Passive Voice คืออะไร
Passive Voice เป็นประโยคที่เน้นว่าวัตถุ (subject) ที่เป็นบุคคลหรือสิ่งที่ได้รับผลกระทบจากการกระทำแทนที่จะเป็นวัตถุที่กระทำ
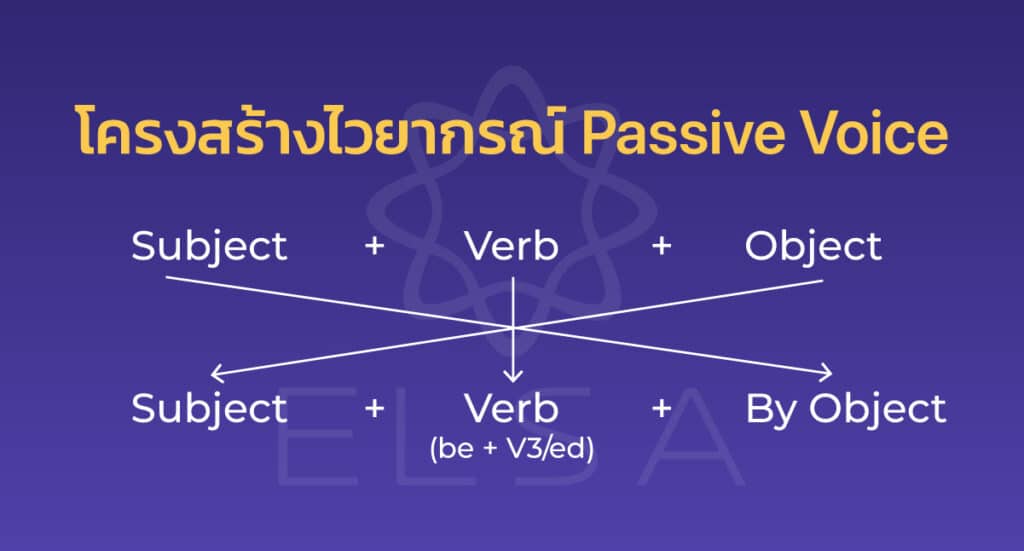
โครงสร้างไวยากรณ์ Passive Voice
โครงสร้างไวยากรณ์ของ Passive Voice คือ
สอบก่อนเข้าฟรี

| Subject + be + V3/ed + (by + doer) + (…). |
* ซึ่งประกอบด้วย
- Subject :วัตถุที่ได้รับผลกระทบจากการกระทำ
- be + V3/ed: ‘be’ จะเปลี่ยนรูปร่างตาม tenses ที่ใช้ในประโยค Active Voice
- V3/ed จะไม่เปลี่ยนรูปร่าง สิ่งที่เปลี่ยนตาม tenses คือ ‘be’
- (by + doer): ‘by’ หมายความว่า “โดย/ด้วย” ใช้ในการแนะนำวัตถุที่ดำเนินการตามหลัง ‘by’
- ‘doer’ คือผู้ที่ดำเนินการ
- ‘by + doer’ อยู่ใน (…) เพราะจะมีกรณีที่ไม่ต้องใช้
- (…): เป็นข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับสถานที่และเวลาที่ subject ได้รับผลกระทบจากการกระทำ โดยส่วนนี้ไม่จำเป็นต้องมี แต่จะขึ้นอยู่กับแต่ละกรณี
ตัวอย่าง
+ She is loved by everyone.
- เธอเป็นที่รักของทุกคน
- วิเคราะห์: คำกริยา ‘love’ ถูกผันในรูปแบบ V-ed: ‘loved’
- กริยา ‘be’ ถูกผันเป็น ‘is’ ใน Present Simple
+ She was loved by everyone.
- เธอเคยเป็นที่รักของทุกคน
- วิเคราะห์: คำกริยา ‘love’ ยังถูกผันในรูปแบบ V-ed: ‘loved’
- คำกริยา ‘be’ ถูกผันเป็น ‘was’ ตาม Past Simple
>>> Read more: Irregular Verbs ในภาษาอังกฤษที่ครบถ้วนที่สุด
วิธีการเปลี่ยนจากประโยค Active เป็นประโยค Passive
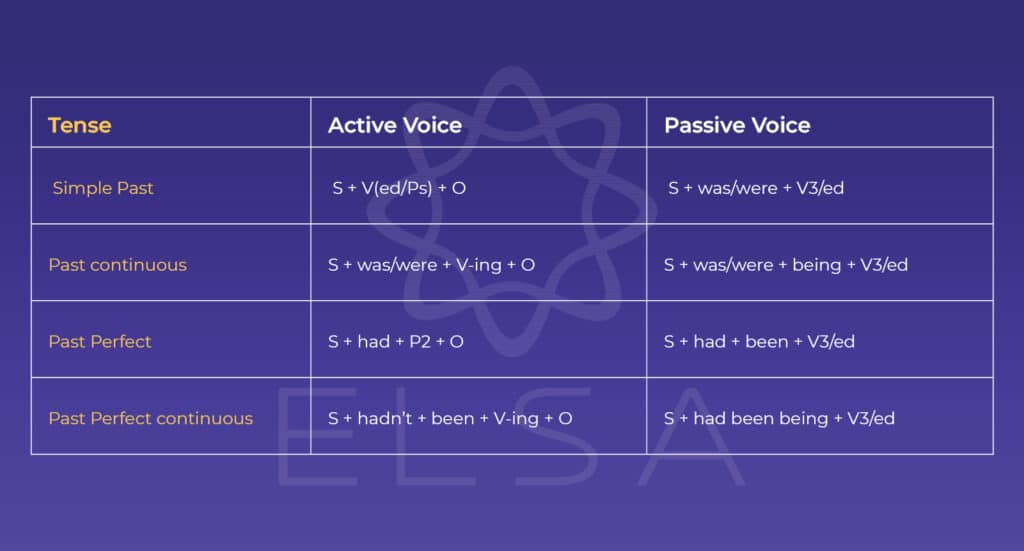
ตารางแปลงสูตรของ passive voice จาก active voice
| Tense (รูปแบบของประโยคที่มีคำกริยา) | Active voice | Passive voice |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | S + V(s/es) + O | S + am/is/are + V3/ed |
| Present Continuous | S + am/is/are + V-ing + O | S + am/is/are + being + V3/ed |
| Present Perfect | S + have/has + P2 + O | S + have/has + been + V3/ed |
| Present Perfect Continuous | S + have/has + been + V-ing + O | S + have/ has been being + V3/ed |
| Simple Past | S + V(ed/Ps) + O | S + was/were + V3/ed |
| Past Continuous | S + was/were + V-ing + O | S + was/were + being + V3/ed |
| Past Perfect | S + had + P2 + O | S + had + been + V3/ed |
| Past Perfect Continuous | S + hadn’t + been + V-ing + O | S + had been being + V3/ed |
| Future Simple | S + will + V-infi + O | S + will + be + V3/ed |
| Future Perfect | S + will + have + P2 + O | S + will + have + been + V3/ed |
| Future Continuous | S + am/is/are going to + V-infi + O | S + am/is/are going to + be + V3/ed |
| Future Perfect Continuous | S + will + have + been + V-ing + O | S + will have been being + V3/ed |
| Modal Verbs | S + Model Verb + V-infi + O | S + Model Verb + be + V3/ed |
>> Read more: แนะนำวิธีการง่าย ๆ เพื่อซื้อคอร์สเรียน ELSA Speak ตลอดชีพ
เปลี่ยนจาก Active เป็น Passive
เพื่อเปลี่ยนจาก Active เป็น Passive ให้ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้
ประโยค Active ที่ต้องการเปลี่ยน
Yesterday, my mother bought a new TV.
→ เมื่อวานแม่ซื้อโทรทัศน์เครื่องใหม่
วิเคราะห์
- สิ่งที่ถูกกระทำ : ‘a new TV’ (โทรทัศน์เครื่องใหม่)
- Tense: Simple Past
- กริยา : ‘bought’
- ผู้กระทำ : ‘my mother’ (แม่)
ขั้นตอนการเปลี่ยน
| ขั้นตอน | ค่อย ๆ กลายเป็นประโยค Passive ในแต่ละขั้นตอน |
|---|---|
| ขั้นตอนที่ 1 เอาผู้ที่ถูกกระทำ หรือเรียกอีกชื่อว่า object ในประโยค Active ให้นำหน้าประโยค | Yesterday, a new TV |
| ขั้นตอนที่ 2 วางคำกริยาไว้หลังผู้ที่ได้รับผลกระทบ เปลี่ยนกริยาเป็น V3/ed ถ้าคำกริยาอยู่ในรูปแบบ V3/ed อยู่แล้ว ก็ปล่อยไว้อย่างนั้น | Yesterday, a new TV bought |
| ขั้นตอนที่ 3 เพิ่ม ‘be’ หน้าคำกริยา เปลี่ยน ‘be’ เป็น tense ของประโยค Active ดังนั้น เราต้องสังเกตกริยาในประโยค Active และองค์ประกอบอื่น ๆ เช่นคำวิเศษณ์บอกเวลา เป็นต้น เพื่อดูว่า Tense ของประโยคเป็นอย่างไร | Yesterday, a new TV was bought |
| ขั้นตอนที่ 4 เพิ่มกลุ่ม ‘by + ผู้/สิ่งกระทำ’ หลังคำกริยา และเขียนส่วนที่เหลือตามหลัง (ถ้ามี) หมายเหตุ → เราสามารถไม่ต้องเพิ่มกลุ่ม ‘by + ผู้/สิ่งกระทำ’ หากผู้กระทำตกอยู่ในสรรพนามที่ไม่เฉพาะเจาะจงและชัดเจนเช่น: ‘they’, ‘everyone’, ‘someone’, ‘somebody’ เป็นต้น → ในกรณีที่ผู้กระทำเป็นหนึ่งในสรรพนามสรรพนาม 7 สรรพนาม ‘I’, ‘we’, ‘you’, ‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’ และ ‘they’ เมื่อย้ายไปหลัง ‘by’ เราต้องผันให้เป็นรูปแบบสรรพนามวัตถุ เช่น ‘me’, ‘us’, ‘you’, ‘him’, ‘her’, ‘it’ và ‘them’. ตัวอย่าง This cake was made by he. → ผิด This cake was made by him. → ถูก | Yesterday, a new TV was bought by my mother. |
โครงสร้างประโยค Passive ตาม Tense
โครงสร้างของประโยค Passive ตามกาลในภาษาอังกฤษผ่านตารางด้านล่างนี้
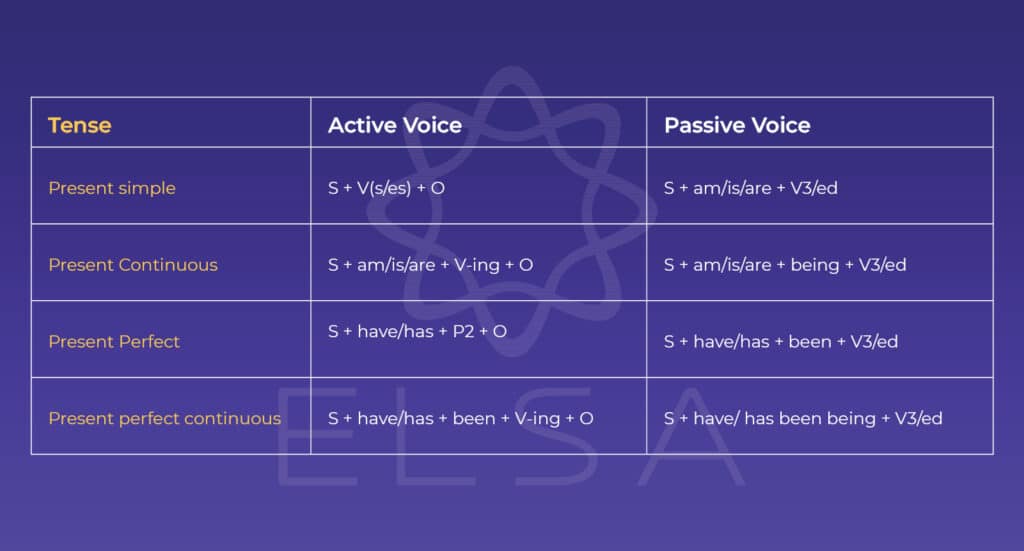
Present
| Tense | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง |
| Present Simple | Subject + am/ is/ are (not) + V3/ed +(by+doer)+(…) โดย → am: ประธานเป็นเอกพจน์บุรุษที่หนึ่ง – I → is: ประธานเอกพจน์บุรุษที่ 3 – he/ she/ it/ my mother/ his cat/… → are: ประธานที่เหลือ – we/ you/ they/ those people/ my parents/… | Those kids are educated well. → เด็กเหล่านั้นได้รับการสั่งสอนที่ดี I am loved by many people. → ฉันเป็นที่รักของผู้คนมากมาย That employee is given lots of tasks. → พนักงานคนนั้นได้รับการมอบหมายงานหลายอย่าง |
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/ is/ are (not) being+V3/ed+(by + doer)+(…) โดย → am: ประธานเป็นเอกพจน์บุรุษที่หนึ่ง – I → is: ประธานเอกพจน์บุรุษที่ 3 – he/ she/ it/ my mother/ his cat/… → are: ประธานที่เหลือ – we/ you/ they/ those people/ my parents/… | Our house is being built this month. → บ้านเรากำลังก่อสร้างในเดือนนี้ I am being scolded by my mother right now. → ฉันกำลังโดนแม่ดุอยู่ตอนนี้ Those trees are being cut down. → ต้นไม้เหล่านั้นกำลังถูกตัดลง |
| Present Perfect | Subject+have/ has (not) been +V3/ed+(by + doer)+(…) โดย → has: ประธานเป็นเอกพจน์บุรุษที่หนึ่ง – he/ she/ it/ my mother/ his cat/… → have: ประธานที่เหลือ – I/ we/ you/ they/ those people/ my parents/… | His favorite vase has been broken buy his little sister. → แจกันใบโปรดของเขาแตกเพราะน้องสาวของเขาทำ Those houses have been sold. → บ้านเหล่านั้นถูกขายไปแล้ว |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject +have/ has (not) been being+V3/ed+(by + doer)+(…) โดย → has: ประธานเป็นเอกพจน์บุรุษที่หนึ่ง – he/ she/ it/ my mother/ his cat/… → have: ประธานที่เหลือ – I/ we/ you/ they/ those people/ my parents/… | That machine has been being used for many years. → เครื่องนั้นนั้นถูกใช้งานโดยไม่หยุดเป็นเวลาหลายปี Those chairs have been being stepped on for hours. → เก้าอี้เหล่านั้นถูกเหยียบและถูกเหยียบอยู่เรื่อยๆ |

Past
| Tense | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง |
| Simple Past | Subject+was/ were (not) + V3/ed+(by + doer) + (…) โดย → ประธานเป็นเอกพจน์บุรุษที่หนึ่ง – I → ประธานเอกพจน์บุรุษที่ 3 – he/ she/ it/ my mother/ his cat/… | 2 months ago, her company was bought by a big corporation. → เมื่อสองเดือนก่อน บริษัทของเธอถูกซื้อกิจการโดยบริษัทขนาดใหญ่ Yesterday, they weren’t chosen to join the race. → เมื่อวานพวกเขาไม่ได้รับเลือกให้เข้าร่วมการแข่งขัน |
| Past continuous | Subject+was/ were (not) being+V3/ed +(by + doer) + (…) โดย → ประธานเป็นเอกพจน์บุรุษที่หนึ่ง – I → ประธานเอกพจน์บุรุษที่ 3 – he/ she/ it/ my mother/ his cat/… → ประธานที่เหลือ – we/ you/ they/ those people/ my parents/… | This morning, when you came, the floor was being mopped. → เช้านี้เมื่อคุณมาถึง พื้นกำลังถูกถูอยู่ Yesterday, when they left, lots of delicious dishes were being cooked. → เมื่อวานนี้ เมื่อพวกเขาออกไป อาหารอร่อยหลายๆ อย่างกำลังถูกทำอยู่ |
| Past Perfect | Subject +had (not) been + V3/ed +(by + doer)+(…) | All the beer had been drunk when we got there. → เบียร์ทั้งหมดถูกดื่มจนหมดเมื่อพวกเราไปถึงที่นั่น |
| Past Perfect Continous | Subject + had (not) been being + V3/ed + (by + doer) + (…) | My laptop hadn’t been being used by my son before I got home. → แลบท๊อปของฉันไม่ได้ถูกลูกชายฉันใช้งานตลอดเวลาก่อนที่ฉันจะกลับถึงบ้าน |
Future
| Tense | โครงสร้าง | ตัวอย่าง |
| Future | Subject +will (not) be +V3/ed + (by + doer) + (…) | Those trees won’t be cut down. → ต้นไม้เหล่านั้นจะไม่ถูกโค่น |
| Future Perfect | Subject +will (not) be being + V3/ed +(by + doer) + (…) | This time next month, these trees will be being cut down. → เวลานี้ในเดือนหน้า ต้นไม้เหล่านี้จะถูกตัดลง |
| Future Continuous | Subject +will (not) have been +V3/ed +(by + doer) +(…) | I think all of the clothes will have been bought by the time we get there. → ฉันคิดว่าเสื้อผ้าทั้งหมดจะถูกซื้อก่อนที่เราจะไปถึงที่นั่น |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will (not) have been being+V3/ed +(by + doer) + (…) | Before I get to the meeting, my group will have been being asked hard questions. → ก่อนที่ฉันจะไปถึงประชุม ทีมของฉันจะถูกถามคำถามยากๆ อยู่เรื่อยๆ |
>> Read more: AM PM คือะไร? วิธีใช้ AM PM อย่างถูกต้องในภาษาอังกฤษ พร้อมรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
กรณีประโยค Passive พิเศษ
ประโยค Active ที่มีสองกรรม (object)
ในภาษาอังกฤษ มีคำกริยาบางคำที่ตามด้วยสองกรรม (object) ตัวอย่างเช่น
+ send:
She sent me a present.
→ เธอส่งให้ฉันของขวัญหนึ่งชิ้น
หรือ
She sent a present to me.
→ เธอส่งของขวัญให้ฉัน
ทั้งสองประโยคนี้มีกรรม (object) อยู่ 2 อย่างที่เป็นผู้ได้รับสิ่งของและสิ่งของที่ถูกส่งไปยังผู้รับ
+ give:
He usually gives me flowers.
→ เขามอบให้ฉันดอกไม้เป็นประจำ
หรือ
He usually gives flowers to me.
→ เขาให้ดอกไม้ฉันเป็นประจำ
ทั้งสองประโยคนี้มีกรรม (object) อยู่ 2 อย่างที่เป็นผู้ได้รับสิ่งของและสิ่งของที่ถูกส่งไปยังผู้รับ
+ buy:
They sometimes buy me new clothes.
→ บางครั้งพวกเขาก็ซื้อให้ฉันเสื้อผ้าใหม่
หรือ
They sometimes buy new clothes for me.
→ บางครั้งพวกเขาก็ซื้อเสื้อผ้าใหม่ให้ฉัน
ทั้งสองประโยคนี้มีกรรม (object) อยู่ 2 อย่างที่เป็นผู้ได้รับสิ่งของและสิ่งของที่ถูกส่งไปยังผู้รับ
โครงสร้างประโยค Passive
ในกรณีนี้ เรามีโครงสร้างประโยค Passive 2 โครงสร้าง ซึ่งเทียบเท่ากับโครงสร้างประโยค Active 2 โครงสร้าง
| โครงสร้าง | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| ผู้รับอยู่หลังวัตถุ | Subject (doer) + verb (ผันกริยา) + person + object ตัวอย่าง Last week, my parents bought me a phone. → อาทิตย์ที่แล้ว พ่อแม่ซื้อให้ฉันโทรศัพท์หนึ่งเครื่อง | Person + be (ผันกริยา) + V3/ed + object + (by + doer). ตัวอย่าง Last week, I was bought a phone by my parents. → อาทิตย์ที่แล้ว ฉัยได้โทรศัพท์ใหม่โดยพ่อแม่ซื้อให้ |
| ผู้รับอยู่หลังวัตถุ | Subject (doer) + verb (ผันกริยา) + object + to/ for/… + person ตัวอย่าง Last week, my parents bought a phone for me. → อาทิตย์ที่แล้ว พ่อแม่ซื้อโทรศัพท์ให้ฉัน | Object + be (ผันกริยา) + V3/ed + to/ for/ … + person + (by + doer). ตัวอย่าง Last week, a phone was bought for me by my parents. → อาทิตย์ที่แล้ว โทรศัพท์เครื่องหนึ่งถูกซื้อให้ฉันโดยพ่อแม่ฉัน |
ประโยคพาสซีฟที่มีกริยารายงาน (Reporting Verbs) – กริยาของความคิดเห็น (Verbs of Opinion)
ในภาษาอังกฤษ จะมีประโยค Active ที่ใช้งานด้วยกริยารายงาน (say, announce, v.v.) หรือกริยาแสดงความคิดเห็น (think, believe, v.v.)
ตัวอย่าง
+ People say that he is famous. (1)
→ ทุกคนบอกว่า เขาเป็นคนดัง
+ They believed that that family had sold the house. (2)
→ พวกเขาเชื่อว่าครอบครัวนี้เคยขายบ้านหลังนี้ไปแล้ว
เมื่อพิจารณาจากสองตัวอย่างข้างต้น คุณจะเห็นว่ามีหลายกรณีที่กริยาที่อยู่ข้างหน้า ‘that’ และกริยาในประโยคที่อยู่หลัง ‘that’ ใช้กาลเดียวกัน (ตัวอย่างที่ 1) หรือต่างกัน (ตัวอย่างที่ 2) จะเป็นการสร้างโครงสร้าง 2 แบบในวิธีที่ 1 ดังภาพด้านล่าง
| กรณี | วิธีที่ 1 | วิธีที่ 2 (รวมให้ทั้ง 2 กรณี) |
|---|---|---|
กรณีที่ 2 กริยาที่อยู่ก่อน ‘that’ และกริยาในประโยคหลัง ‘that’ ใช้กาลต่างกัน → Present Simple – Past Simple → Past – Past Perfect | Active voice Subject 1 + verb 1 (ผัน) + that + subject 2 + verb 2 (ผัน) + … ตัวอย่าง They say that Rebecca is friendly → พวกเขาบอกว่ารีเบคก้าเป็นคนที่เป็นมิตร | Active voice Subject 1 + verb 1 (ผัน) + that + subject 2 + verb 2 (ผัน) + … ตัวอย่าง People believed that they had left the town in the middle of the night. ⟶ ทุกคนเชื่อกันว่าพวกเขาออกจากเมืองตอนกลางดึก |
| Passive Voice Subject 2 + be (ผันตาม verb 1 ในประโยค Active) + verb 1 (V3/ed) + to + V-infi + … ตัวอย่าง Rebecca is said to be friendly. → รีเบคก้าได้รับการอธิบายว่าเป็นคนเป็นมิตร | Passive Voice It + be (ผันตาม verb 1 ในประโยค Active) + that + ซ้ำกับส่วนในประโยค Active. ตัวอย่าง It was believed that they left the town in the middle of the night. | |
กรณีที่ 2 กริยาที่อยู่ก่อน ‘that’ และกริยาในประโยคหลัง ‘that’ ใช้กาลต่างกัน → Present Simple – Past Simple → Past – Past Perfect | Active voice Subject 1 + verb 1 (ผัน) + that + subject 2 + verb 2 (ผัน) + … ตัวอย่าง They believed that he had stolen her wallet. | |
| Passive Voice Subject 2 + be (ผันตาม verb 1 ในประโยค Active) + verb 1 (แบบ V3/ed) + to + have + V3/ed + … ตัวอย่าง He was believed to have stolen her wallet. → เชื่อกันว่าเขาเคยขโมยกระเป๋าสตางค์ของเธอมาก่อน |
ประโยคขอให้ใครทำอะไร ด้วยคำว่า ‘get’ และ ‘have’
ในภาษาอังกฤษ เพื่อขอให้ใครทำอะไรให้ เรามักจะใช้ ‘get’ และ ‘have’ ในสองโครงสร้างต่อไปนี้:
| Subject + have (ผันกริยา) + somebody + V-infi + something |
| Subject + get (ผันกริยา) + somebody + to + V-infi + something |
โครงสร้างทั้งสองนี้เมื่อแปลงเป็น Passive Voice จะกลายเป็น
| Subject + have/get (ผันกริยา) + something + V3/ed + by + somebody. |
| Subject + have/get (ผันกริยา) + something + V3/ed + by + somebody. |
ตัวอย่าง
+ Active Voice
Yesterday, I got/had a plumber to fix the pipe.
→ เมื่อวาน ฉันได้ขอให้ช่างมาซ่อมท่อประปา
+ Passive Voice
Yesterday, I got/ have the pipe fixed by a plumber
→ เมื่อวาน ท่อประปาได้ถูกแก้ไขโดยช่างประปาคนหนึ่ง

ประโยคแสดงความเป็นกรรมวาจกด้วย Need + V-ing
เมื่อเราต้องการแสดง ผู้/สิ่งใดที่ต้องถูกกระทำ เราสามารถใช้โครงสร้างต่อไปนี้
| Subject + need (ผันกริยา) + V-ing |
ตัวอย่าง
→ ถ้าเราต้องการพูดว่า “โต๊ะนี้ต้องการทำความสะอาด” ให้พูดว่า: This table needs cleaning
→ ถ้าเราต้องการพูดว่า “เมื่อวาน ผมต้องการตัดผม” ให้พูดว่า: Yesterday, my hair needed cutting.
>> Read more: วิธีเปิดใช้งาน ELSA Speak/ELSA Pro ได้เร็วที่สุด
ประโยค Passive Voice ที่มีคำกริยาแสดงประสาทสัมผัสการรับรู้
ในภาษาอังกฤษ มีบางกรณีที่ผู้ที่เป็นประธานใช้กริยาแสดงประสาทสัมผัสการรับรู้ (see, hear, notice, v.v.) และพยาน/ได้ยิน/… ใคร (กำลังทำ) อะไรบางอย่าง
เมื่อประโยค Active อยู่ในกรณีนี้ เราจะเปลี่ยนเป็นประโยค Activeในสองกรณีต่อไปนี้
| กรณี | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| คนที่ได้เห็น/ได้ยิน/… การกระทำทั้งหมดของผู้อื่น | Subject + verb (ผัน) + object + V-ing + … ตัวอย่าง Yesterday, Josh heard Mary singing. → เมื่อวานนี้ Josh ได้ยิน Mary ร้องเพลง (ได้ยินเพียงบางส่วน) | Subject (object ในประโยค Active) + be (ผัน) + V3/ed + V-ing + by + doer (ประธานประโยค Active) ตัวอย่าง Yesterday, Mary was heard singing by Josh. → เมื่อวาน Mary กำลังร้องเพลง ก็ถูก Josh ได้ยิน |
| คนที่ได้เห็น/ได้ยิน/… การกระทำทั้งหมดของผู้อื่น | Subject + verb 1 (ผัน) + object + V-infi + … ตัวอย่าง Yesterday, Josh heard Mary sing. → เมื่อวานนี้ Josh ได้ยิน Mary ร้องเพลง (ตั้งแต่ต้นจนจบ) | Subject (object ในประโยค Active) + be (ผัน) + V3/ed + to + V-infi + by + doer (subject ในประโยค Active) ตัวอย่าง Yesterday, Mary was heard to sing by Josh. → เมื่อวาน Mary กำลังร้องเพลง ก็ถูก Josh ได้ยิน (ตั้งแต่ต้นจนจบ) |
หมายเหตุเมื่อแปลงเป็นประโยค Passive Voice
การแปลง Object Pronoun (สรรพนามรูปกรรม) เป็นคำ Subject pronoun (คำสรรพนามที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นประธาน)
→ ถ้ารูปกรรม (ผู้ที่ถูกกระทำ) ในประโยค Active เป็นสรรพนามรูปกรรม: : ‘me’, ‘us’, ‘you’, ‘him’, ‘her’, ‘it’ และ ‘them’,เมื่อเรานำคำเหล่านี้ไปนำหน้าเพื่อให้เป็นประธานของประโยค Passive เราต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นสรรพนามประธาน: ‘I’, ‘we’, ‘you’, ‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’ และ ‘they’
| Subject | Object |
|---|---|
| I | Me |
| We | Us |
| You | You |
| He | Him |
| She | Her |
| It | It |
| They | Them |
ตัวอย่าง
+ Active Voice: He likes her.
+ Passive Voice
Her is liked by him. → ผิด
She is liked by him. → ถูก
ลำดับของสถานที่ ‘by…’ และเวลา
ในประโยค Passive Voice ลำดับของสถานที่ ‘by…’ และเวลาจะถูกเรียงไว้ดังนี้
| สถานที่ ⟶ ‘by…’ ⟶ เวลา |
แม้หนึ่งในสามองค์ประกอบนี้จะขาดหายไป ลำดับข้างต้นจะไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง
ตัวอย่าง
+ Milk is left in front of our house (สถานที่) by a kind person (by + doer) every morning (เวลา).
→ นมถูกวางไว้หน้าบ้านโดยผู้ใจดีคนหนึ่งทุกเช้า
+ Milk is left in front of our house (สถานที่) by a kind person (by + doer)
→ นมถูกวางไว้หน้าบ้านโดยผู้ใจดีคนหนึ่ง
+ Milk is left in front of our house (สถานที่) every morning (เวลา).
→ นมถูกวางไว้หน้าบ้านเราทุกเช้า
‘by…’ หรือ ‘with…’?
ผู้เรียนหลายคนอาจสงสัยว่าเราใช้ ‘by’ นำหน้าผู้กระทำ แล้วเราจะใช้อะไรนำหน้าเครื่องมือการกระทำ คำตอบคือ ใช้ ‘with’
ผู้เรียนหลายคนเวลาพูดมักจะแปลจากภาษาไทยเป็นภาษาอังกฤษ และคำว่า ‘by’ ที่มีความหมายในภาษาไทยว่า ‘โดย’ (ใช้กับพาหนะ)
แต่ในประโยค Passive Voice เมื่อคุณต้องการพูดถึงวัตถุที่ใช้เพื่อกระทำต่อผู้ที่ถูกการกระทำ เราจะใช้ ‘with’
ตัวอย่าง
The window was broken by a hammer. → ผิด
The window was broken with a hammer. → ถูก
หมายเหตุ: การใช้ Passive Voice เป็นหนึ่งในการถอดความที่มีประสิทธิภาพมากที่สุดใน IELTS Writing
แบบฝึกหัดประโยค Passive Voice
Passive Voice กับ 12 Tenses
Change the active sentences below into passive sentences
1. Yesterday, a strange sound woke me up in the middle of the night.
2. Her children respect her.
3. That family have used that car for more than 15 years.
4. They had eaten all the food before we arrived at the party.
5. By the time we get to the store, other customers will have bought all of the clothes.
6. They are cutting down the apple tree in front of our house.
7. This morning, when I came, he was baking a delicious cake.
8. I think our boss will choose that hard-working employee for that position.
9. Our children have been watching that TV series since 7 pm.
10. I think that when we get to the meeting, the bosses will be asking our team a lot of questions.
11. By the time we got home, our children had been using the air conditioner for hours.
12. They will have been driving that expensive car for years when we buy it.
คำตอบ
1. Yesterday, I was woken up by a strange sound in the middle of the night.
2. She is respected by her children.
3. That car has been used by that family for more than 15 years.
4. All the food had been eaten before we arrived at the party.
5. By the time we get to the store, all of the clothes will have been bought by other customers.
6. The apple tree in front of our house is being cut down.
7. This morning, when I came, a delicious cake was being baked by him.
8. I think that hard-working employee will be chosen for that position by our boss.
9. That TV series has been being watched by our children since 7 pm.
10. I think that when we get to the meeting, our team will be being asked a lot of questions by the bosses.
11. By the time we got home, the air conditioner had been being used by our children for hours.
12. That expensive car will have been being driven for years when we buy it.

Passive Voice พิเศษ
Change the active sentences below into passive sentences
1. You really need to cut your long hair.
2. Last night, that family saw a stranger trying to steal your motorbike.
3. People said that a poor man in our district had won a lottery.
4. This morning, I got a professional mechanic to fix my car.
5. We really need to wash this dirty and dusty armchair.
6. They believe that Sophie’s family is very rich.
7. Yesterday, when they were walking pass that room, they heard someone singing inside.
8. This afternoon, one of my employees witnessed a stranger sneak into our office.
9. I will have my father take care of my plants when I’m on my business trip.
10. 2 days ago, her parents bought her a laptop.
คำตอบ
1. Your long hair really needs cutting.
2. Last night, a stranger was seen trying to steal your motorbike by that family.
3. A poor man in our district was said to have won a lottery.
4. This morning, I got my car fixed by a professional mechanic.
5. This dirty and dusty armchair really needs washing.
6. Sophie’s family is believed to be very rich.
7. Yesterday, when they were walking pass that room, someone was heard singing inside by them.
8. This afternoon, a stranger was witnessed to sneak into our office.
9. I will have my plants taken care of by my father when I’m on my business trip.
10. 2 days ago, she was bought a laptop by her parents.
ทั้งหมดข้างต้นคือการสรุปความรู้ที่สำคัญเกี่ยวกับประโยค Passive ELSA Speak หวังว่าบทความนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเชี่ยวชาญและใช้ความรู้ด้านไวยากรณ์นี้ได้อย่างมั่นใจ ขอบคุณมากๆ ค่ะที่อ่านบทความนี้จนจบ แล้วพบกันใหม่บทความต่อไปนะคะ!








