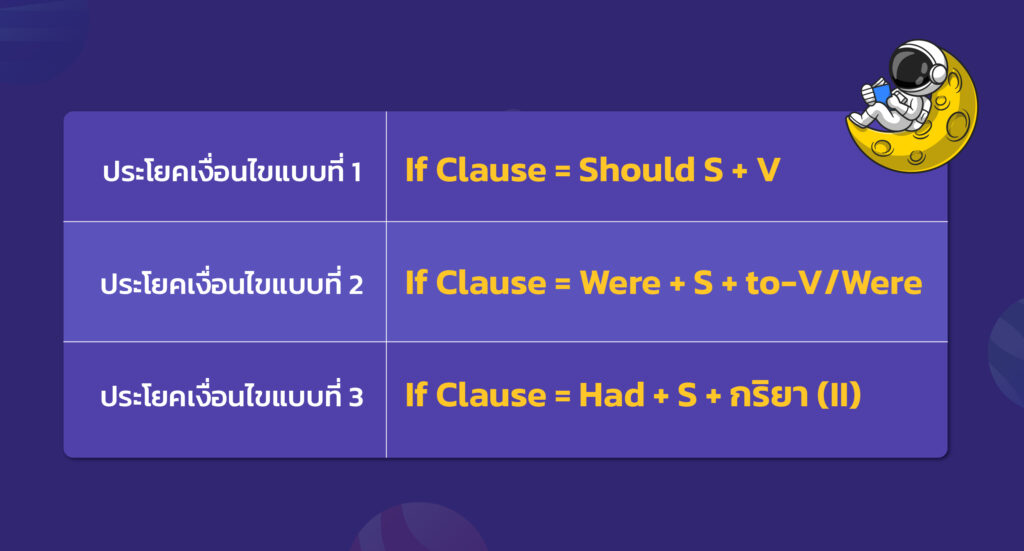
คุณสามารถประยุกต์ใช้โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion) ในประโยคเงื่อนไขแบบที่ 1 2 และ 3 ได้
ประโยคเงื่อนไขแบบที่ 1
If Clause = Should S + V
ตัวอย่าง
• If I leave, I won’t meet her again = Should I leave, I won’t meet her again. (ถ้าฉันจากไป ฉันจะไม่พบเธออีก)
• If he has a lot of money, he will help the poor = Should he have a lot of money, he will help the poor. (ถ้าเขามีเงินเยอะ เขาจะช่วยเหลือคนที่ยากจน)
ประโยคเงื่อนไขแบบที่ 2
If Clause = Were + S + to-V/Were
ตัวอย่าง
• If I were you, I would help poor people = Were I you, I would help poor people. (ถ้าฉันเป็นคุณ ฉันจะช่วยเหลือคนที่ยากจน)
• If I earned more money, I would buy that dress = Were I to earn more money, I would by that dress. (ถ้าฉันหาเงินได้มากขึ้น ฉันจะซื้อชุดนั้น)
ประโยคเงื่อนไขแบบที่ 3
If Clause = Had + S + กริยา (II)
ตัวอย่าง
If Helen had played volleyball yesterday, she would have won = Had Helen played volleyball yesterday, she would have won. (ถ้าเฮเลนเล่นวอลเลย์บอลเมื่อวาน เธอคงชนะไปแล้ว)
>>> Read more: ประโยคปัจจุบันกาล (Present Simple Tense)
แบบฝึกหัด
จงใช้โครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ (inversion) เพื่อเขียนประโยคต่อไปนี้ใหม่
1. You come to realize the significance of the murder only in the last few pages of the book.
Only in the last __________________________________________________
2. The demands of her job are such that she is rarely able to take a holiday.
Such _________________________________________________________
3. The matter could be explained in no other way.
In _____________________________________________________________
4. I have seldom heard such beautiful singing.
Seldom _________________________________________________________
5. Peter didn’t realize that he had lost his keys until he got home.
Not ____________________________________________________________
6. If Mr Chan had been kinder to his employees, his business would not have collapsed.
________________________________________________________________
7. There are no circumstances where audience members may consume alcohol.
Under no circumstances ____________________________________________
8. They started to argue soon after they had got married.
No sooner _______________________________________________________
9. You can’t use my new car at any time.
At no time ______________________________________________________
10. The gang didn’t know that the police had them under surveillance.
Little __________________________________________________________
11. We won’t consider you for the basketball team until you grow up.
Not until _________________________________________________________
12. Nobody has won so many matches for his team since 1994.
Not since ________________________________________________________
13. You will not be allowed to enter the auditorium under any circumstances once the play has started.
Under no circumstances ____________________________________________
14. He would never play in front of a live audience again.
Never ___________________________________________________________
15. Amy had not enjoyed herself so much since she went to the circus as a child.
Not since ________________________________________________________
16. I have never seen such a terrible performance of Hamlet before.
q. Never before ___________________________________________________
17. They only realized the painting had been hung upside down when someone complained at reception.
Only when _______________________________________________________
18. I had been in the room for a few minutes when I realized that everyone was staring at me.
Only after _______________________________________________________
คำตอบแบบฝึกหัดโครงสร้างประโยคย้อนกลับ
1. Only in the last few pages of the book do you come to realise the significance of the murder.
2. Such are the demands of her job that she is rarely able to take a holiday
3. In no other way could the matter be explained.
4. Seldom have I heard such beautiful singing.
5. Not until he got home did Peter realize that he had lost his keys.
6. Had Mr Chan been kinder to his employees, his business would not have collapsed.
7. Under no circumstances may audience members consume alcohol
8. No sooner had they got married than they started to argue.
9. At no time can you use my new car.
10. Little did the gang know that the police had them under surveillance.
11. Not until you grow up will we consider you for the basketball team.
12. Not since 1994 has anybody won so many matches for his team.
13. Under no circumstances will you be allowed to enter the auditorium once the play has started.
14. Never would he play in front of a live audience again. Never again would he play in front of a live audience.
15. Not since she went to the circus as a child had Amy enjoyed herself so much.
16. Never before have I seen such a terrible performance of Hamlet.
17. Only when someone complained at reception did they realize the painting had been hung upside down.
18. Only after I had been in the room for a few minutes did I realize that everyone was staring at me.
ข้อมูลข้างต้นเป็นความรู้ทั้งหมดเกี่ยวกับ Inversion grammar ในภาษาอังกฤษพร้อมแบบฝึกหัดให้คุณฝึกฝน ภาษาอังกฤษจะไม่ใช่อุปสรรคใหญ่อีกต่อไปถ้าเรารู้วิธีใช้และฝึกฝนทุกวัน ติดตาม ELSA Speak เพื่อเรียนไวยากรณ์ภาษาอังกฤษที่มีประสิทธิภาพและพัฒนาทักษะภาษาอังกฤษของคุณให้ดีขึ้นนะ