คำกริยารูปปกติ (Infinitive) เป็นความรู้ขั้นพื้นฐานที่ไม่สามารถมองข้ามได้หากคุณต้องการพิชิตคะแนนสูงสุดในการสอบคัดเลือกเข้าเป็นนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาหรือการสอบ IELTS ในบทความของวันนี้ ELSA Speak จะแบ่งปันความรู้ที่สมบูรณ์ที่สุดที่ควรทราบเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อไวยากรณ์นี้กับคุณ ศึกษาบทความตอนนี้เลยเพื่อเรียนให้ดีขึ้นทุกวัน!
ภาพรวมของคำกริยา infinitive
Verb infinitive คืออะไร?
Verb infinitive คือรูปแบบพื้นฐานของคำกริยาในภาษาอังกฤษ กริยารูปนี้มี 2 แบบ คือ มี to และไม่มี to:
สอบก่อนเข้าฟรี

- Infinitive มี “to” ตัวอย่าง: She decided to go to Korea. (เธอตัดสินใจไปเกาหลี)
- Infinitive ไม่มี “to” ตัวอย่าง: I’d rather not eat chicken. (ฉันไม่อยากกินไก่)
ตัวอย่างอื่นๆ:
- I want to eat bread.
- I must wash dishes.
รูปแบบของ verb infinitive
ในภาษาอังกฤษ เมื่อพูดถึง infinitive โดยปกติเราจะพูดถึง infinitive ในรูปแบบ Present ซึ่งเป็นรูปแบบที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุดและได้เจอมากที่สุด อย่างไรก็ตาม infinitive ยังมีรูปแบบอื่นอีกสี่รูปแบบ ได้แก่:
- Infinitive ในรูปของ perfect
- Infinitive ในรูปของ perfect continuous
- Infinitive ในรูปของ continuous
- Infinitive ในรูป passive
อย่างไรก็ตาม ในบทความนี้เราจะเน้นไปที่การแนะนำเกี่ยวกับ infinitive ในรูปแบบ Present เท่านั้น โดย infinitive ในรูปแบบ Present มี 2 รูปแบบดังนี้:
- Infinitive มี “to” = to + ส่วนดั้งเดิม
- Zero infinitive = ส่วนดั้งเดิม
ตัวอย่าง:
| infinitive มี “to” | Zero infinitive |
| to go | go |
| to become | become |
| to eat | eat |
| to wash | wash |
Infinitive รูปแบบปฏิเสธในภาษาอังกฤษเกิดจากการวางคำ “not” หน้ารูป infinitive ใดๆ ตัวอย่างเช่น:
- I decided not to go to Thailand. (ฉันตัดสินใจว่าจะไม่ไปประเทศไทย)
- I’d rather not vegetable. (ฉันไม่อยากกินผัก)
>>> Read more:
- รูปแบบของ verb to be มีอะไรบ้าง
- Gerund and infinitive – หลักการใช้และแบบฝึกหัด
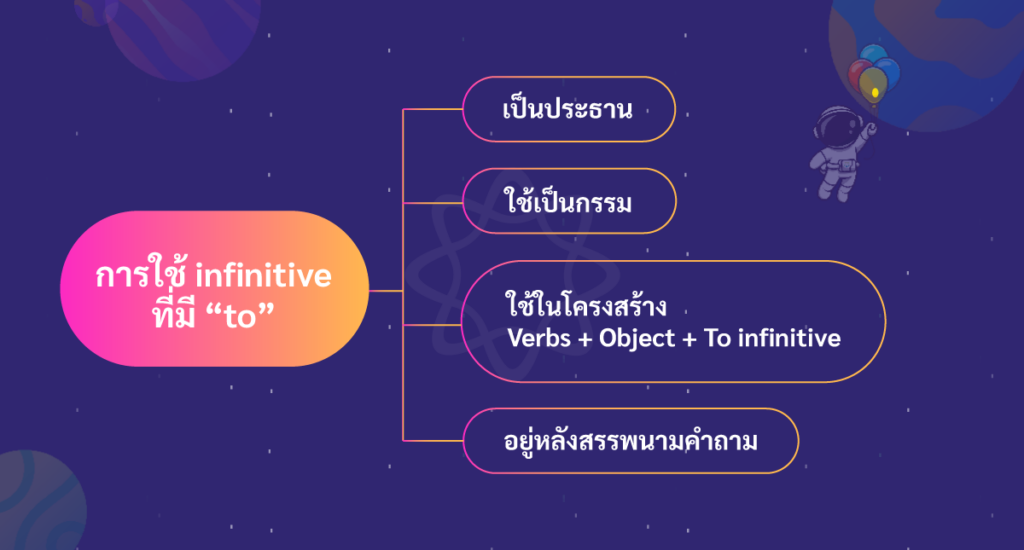
โครงสร้างและการใช้ infinitive ที่มี “to”
Infinitive ใช้เป็นประธานในประโยค
กริยา infinitive ที่มี “to” มักใช้เป็นประธานในประโยค ตัวอย่างเฉพาะได้แก่:
- To visit Korea is my life-long dream. (การได้ไปเที่ยวเกาหลีคือความฝันตลอดชีวิตของฉัน)
- To become a famous writer is her goal. (การเป็นนักเขียนที่มีชื่อเสียงคือเป้าหมายของเธอ)
Infinitive ใช้เป็นกรรมในประโยค
Infinitive ใช้เป็นกรรมของกริยา
กรรมของกริยา: ความรู้ทางไวยากรณ์นี้มาหลังคำกริยาบางคำ (เรียนรู้ที่นี่) ซึ่งใช้เป็นกรรมของคำกริยาเหล่านั้น
ตัวอย่างเช่น: It’s very important for Anna to be patient with her little brother ตารางคำกริยาบางคำที่ตามด้วย “to infinitive” (คำกริยา + to V infinitive):
| ลําดับ | กริยา (Verbs) | ความหมาย (Meaning) | ลําดับเลขที่ | กริยา (Verbs) | ความหมาย (Meaning) |
| 1 | Hope | หวัง | 13 | seem | ดูเหมือน |
| 2 | Offer | แนะนำ | 14 | Decide | ตัดสินใจ |
| 3 | Expect | คาดหวัง | 15 | Manage | จัดการ |
| 4 | Plan | วางแผน | 16 | Agree | เห็นด้วย |
| 5 | Refuse | ปฏิเสธ | 17 | Afford | ตอบสนอง |
| 6 | Want | ต้องการ | 18 | Arrange | จัด |
| 7 | Promise | สัญญา | 19 | Appear | ดูเหมือน |
| 8 | Pretend | แกล้งทำ | 20 | Learn | เรียนรู้ |
| 9 | Fail | ล้มเหลว | 21 | Would like | อยากจะ |
| 10 | Attempt | พยายาม | 22 | Offer | เสนอ |
| 11 | Tend | มีแนวโน้ม | 23 | Intend | ตั้งใจ |
Infinitive ใช้เป็นกรรมของคำคุณศัพท์
นอกจากนี้ infinitive ยังใช้เป็นกรรมของคำคุณศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษอีกด้วย ตัวอย่างเช่น:
- It’s good to talk with you. (ดีใจที่ได้คุยกับคุณ)
- It’s important for Tony to be patient with his little sister. (สิ่งสำคัญคือโทนี่จะต้องอดทนกับน้องสาวของเขา)
Infinitive ใช้ในโครงสร้าง Verbs + Object + To infinitive
เรามักจะใช้โครงสร้าง “to + V infinitive” ถ้ามีกริยาต่อไปนี้อยู่ข้างหน้า:
| เลขที่ | กริยา (Verbs) | ความหมาย (Meaning) | เลขที่ | กริยา (Verbs) | ความหมาย (Meaning) |
| 1 | Advise | แนะนำ | 14 | Invite | เชิญ |
| 2 | Allow | อนุญาต | 15 | Need | ต้องการ |
| 3 | Ask | ถาม | 16 | Order | สั่ง |
| 4 | Beg | ร้องขอ | 17 | Permit | อนุญาต |
| 5 | Cause | ทำให้ | 18 | Persuade | โน้มน้าวใจ |
| 6 | Challenge | ท้าทาย | 19 | Remind | เตือน |
| 7 | Convince | โน้มน้าวใจ | 20 | Require | ขอ |
| 8 | Encourage | ให้กำลังใจ | 21 | Recommend | แนะนำ |
| 9 | Expect | คาดหวัง | 22 | Teach | สอน |
| 10 | Forbid | ห้าม | 23 | Tell | บอก |
| 11 | Force | บังคับ | 24 | Urge | กระตุ้น |
| 12 | Hire | จ้าง | 25 | Want | ต้องการ |
| 13 | Instruct | สั่งสอน | 26 | Warn | เตือน |
ตัวอย่างเช่น:
- My teach allowed me to use her headphones. (ครูของฉันอนุญาตให้ฉันใช้หูฟังของเธอ)
- I ask my mom recipe to cook a meal. (ฉันขอสูตรทำอาหารจากแม่)
Infinitive อยู่หลังสรรพนามคำถาม
นอกจากนี้ infinitive ในภาษาอังกฤษยังมาหลังสรรพนามคำถามอีกด้วย อย่างไรก็ตาม เราควรทราบว่า to V infinitive จะไม่อยู่หลังคำใช้เพื่อถาม Why ตัวอย่างเช่น:
- My mom asked me how to use an oil-free fryer. (แม่ถามฉันวิธีใช้หม้อทอดไร้น้ำมัน)
- You can tell me when to press the button. (คุณสามารถบอกฉันได้ว่าจะกดปุ่มเมื่อใด)
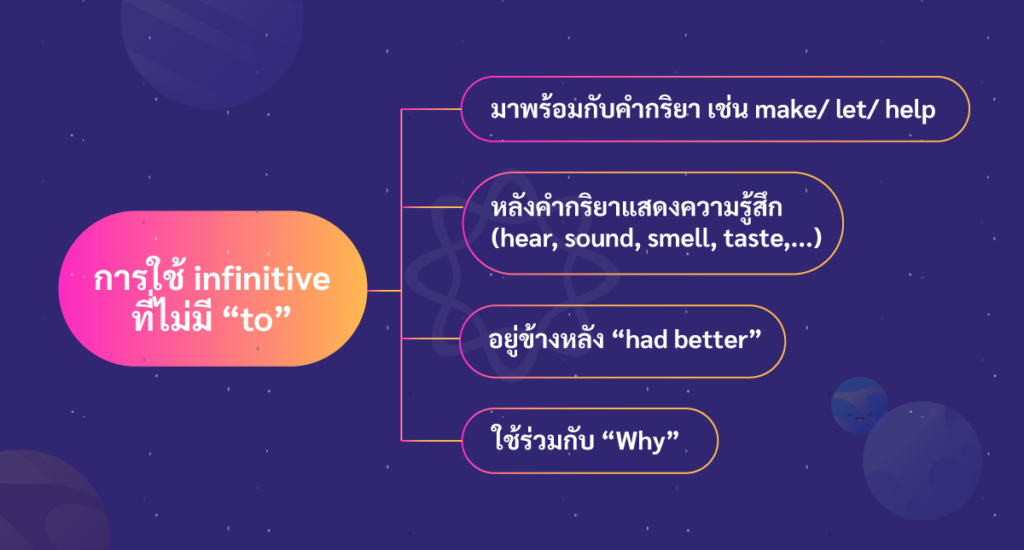
โครงสร้างและการใช้ infinitive ที่ไม่มี “to”
Infinitive มาพร้อมกับคำกริยา เช่น make/ let/ help
S + Make/ Let/ Help + Object + V infinitive
ตัวอย่างเฉพาะ:
- His parents let him stay out late. (พ่อแม่ของเขาปล่อยให้เขาออกไปข้างนอกสาย)
- Let’s go to the station tonight. (คืนนี้ไปที่สถานีกัน)

Infinitive มาหลังคำกริยาแสดงความรู้สึก
S + Verbs of perception + Object + V infinitive/ V-ing
- กิริยาที่บ่งบอกการรับรู้ (hear, sound, smell, taste, feel, watch, notice, see, listen, find,…) + O + V infinitive
- กิริยาที่บ่งบอกการรับรู้ (hear, sound, smell, taste, feel, watch, notice, see, listen, find,…) + O + V-ing
ตัวอย่างเฉพาะ:
- I saw my friend get on the taxi. (ฉันเห็นเพื่อนขึ้นแท็กซี่)
- We saw him closing his eyes. (เราเห็นเขากำลังหลับตาลง)
Infinitive อยู่ข้างหลัง “had better”
ตัวอย่างรายละเอียดบางอย่างของ infinitive ที่ไม่มี “to” อยู่หลัง “had better” ได้แก่:
- They had better take some warm clothing. (พวกเขาควรจะสวมเสื้อผ้าที่อบอุ่น)
- You’d better give your friend your address. (คุณควรให้ที่อยู่ของคุณแก่เพื่อนของคุณ)
| วิธีใช้ had better และ modal verb อื่น ๆ คืออะไร? มาศึกษาจากบทความเรื่อง “Modal Verb คืออะไร? คำจำกัดความ ตัวอย่าง วิธีใช้งานที่เข้าใจง่าย” ด้านล่างนี้เลย |
Infinitiveใช้ร่วมกับ Why
การใช้ infinitive ที่ไม่มี “to” ร่วมกับ Why เมื่อให้คำแนะนำ เช่น
- Why wait until tomorrow? (ทำไมต้องรอถึงพรุ่งนี้)
- Why walk when we can go in the car? (จะเดินทำไมในเมื่อเราใช้รถยนต์ได้?)
>>> Read more:
แบบฝึกหัด Infinitive ด้านไวยากรณ์ในภาษาอังกฤษ
เพื่อให้เข้าใจความรู้ด้านไวยากรณ์ของ Infinitive ในภาษาอังกฤษได้ดีขึ้น ให้ฝึกฝนแบบฝึกหัดต่อไปนี้:
แบบฝึกหัด: ใส่รูปแบบคำกริยาที่ถูกต้องในวงเล็บ:
- He wanted (see) _____________________the house where the president was born.
- He is expected (arrive) _____________________in a few days.
- I would like him (go) ________ to a university but I can’t (make) ________ him go.
- I arranged (meet) _____________________them there.
- He urged us (work) _____________________faster.
- I wish (see) _____________________the manager.
- He warned her (not touch) _____________________the wire.
- Don’t forget (lock) _____________________the door before going to bed.
- My mother told me (not speak) _____________________to anyone about it.
- He tried (explain) ________but she refused (listen) ______.
- He decided (disguise) __________________ himself by dressing as a woman.
- I am prepared (wait) _____________________here all night if necessary.
- Would you mind showing me how (work) _____________________the lift.
- After walking for three hours we stopped (rest) ________ and let the others (catch) ____ up with us.
- I am beginning (understand) _____________________what you mean.
- I regret (inform) _____________________you that your application has been refused.
- I don’t allow my family (smoke) _____________________at all.
- I tried (persuade) ____________him (agree) _________with your proposal.
- Your windows need (clean) __________. Would you like me (do) ___________them for you?
- Stop (talk) _____________. I am trying (finish) ________a letter.
- His doctor advised him (give) _____________________up jogging.
- Some people seem (have) _____________the passion for writing to the newspapers.
- He expects me (answer) _____________by return but I have no intention of replying at all.
- He postponed making a decision until it was too late (do) _____________anything.
- Try (forget) _____________it. It isn’t worth worrying about it.
- The horse won’t be well enough (run) _______ in tomorrow’s race. He doesn’t seem (have) _______ recovered from his long journey.
- It wouldn’t be safe (start) _____________down now; we will have (wait) _____________till the mist clears.
- It’s not much use having a bike if you don’t know how (use) _____________it.
- I distinctly remember (pay) _____________him. I gave him 2$.
- Did you remember (give) _____________him the key of the safe? – No, I didn’t. I will go and do it now.
| คุณสามารถทำแบบฝึกหัดเพิ่มเติมเพื่อเข้าใจ have has ใช้ยังไง ในบทความนี้ มาลองอ่านบทความเพื่อเรียนรู้วิธีใช้ have และ has ให้ถูกต้องกันเถอะ |
คำตอบ:
| 1. to see | 2. to arrive | 3. to go – make | 4. to meet |
| 5. to work | 6. to see | 7. not to touch | 8. to lock |
| 9. not to speak | 10. to explain – to listen | 11. to disguise | 12. to wait |
| 13. to work | 14. to rest – catch | 15. to understand/ understanding | 16. to inform |
| 17. to smoke | 18. to persuade – to agree | 19. to be cleaned/ cleaning – to do | 20. talking – to finish |
| 21. to give | 22. to have | 23. to answer | 24. to do |
| 25. to forget | 26. to run – to have | 27. to start – to wait | 28. to use |
| 29. paying | 30. giving |
ข้างต้นคือความรู้ทั้งหมดเกี่ยวกับกริยา infinitive ในภาษาอังกฤษ หวังว่าความรู้เหล่านี้จะช่วยให้คุณพิชิตความรู้ด้านไวยากรณ์อย่างง่ายที่สุด หากคุณยังคงมีคำถามเกี่ยวกับความรู้ด้าน infinitive โปรดติดต่อ ELSA Speak โดยตรงเพื่อขอคำแนะนำและคำตอบที่ละเอียดที่สุดจากเรา!





